Updated May 2, 2023
Introduction on PostgreSQL WHERE Clause
The PostgreSQL WHERE clause is used to control a query. The WHERE clause eliminates all rows from the output that do not meet the condition. It is generally used with SELECT, UPDATE, and DELETE statements to filter the results. It returns the specific result only when the condition is satisfied. The WHERE clause specifies a condition while fetching data from a table or joining multiple tables. WHERE condition can be used with logical operators such as >, <, =, LIKE, NOT, OR, etc.
Syntax:
WHERE search_conditionsParameter:
| Parameter | Description |
| search_conditions | A value expression. It returns a value of type boolean. |
How does the WHERE clause work in PostgreSQL?
The condition must evaluate as true, false, or unknown. It can be a Boolean expression or a combination of Boolean expressions using AND and OR operators. The query returns the rows that satisfy the condition in the WHERE clause. In other words, only rows that cause the condition.
Check OR condition. If one of the condition is null, check like this:
WHERE {user_id} IS NULL OR sr.user_id = {user_id}The WHERE clause evaluates as follows:
If the user_id is empty, then the WHERE clause evaluates to true; hence nothing is filtered. If user_id is not empty, it checks the next OR condition.
Examples of PostgreSQL WHERE Clause
Let’s practice with some examples of using the WHERE clause with conditions. We will use the student table.
Create Table
Code:
CREATE TABLE student (
rollno int PRIMARY KEY,
firstname VARCHAR (50) NOT NULL,
lastname VARCHAR (50) NOT NULL,
branch VARCHAR (50) NOT NULL,
result boolean,
joining_date DATE NOT NULL
);Insert data
Code:
INSERT INTO student (rollno, firstname, lastname, branch, result, joining_date)
values
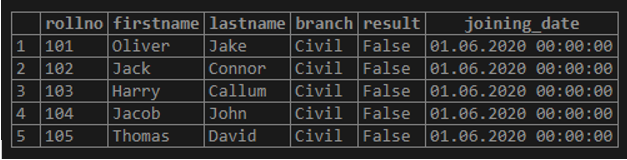
('101', 'Oliver','Jake', 'Civil', false, '2020-06-01'),
('102', 'Jack','Connor', 'Civil', false, '2020-06-01'),
('103', 'Harry','Callum', 'Civil', false, '2020-06-01'),
('104', 'Jacob','John', 'Civil', false, '2020-06-01'),
('105', 'Thomas','David', 'Civil', false, '2020-06-01');
SELECT * FROM student;Data available in the table:
Example #1 – Equal (=) operator
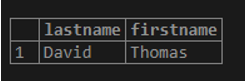
If you want to get all students whose first names are ‘Thomas.’
Code:
SELECT lastname, firstname
FROM student
WHERE firstname = 'Thomas';Output:
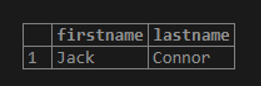
Example #2 – AND operator
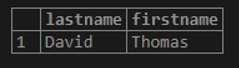
The following example finds the student whose first name is Thomas, and last name is David by using the AND logical operator to combine two Boolean expressions.
Code:
SELECT lastname, firstname
FROM student
WHERE firstname = 'Thomas' AND lastname = 'David';Output:
Example #3 – OR operator
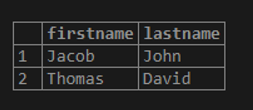
Using the OR operator, this example finds the students whose ‘lastname’ is ‘David’ or ‘firstname’ is ‘Jacob’.
Code:
SELECT firstname, lastname
FROM student
WHERE lastname = 'David' OR firstname = 'Jacob';Output:
Example #4 – IN operator
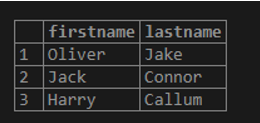
You can use the IN operator to match a string with any string in a list. For example, the following statement returns students whose ‘firstname’ is ‘Oliver’, ‘Jack’, or ‘Harry’.
Code:
SELECT firstname, lastname
FROM student
WHERE firstname IN ('Oliver', 'Jack', 'Harry');Output:
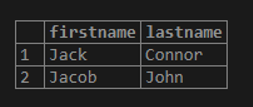
Example #5 – LIKE operator
You use the LIKE operator to find a string that matches a specified pattern. The following examples return all students whose names start with the string ‘Ja.’
Code:
SELECT firstname, lastname
FROM student
WHERE firstname LIKE 'Ja%';Output:
The % is called a wildcard that matches any string. The ‘Ja%’ pattern matches any string that starts with ‘Ja’.
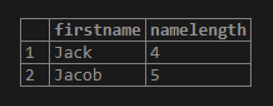
Example #6 – BETWEEN operator
The following example uses the BETWEEN operator to find students whose first names start with the letter J and whose lengths are between 3 and 5. Note that the BETWEEN operator returns true if a value is in a range of values.
Code:
SELECT firstname, LENGTH (firstname) namelength
FROM student
WHERE firstname LIKE 'J%' AND LENGTH (firstname) BETWEEN 3 AND 5
ORDER BY namelength;Output:
In this example, we used the LENGTH () function returns the number of characters of the input string.
Example #7 – Not equal operator (<>) or (! =)
This example finds students whose first name starts with ‘Ja’ and the last name is notJohn.’
Code:
SELECT firstname, lastname
FROM student
WHERE firstname LIKE 'Ja%' AND lastname <> 'John';Output:
Note that you can use != operator instead of <> operator. They have the same effect.
Example #8 – Combining AND & OR conditions
Execute the following query
Code:
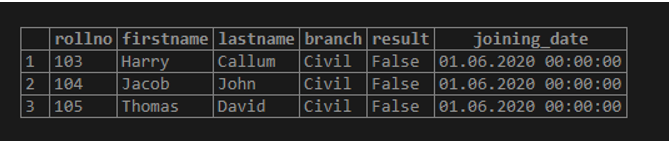
SELECT *
FROM student
WHERE (lastname = 'David' AND firstname = 'Thomas') OR (rollno >= 103);Output:
Example #9 – Joining Tables
Execute the following query
Code:
SELECT student.firstname, temp_student.result
FROM student
INNER JOIN temp_student
ON student.rollno = temp_student.rollno
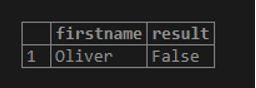
WHERE student.firstname = 'Oliver';Output:
The above WHERE clause is used to join multiple tables together in a single SELECT statement. This SELECT statement would return all firstname and result values with a matching record in the student and temp_student tables based on rollno and where the firstname is ‘David’.
Conclusion
The PostgreSQL WHERE clause filters rows with SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE statement. This article intends to introduce you to where clause in PostgreSQL.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL WHERE Clause” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.