Updated March 24, 2023
Introduction to PowerShell Set-Location
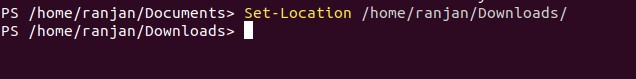
We know about the Get-Location function, it gives us the current directory path. Now let’s suppose, we want to change our current directory to any other directory, So we have PowerShell Set-Location. The set-location command will change your current directory to any other directory or registry. Set-Location can change your current location to another directory, registry or any subdirectory. You might be thinking about why we need this. Suppose you are in “/home/ranjan/Document” directory and you want to switch to “/home/ranjna/Download”, so for that, you do not require to do a lot more you just have to set the location to “/home/ranjan/Download”.look at the given below example.
Set-Location /home/ranjan/Downloads/
Output:
We can use location as stack and we can Push location and pop location with the command Push-Location and Pop-Location respectively.
Syntax for PowerShell Set-Location
A very simple syntax for PowerShell Set-Location is given below. There are three main syntaxes of it.
1) – Path Command: Here we can pass wildcard and it will show us match pattern see the below syntax.
Set-Location
[[-Path] <string path>]
[-PassThru<rreturn object of representing location>]
[<CommonParameters>]
2) – LiteralPath Command: Here we can not pass wildcard and it will take the exact path, see the below syntax.
Set-Location
-LiteralPath <Only exact match will work no wildcard works here>
[-PassThru]
[<CommonParameters>]
3) – Stackname Command: Here it will return result from the stack, which holds up to 20 last pushed addresses inside memory, we can pop these addresses in a reverse manner. See the below syntax. In the example, we will discuss it more.
Set-Location
[-PassThru(return object of representing location)]
[-StackName <string stack name like alias>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Parameters of PowerShell Set-Location
Following are some parameters of the PowerShell set-location explained below:
1) – LiteralPath
Its name is reflecting it’s utility. -Literalpath command is used to find the path which completely matches, it means wildcards are not allowed. For example, suppose you are searching for any specific directory and you know the exact name of that directory then you can use this command. Always remembers this is useful for situations where you know the exact name.
2) – PassThru
It returns the object containing a representing the location. It does not return anything by default. This is the only command which returns Object in Set-Location command.
3) – Path
The path represents where we are working or going to work. Whenever we write pathname it assigns the pathname to that. It supports wildcard, and whenever we are using any wild card, in that case, it reads the first match wildcard pattern. Remember PowerShell has the capability to remember 20 locations that you have set and up to this you get. So for example if you are writing Set-Location -path “/ran” and then you clicked the tab to search match directory, it will show you “ranjan” and other match patterns.
4) – StackName
In very simple words, This command makes the whatever stack name we are giving as current location stack. In stock you can get your stored address in reverse order, let’s take an example, first, we pushed “/home/ranjan/Document”, second we pushed “/home/ranjan/Download” and 3rd we pushed location “/home/ranjan/Desktop”, so when we will try to pop the locations, first we will get “/home/ranjan/Desktop” which was the last entry pushed and then “/home/ranjan/Download” and finally, in last we will get “/home/ranjan/Document”.
Examples to Implement PowerShell Remove-Item
Below are the different examples to implement PowerShell remove-item:
Example #1
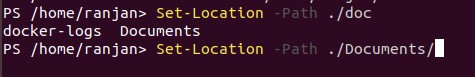
In the explanation of the above parameters we discuss -path, and we learned that it can take wildcard and on search. It returns the last 20 matches. In the below example we are setting current working directory to “/home/ranjan/Document” from “/home/ranjan”. So in search, we write like below example and click the tab to search related path (tab click).
Set-Location -Path ./doc
It will return below out as there 3 characters are matching. We can see the output screens in this example below.
docker-logs Documents
Output:
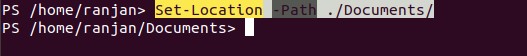
And if we are writing full path and click enters it will change the current path. See the example and screen of output in the below example.
Set-Location -Path ./Documents/
Output:
Example #2
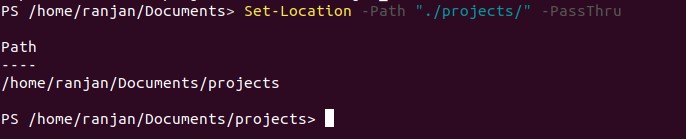
Let’s talk about -PassThru, this example will show us how this command returns currently selected path. Here we are checking for “./projects” and in the output, it returns root path to “/home/ranjan/Documents/projects”. It always returns Object.
Set-Location -Path "./projects/" -PassThru
Output:
Example #3
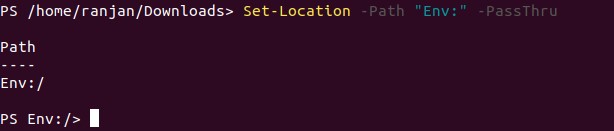
See this example, it’s a very unique type of situation, where we wanted to directly reach to the root path of “Env”. PowerShell has the power to find it’s root directory without writing any extra line of code. Many times, when you are writing any script you may need to know or find the root directory. This command will be very useful for that kind of situation.
Set-Location -Path "Env:" -PassThru
Output:
Example #4
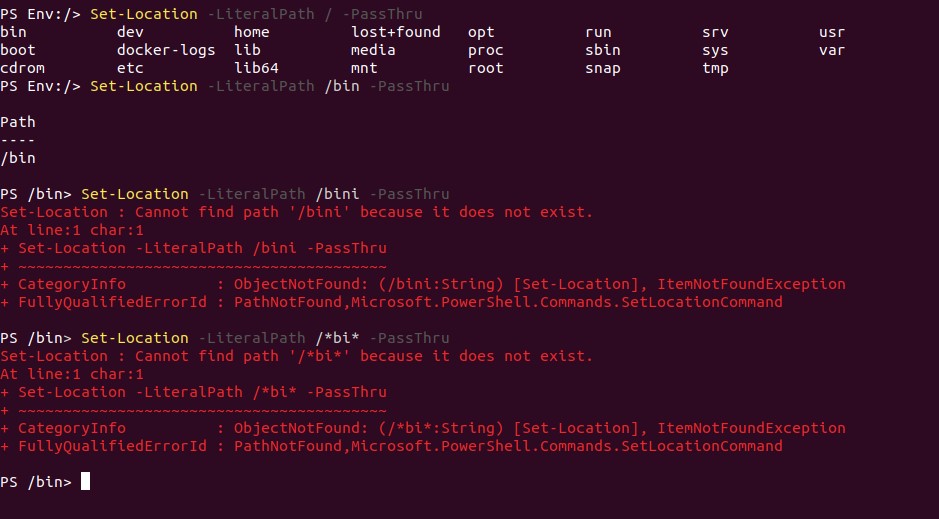
In the below example you can see we are passing “/bin” in the LiteralPath, and once clicking enter we directly reached /bin directory without writing full path of it. We have already discussed that -LiteralPath always take a complete path, that means we can not pass a wildcard path. Here we need to mention the exact path only to go to that directory. In this example, we were trying to pass /bi or little match it was not working, As we said it will take a complete path only, not wildcard will work here.
Set-Location -LiteralPath /bin -PassThru
Output:
Example #5
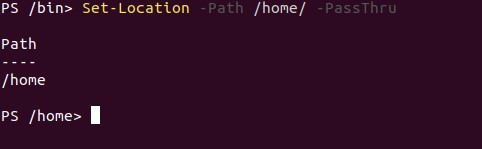
The below example shows how we are changing our directory from /bin to /home. If we will try to do the same without knowing the root path of /home will be a very hard job. So here PowerShell makes our life very easy by providing this command, where without knowing the exact path I can switch to that path .let’s see the example below along with the screen. From all examples, one thing you should notice that Get-Location does not return any output until we are not using -PassThru command.
Set-Location -Path /home/ -PassThru
Output:
Here output returns root path along with a switch to /home. here -PassThru return Object.
Conclusion
PowerShell Set-Location, I am expecting that we are able to understand the basic uses of PowerShell Set-Location. Set-Location command does not return any output until we are not using the command -PassThru. Set-Location allows us to move one directory to any directory without knowing too much about the directory structure.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to PowerShell Set-Location. Here we discuss the syntax, parameters, and examples to implement PowerShell Set-Location in detail. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –