Updated May 16, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL WITH Clause
PostgreSQL with clause is used to write the auxiliary statement to use large query, with clause is helpful when we have executing complicated large queries into the simple forms. While using with clause, the output of this clause is easily readable, with clause is also called as common table expressions or CTE, it is also define as a temporary table which only exist only that specific query. We can execute multiple Subquery by using multiple queries in PostgreSQL, it is helpful by using multiple temporary tables.
Syntax and Parameters
Below is the syntax of with clause in PostgreSQL.
- With name_of_CTE (list_of_column) AS (Select query statement)
Select column_list
From name_of_table
Where condition (select column_list from name_of_table)
Order by name_of_column;- With name_of_CTE (list_of_column) AS (
Definition of CTE query)
Statement;Below is the parameter description syntax of with clause in PostgreSQL.
- With clause: In PostgreSQL, we define this clause as one that executes the Subquery and large Subquery.
- Name of CTE: This is the defined name of the common table expression we used with clause.
- AS: We define this as the usage of an alias name for a common table expression in the with clause.
- List of the column: It is defined as a column list that we have used in with clause.
- Select query statement: We used a select query statement with a common table expression and the clause in PostgreSQL. We are using multiple select statements in with clause.
- Name of a table: It is defined as the name of the table from which we have retrieving data by using with a clause in PostgreSQL. We can use multiple tables to retrieve data from multiple tables using a clause in PostgreSQL.
- Where condition: It is defined as the condition by using the same we have retrieved data from the table. Where the condition is useful when we have to retrieve specified data from the table.
- Order by: When used with the where clause, the order by clause defines the retrieval of data with ascending or descending order.
- Definition of common table expression: This is defined as a definition query of CTE, which we used in with clause.
How WITH Clause works in PostgreSQL?
We can specify the column list by using the common table expression in PostgreSQL. In PostgreSQL, we may also join the table by utilising a clause. We have also use the recursive with a clause in the query. To execute the with clause statement, we need to have select privileges on a table, or we need to have superuser privileges to execute the with clause statement.
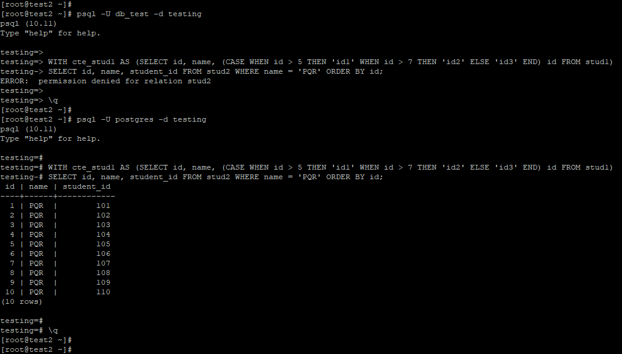
The example below shows that a clause statement requires select privileges on table or superuser privileges to execute with a clause statement.
Code:
psql -U db_test -d testing
WITH cte_stud1 AS (SELECT id, name, (CASE WHEN id > 5 THEN 'id1' WHEN id > 7 THEN 'id2' ELSE 'id3' END) id FROM stud1)SELECT id, name, student_id FROM stud2 WHERE name = 'PQR' ORDER BY id;
psql -U postgres -d testing
WITH cte_stud1 AS (SELECT id, name, (CASE WHEN id > 5 THEN 'id1' WHEN id > 7 THEN 'id2' ELSE 'id3' END) id FROM stud1)SELECT id, name, student_id FROM stud2 WHERE name = 'PQR' ORDER BY id;Output:
Explanation: In the above first example, we have used the user as db_test, this user doesn’t have privileges of select on stud1 and stud2 table or superuser, so it will issue an error while executing the with clause statement. In the second example, we have selected the table rows using the username as Postgres, after using this user, we have selected the column from the stud1 and stud2 table. Postgres users have superuser privileges in PostgreSQL.
Examples to Implement PostgreSQL WITH Clause
Below is an example of with clause in PostgreSQL.
We are using stud1 and stud2 table to describe an example of with clause in PostgreSQL are as follows.
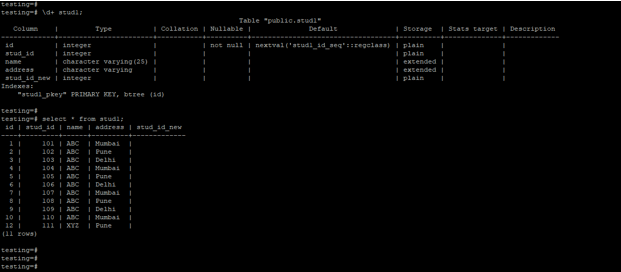
- Below is the table and data description of the stud1 table.
Code:
\d+ stud1;
select * from stud1;Output:
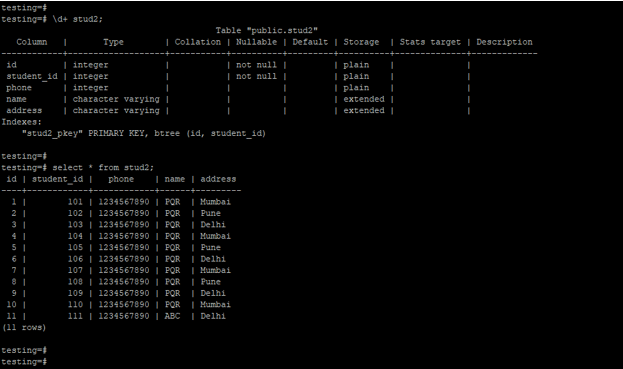
- Below is the table and data description of the stud2 table.
Code:
\d+ stud2;
select * from stud2;Output:
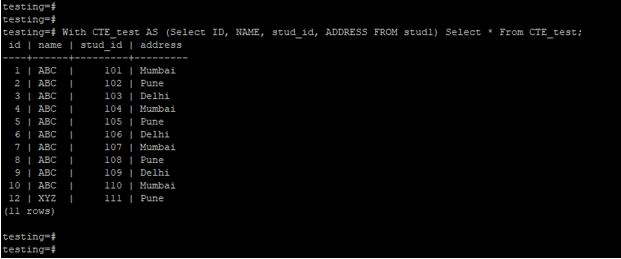
1. Simple with clause.
Below example shows that with clause are as follows. We have use CTE name as CTE_test.
Code:
With CTE_test AS (Select ID, NAME, stud_id, ADDRESS FROM stud1) Select * From CTE_test;Output:
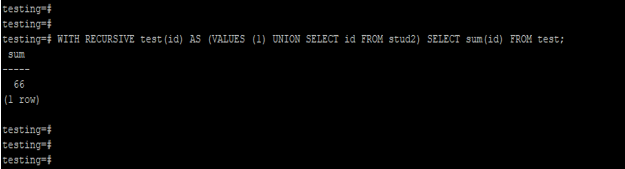
2. Recursive With clause
Below example shows that recursive with clause are as follows. We have use CTE name as test(id).
Code:
WITH RECURSIVE test(id) AS (VALUES (1) UNION SELECT id FROM stud2) SELECT sum(id) FROM test;Output:
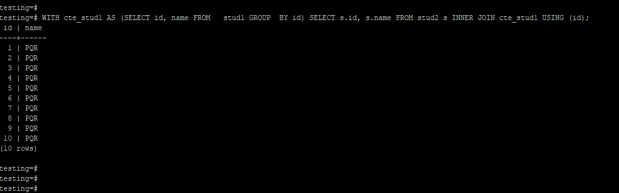
3. With the clause in join operations
Below example shows that with a clause in join, operations are as follows. We have used stud1 and stud2 tables to join operation using with clause.
Code:
WITH cte_stud1 AS (SELECT id, name FROM stud1 GROUP BY id) SELECT s.id, s.name FROM stud2 s INNER JOIN cte_stud1 USING (id);Output:
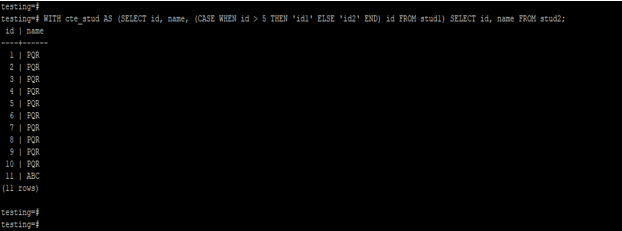
4. With clause using condition
Below example shows with clause using condition.
Code:
WITH cte_stud AS (SELECT id, name, (CASE WHEN id > 5 THEN 'id1' ELSE 'id2' END) id FROM stud1) SELECT id, name FROM stud2;Output:
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL WITH Clause” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.