Updated May 24, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL INSERT INTO
PostgreSQL provides an insertion operation we call as INSERT INTO statement. Insert into statement performs essential functions in the database administration system. With the help of insert into statements, we can insert single records or multiple records into database tables at a time. Before the insertion operation, we need a table, without the creation of the table, we cannot perform insert into statement. Insert into comes under the data manipulation category. The set of manipulation commands is used to manipulate data stored in databases. Under insert into the statement, we can perform different operations on the table.
Syntax:
INSERT INTO SPECIFIED TABLE NAME (COLUMN NAME 1, COLUMN NAME 2, COLUMN NAME 3 ............. COLUMN NAME N) VALUES (VALUE 1, VALUE 2, VALUE 3, .................. VALUE N);Explanation:
- In the above syntax where insert into, values are keywords, table name means specified table name that we need to insert data after column name means specified column name in the table in which we need to insert data, and value means an actual value that we need to insert into the table.
- Column and values are separated using a comma. If the data is a string, then use a double inverted comma.
How PostgreSQL INSERT INTO Statements work?
- We must install PostgreSQL in our system.
- Require basic knowledge about PostgreSQL.
- We must require tables to perform the insert operation.
Different Methods to insert into the statement are as follows:
Let’s create a table to perform insert into a statement using a create table statement. So we use the following statement to create a table.
Syntax:
create table table name ( column name_1 data type (null | not null), column name_2 data type ( null | not null),……………. Column name_N);Explanation:
- In the above syntax where create the table is a keyword, table name means new table name that we need to develop, and column names 1 and 2 specified column name in the table with data type and operator.
- We are separating the name of the columns by using the comma.
Example:
Code:
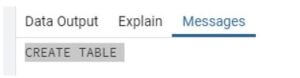
CREATE TABLE emp_info (
emp_id INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
emp_name TEXT NOT NULL,
emp_age INT NOT NULL,
address CHAR(50),
salary REAL);Explanation:
- In the above statement, we create a table name as emp_info using create table statement. In the emp_info table, we created 5 columns such as emp_id, emo_name, emp_age, emp_address, and salary with different data types and also we defined emp_id as the primary key with not null constraint, and we use real data type to salary column because salary may be a float.
- Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Output:
Now we perform insert into a statement on the table using the following methods.
Basically, we use two methods for insertion operation as follows:
1. Single row insert into operation.
In a single row insertion operation, we can insert a single row at a time in the table.
Syntax:
Inset into table name (column 1, column 2, …………………column n ) values (value 1, value 2, …………….value n);Explanation:
- In the above syntax, where insert into is a keyword, where the table name is the specified table name, column 1, column 2, column n column name in the table, and values means that we need to insert.
Example:
Code:
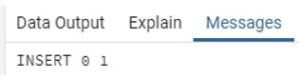
INSERT INTO emp_info (emp_id, emp_name, emp_age, address, salary)
VALUES (1, 'poll', 28, 'london', 30000.00);Explanation:
- In the above statement table name is emp_info that table we already created with the above columns, so we need to add values in the table.
- Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Output:
2. Multiple row insertion operations.
In this method, we insert multiple rows at a time using the following syntax.
Syntax:
Code:
Inset into table name (column 1, column 2, …………………column n ) values (value 1, value 1, …………….value n),
(value 2, value 2, …………….value n),
(value 3, value 3, …………….value n);Explanation:
- Suppose we need to insert multiple rows at a time, that time, we use the above syntax similarly where to insert into is a keyword, the table name is the specified table name, column 1 is a column name in the table values that we need to insert.
- Column name and values are separated by using a comma.
Example:
Code:
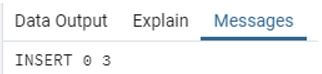
INSERT INTO emp_info (emp_id, emp_name, emp_age, address, salary)
VALUES (2, 'alex', 30, 'Hongkong', 40000.00),
(3, 'john', 35, 'Newyork', 50000.00),
(4, 'bob', 32, 'Sydney', 20000.00);Explanation:
- In the above example, we have emp_info table, emp_id, emp_name, e,p_age, address, and salary, which are the column names in which we need to insert data and values to insert value in the column.
- If the data is a string, then use a double inverted comma.
- Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Output:
Another way to perform insert into a statement is by using the following statement.
Example:
Code:
INSERT INTO emp_info VALUES (8, 'paul', 30, 'perth', 40000.00);Explanation:
- In the above statement, we insert values directly into the table without the column name.
- Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Output:
Getting the last insert row in the table.
We use the following statement to get the last inserted row in the table.
Code:
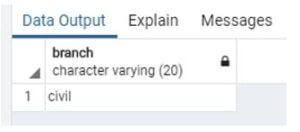
insert into college (branch, no_of_student) values ('civil', 60) returning branch;Explanation:
- In the above statement, we created a table name as college and a two-column branch and no of students, and we insert value civil in-branch column and 60 in no of students, and the returning branch is used to know the last inserted branch in the table result of returning clause is similar with select clause.
- Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Output:
Output Notation Message:
- Insert oid 1: The meaning of the above message is it returns only one row.
- Insert 0 #: The meaning of the above message is it returns multiple rows. # is used to show the number of rows inserted.
Conclusion
From the above article, we saw the basic syntax of the insert into statement then we also saw how we can use insert into a statement by using different methods like single row and multiple rows with examples. From this article, we saw how we can handle insert into statements correctly.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL INSERT INTO” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.