Updated May 31, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL Timestamp with Timezone
PostgreSQL timestamp with timezone is defined as showing timestamp with timezone, which we have defined to the database server. In PostgreSQL, two data types of timestamp are available, i.e., timestamp with timezone and timestamp without a timezone; the timestamptz is defined as timestamp with timezone. Timestamptz is a zone-aware data type of date and time, the default timezone of the PostgreSQL database is UTC which means when we insert any value in the timestamptz data type column, it will automatically convert into UTC. When we query timestamptz to table the same time, the UTC value again converts back to the time. In this topic, we will learn about PostgreSQL Timestamp with Timezone.
Syntax
Below is the syntax of timestamp with timezone in PostgreSQL.
Create a table to define the column data type as timestamp with timezone.
Create table name_of_table (name_of_column1 data_type, name_of_column2 TIMESTAMPTZ, name_of_column3 data_type, …, name_of_columnN data_type);Select timestamp with timezone
Select 'Date time':: timestamptz as "Select timestamp with time zone in PostgreSQL";OR
select date time::timestamptz;OR
SELECT 'Date time':: timestamptz at time zone 'timezone' as "name_of_timezone";Set timezone
SET TIME ZONE 'name_of_timezone';Below is the parameter description syntax of timestamp with timezone in PostgreSQL.
- Select –This is defined as a select timestamp with a timezone in PostgreSQL. We can select the same from the table column and the system time.
- Create table –create the table by defining the data type as timestamp with time zone to the specified column.
- Name of the table – It is used to define the table name, uniquely identified from which table column we have defined data type as timestamp with the time zone in PostgreSQL.
- Name of the table – This is defined as the column’s name from which the table column defines the data type as a timestamp with the time zone in PostgreSQL.
- Data type –This is defined as the column’s data type at the time of table creation in PostgreSQL. We can define any data type in the column at the time of table creation.
- Set time zone –This is defined as a set time zone for the database server. We can set the server’s time zone using the set time zone command.
- Date and time –We use date and time when setting timestamp with timezone in PostgreSQL.
How Timestamp with Timezone works in PostgreSQL?
Below is the working timestamp with the timezone in PostgreSQL.
We can use a timestamp data type in PostgreSQL with and without the time zone. If we want to use a without a time zone, we need to use a timestamp data type; if we’re going to use a timestamp with a time zone, we need to use a timestamp data type.
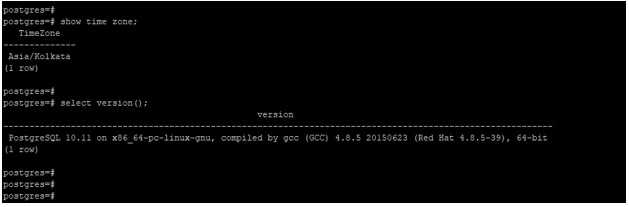
We can see the server’s timezone by using the show timezone command. The example below shows how to see the server timezone in PostgreSQL as follows.
showtime zone;Output:
In the above example, the current timestamp with the timezone is Asia/Kolkata; we can change the same by using the set time zone command.
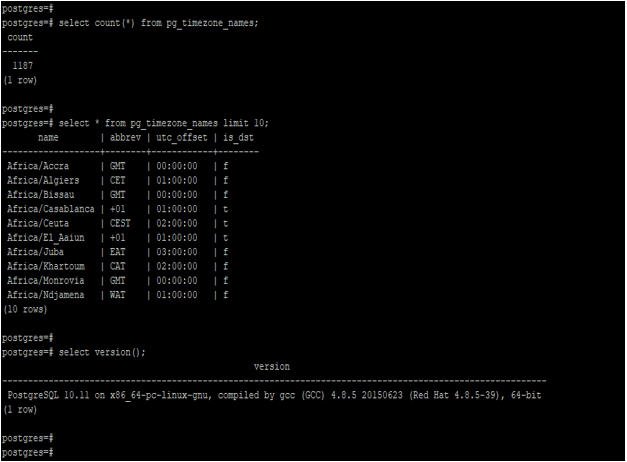
There is an 1187 timezone available in PostgreSQL version 10. Below is an example of the timezone which was available in PostgreSQL.
select count(*) from pg_timezone_names;
select * from pg_timezone_names limit 10;Output:
The above example shows that the pg_timezone_names catalog table contains all timezone names available in PostgreSQL version 10.
In PostgreSQL, the timestamp with timezone data type includes the utilized timezone name and its abbreviation.
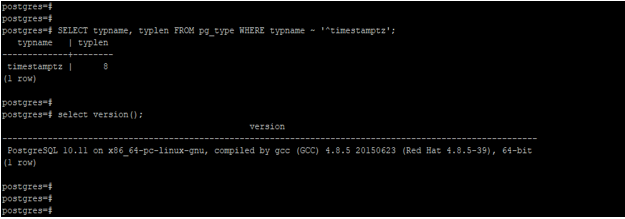
The timestamp with time zone data type storage size is 8 bytes. The below example shows the size of the timestamptz data type in PostgreSQL.
SELECT typname, typlen FROM pg_type WHERE typname ~ '^timestamptz';Output:
PostgreSQL stores the timestamp with timezone data type in UTC format. Thus, when inserting the date and time into a table, the timestamp with the timezone data type changes its value.
Its value remains unchanged after inserting a timestamp without the timezone data type into the table.
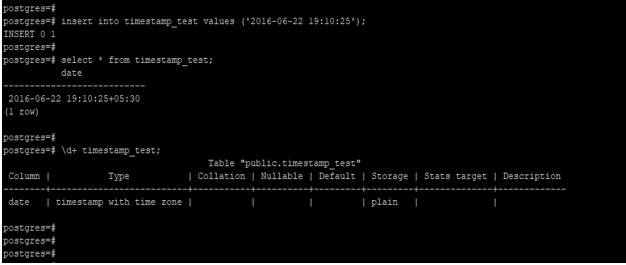
The following example demonstrates the automatic addition of the timezone when defining the timestamptz data type for a column.
insert into timestamp_test values ('2016-06-22 19:10:25');
select * from timestamp_test;
\d+ timestamp_test;Output:
Examples
Below is an example of a timestamp with the time zone in PostgreSQL.
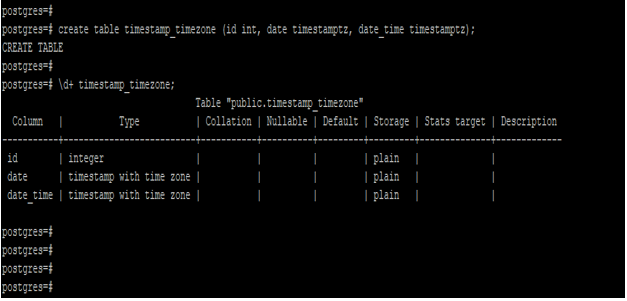
Example #1 – Create a table to define timestamptz data type to the column
The below example shows that create a table and define the timestamptz data type to the column.
We have defining the timestamp with time zone data type to the date and date_time column.
create table timestamp_timezone (id int, date timestamptz, date_time timestamptz);
\d+ timestamp_timezone;Output:
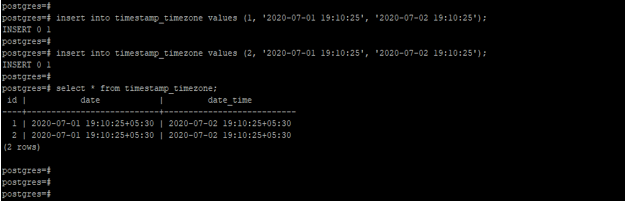
Example #2 – Insert date into the timestamptz datatype column
The below example shows that insert date into the timestamptz data type column.
insert into timestamp_timezone values (1, '2020-07-01 19:10:25', '2020-07-02 19:10:25');
insert into timestamp_timezone values (2, '2020-07-01 19:10:25', '2020-07-02 19:10:25');
select * from timestamp_timezone;Output:
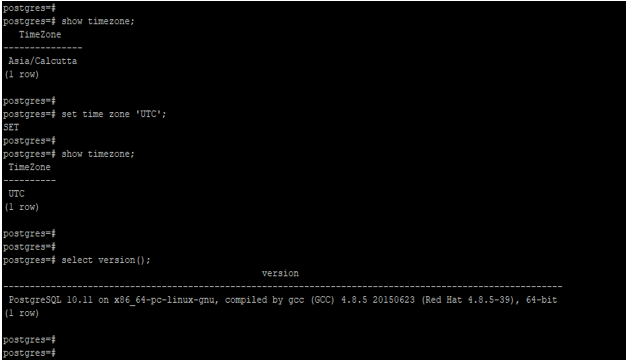
Example #3 – Change the timezone
The below example shows changes in the timezone of the database in PostgreSQL.
In the below example, we have to change the timezone from Asia/Calcutta to UTC.
show timezone;
set time zone 'UTC';
show timezone;Output:
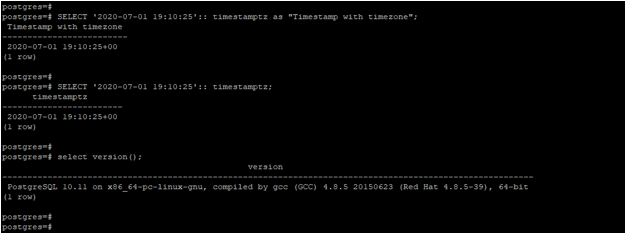
Example #4 – Select the timestamp with the timezone of the date
The below example shows that select the timestamp with the timezone of date in PostgreSQL.
In the below example, we have selected a timestamp with a timezone for the date of ‘2020-07-01 19:10:25’.
SELECT '2020-07-01 19:10:25':: timestamptz as "Timestamp with timezone";
SELECT '2020-07-01 19:10:25':: timestamptz;Output:
Conclusion
Two types of timestamp data types are available in PostgreSQL, i.e., timestamp and timestamptz. We define a timestamp with a timezone as a column value in a time zone format. There is an 1187 timezone available in PostgreSQL version 10. PostgreSQL database uses the UTC zone as its default time zone.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL Timestamp with Timezone” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.