Updated May 15, 2023
Introduction to hstore in PostgreSQL
In order to consider the key-value pair as a single entity, the PostgreSQL hstore module implements the hstore data type, which can be used in various cases, like semi-structured data or a row with multiple attributes we cannot try to fetch very often. The data type of keys and values is a string. The PostgreSQL hstore data type is a similar dictionary we use with other programming languages; The PostgreSQL hstore is specific to the column. It is not necessary to define the keys beforehand.
Syntax
column_name hstoreExplanation: The name of the column whose data type will be store.
How hstore data type works in PostgreSQL?
We need to enable the hstore extension in order to use the hstore data type. We can load the contrib module to the PostgreSQL instance with the help of the hstore extension. Syntax to create the extension for hstore is as follows:
CREATE EXTENSION hstore;Hstore store the key and value pair where we have to add a double quote around both key and value fields as follows:
"<key>":"<value>"The PostgreSQL hstore data type is used if the column’s value does not fit into the relational column. The PostgreSQL hstore column works dynamically, which means you do not need to specify the key prior to the table creation; you can create a table with the hstore column and insert values with different keys later.
Examples to Implement hstore data type in PostgreSQL
In order to understand the examples of the hstore data type, we will create a table named ’employee’ containing the hstore data type.
Create a table ’employee’ with hstore data type using CREATE TABLE statement as follows:
CREATE TABLE employee (
id serial primary key,
name VARCHAR (255),
data hstore
);the data column will have the properties of the employee, like job type, salary, and contact number. The data column of the employee table is of the hstore data type.
Now, we will insert rows into the employee table with the help of the following INSERT INTO statement as follows:
INSERT INTO employee (name, data)
VALUES
(
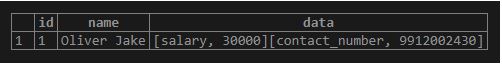
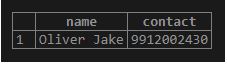
'Oliver Jake',
'"contact_number" => "9912002430",
"salary" => "30000",'
);Here you can see the list of comma-separated key-value pairs data is inserted into the hstore column. Illustrate the content of the employee table using the following SELECT statement and snapshot:
SELECT * FROM employee;Now we will insert another row using the INSERT INTO statement as follows.
INSERT INTO employee (name, data)
VALUES
(
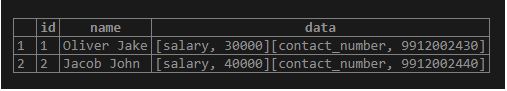
'Jacob John',
'"contact_number" => "9912002440",
"salary" => "40000",'
);Illustrate the content of the employee table using the following SELECT statement and snapshot:
SELECT * FROM employee;Example #1 – Retrieve the data from hstore column
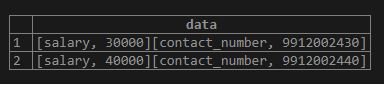
We can fetch the data from the hstore column by using the following statement.
Code:
SELECT
data
FROM
employee;Output:
Example #2 – Retrieve the data for the specific key of hstore
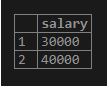
In order to fetch the particular key of the data column of the hstore type, we can use the arrow (->) operator as follows:
Code:
SELECT
data -> 'salary' AS salary
FROM
employee;Output:
Example #3 – Where clause with key-value
We can add a condition in the where clause in order to filter the rows with the help of the arrow (->) operator:
Code:
SELECT
name,
data -> 'contact_number' AS Contact
FROM
employee
WHERE
data -> 'salary' = '30000';Output:
Example #4 – INSERT a key-value pair
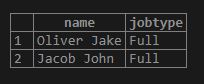
We can add a key-value pair by using the hstore column. Here we will add the job type in the data column of the Employee table by using the following statement:
Code:
SELECT
name,
data -> 'job_type' AS JobType
FROM
Employee;Output:
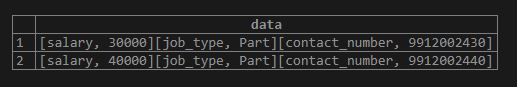
Example #5 – Update the key-value pair
We can modify the key-value pair of the hstore column. Use the following statement to update the value of the “job_type” key to “Part”.
Code:
UPDATE employee
SET data = data || '"job_type"=>"Part"' :: hstore;Output:
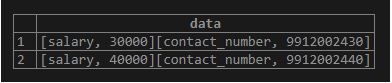
Example #6 – Delete the key-value pair
We can delete the key-value pair from the data column, which is of type store, by using the following statement.
Here we will delete the key-value pair “job_type” => “Part” in the data column:
Code:
UPDATE employee
SET data = delete(data, 'job_type');Output:
Example #7 – Fetch all keys stored in hstore column
In order to fetch all keys stored in hstore type column, we have to use the keys() function or skey() function as follows:
Code:
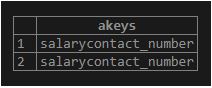
SELECT
akeys (data)
FROM
employee;Output:
The skey() function provided by PostgreSQL is used to fetch the result as a set:
Code:
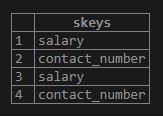
SELECT
skeys (data)
FROM
employee;Output:
Example #8 – Fetch all values from the data column
Similar to the keys, we can fetch all values from the data column, which is of hstore type, by using the avals() function or svals() function provided by PostgreSQL:
Code:
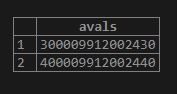
SELECT
avals (data)
FROM
employee;Output:
The svals() function provided by PostgreSQL is used to fetch the result as a set:
Code:
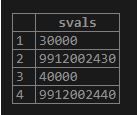
SELECT
svals (data)
FROM
employee;Output:
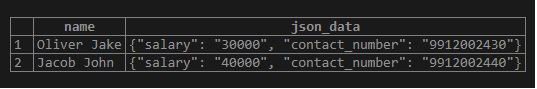
Example #9 – Convert hstore data to JSON data
We can use PostgreSQL’s hstore_to_json() function for converting the hstore data to JSON:
Code:
SELECT
name,
hstore_to_json (data) json_data
FROM
employee;Output:
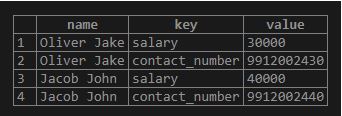
Example #10 – Convert hstore data to sets
We can use PostgreSQL’s each() function for converting the hstore data to sets.
Code:
SELECT
name,
(EACH(data) ).*
FROM
employee;Output:
Conclusion
We hope from the above article you have understood how to use the PostgreSQL hstore data type and how the PostgreSQL hstore data type works to store the data in key-value pair. Also, we have added some examples of the PostgreSQL hstore to understand it in detail.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “hstore in PostgreSQL” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.