Updated May 11, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL REINDEX
We generally use the PostgreSQL REINDEX statement to reconstruct one or more indexes. Sometimes due to software problems or bugs or some hardware failures, the indexes got corrupted; in such cases, we can use this statement to recover the index. We can recreate the index for TABLE, SCHEMA, DATABASE, or SYSTEM DATABASE and recreate the INDEX. The PostgreSQL REINDEX statement first drops all indexes and then creates all, which means it builds all indexes from scratch. The PostgreSQL REINDEX statement uses locking mechanisms to reconstruct the contents of the index.
Syntax
Consider the following syntax to understand the statements:
Syntax:
REINDEX
[ ( VERBOSE ) ]
{SCHEMA | DATABASE | TABLE |SYSTEM | INDEX }
name;Explanation
- VERBOSE: This keyword is optional. The statement shows the progress report when the VERBOSE is defined while indexes are being reindexed.
- INDEX: Reconstruct the defined index.
- TABLE: Reconstruct all indexes of the defined table.
- DATABASE: Reconstruct all indexes of the defined database.
- SYSTEM: Reconstruct all indexes on the system of the defined database.
- name: This field defines the name of the index, table, database, or schema.
We can recreate the index for TABLE, SCHEMA, DATABASE, or INDEX.
Let’s understand the syntax for each of them as follows:
1. Recreate a Single Index.
REINDEX INDEX index_name;2. Recreate all the indexes of a table.
REINDEX TABLE table_name;3. Recreate all indices in a schema.
REINDEX SCHEMA schema_name;4. Recreate all indices in a particular database.
REINDEX DATABASE database_name;5. Recreate all indices in a system database.
REINDEX SYSTEM database_name;How PostgreSQL REINDEX Works?
It drops and recreates of the indexes, which means it rebuilds all indexes from scratch. The statement uses locking mechanisms to recreate the indexes.
To use the REINDEX statement, we need to own the INDEX, TABLE, or DATABASE. Superusers can use the PostgreSQL REINDEX statement with anything.
Examples to Implement
Below are the examples:
Example #1 – Recreate a Single Index
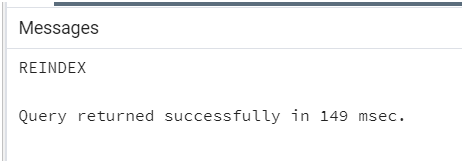
Consider the following statement where we need to define the index name after the PostgreSQL REINDEX INDEX clause; consider we have an index of name student_index, then we can recreate it using the PostgreSQL REINDEX statement.
Query:
REINDEX INDEX student_index;Output:
Example #2 – Recreate all the Indexes of a Table
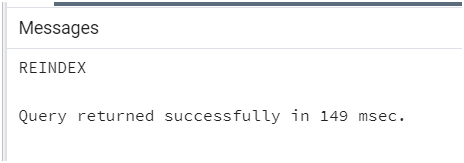
Consider the following statement where we need to define the table name after the REINDEX TABLE clause. Consider we have a table of name student_table, then we can recreate all indexes using the PostgreSQL REINDEX statement.
Query:
REINDEX TABLE student_table;Output:
Example #3 – Recreate all Indices in a Schema
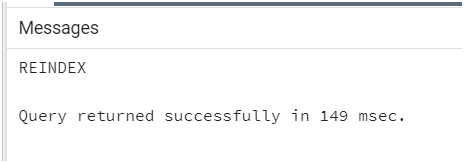
Consider the following statement where we need to define the schema name after the REINDEX SCHEMA clause. Consider we have a schema of name student_schema, then we can recreate all indexes using the statement.
Query:
REINDEX SCHEMA student_schema;Output:
Example #4 – Recreate all Indices in a Particular Database
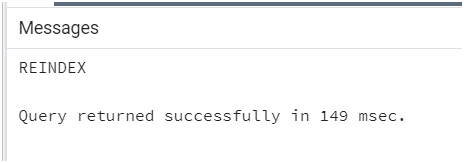
Consider the following statement where we need to define the database name after the PostgreSQL REINDEX DATABASE clause. Consider we have a database of name student_database, then we can recreate all indexes using the REINDEX statement.
Query:
REINDEX DATABASE student_database;Output:
Example #5 – Recreate all Indices in a System Database
Consider the following statement where we need to define the database name after the PostgreSQL REINDEX SYSTEM clause. Consider we have a system database of name system_db, then we can recreate all indexes by using the REINDEX statement.
Query:
REINDEX SYSTEM system_db;Output:
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL REINDEX” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.