Updated May 9, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL replace
The following article provides an outline on PostgreSQL replace. When we manipulate strings or work with strings in PostgreSQL, we require many functions to perform operations. PostgreSQL provides us with many string manipulating functions. The REPLACE() method can replace a substring from the original string with another substring you wish to. Besides this, we can even replace the strings that match the particular regular expression we know using the REGEXP_REPLACE() method. The TRANSLATE() method is available that helps us replace the set of substrings with a particular substring in the original string.
Syntax:
REPLACE(original_string, old_sub_string, new_sub_string );- original_string: This is the source string, the original string containing some substring you wish to replace.
- old_sub_string: This is the substring that is present in the original string and which you want to replace. It can be present at any number of times in the source string.
- new_sub_string: This is the substring with which the old substring value should be replaced.
The replace() Function replaces all the occurrences of old_sub_string to new_sub_string in the original_string.
Examples of PostgreSQL replace
Given below are the examples mentioned:
Example #1
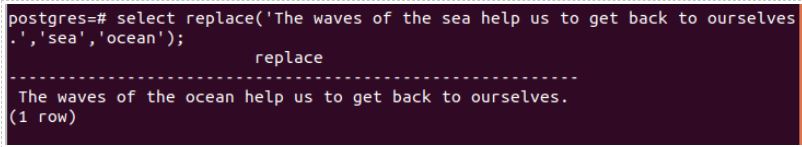
Consider one string, “The waves of the sea help us to get back to ourselves.” We want sea words to replace the ocean. We can do so by using the replace() Function in the following way.
Code:
select replace('The waves of the sea help us to get back to ourselves.', 'sea', 'ocean');Output:
Example #2
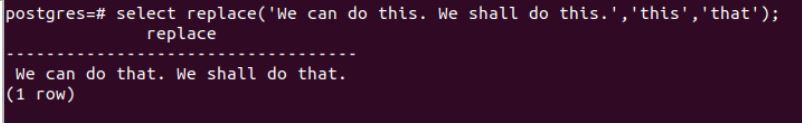
‘We can do this. We shall do this.’ This is the sentence in which we want to replace the “this” word with the “that” word. For this, we will use the following query statement.
Code:
select replace('We can do this. We shall do this.','this','that');Output:
The REPLACE() method replaces both occurrences of the word ‘this’ with the word ‘that’ in the given string.
Example #3
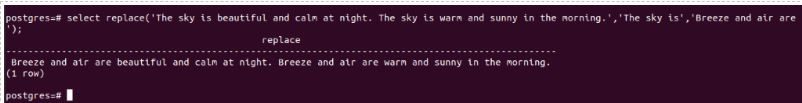
Instead of replacing the word, let us replace the substring in the original string. Consider a string “The sky is beautiful and calm at night. The sky is warm and sunny in the morning.” and replace the substring “The sky is” with the “Breeze and air are” substring. We will again use the replace() method to do this, and our query statement will be as follows.
Code:
select replace('The sky is beautiful and calm at night. The sky is warm and sunny in the morning.','The sky is','Breeze and air are');Output:
Example #4
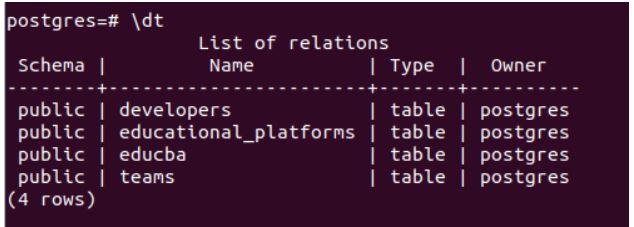
Now, we will replace the substring of the particular column of the table with some other substring. Let us fire \dt command to see all the tables present in my database.
Code:
\dtOutput:
Example #5
Now, let us see the contents by firing the following query statement.
Code:
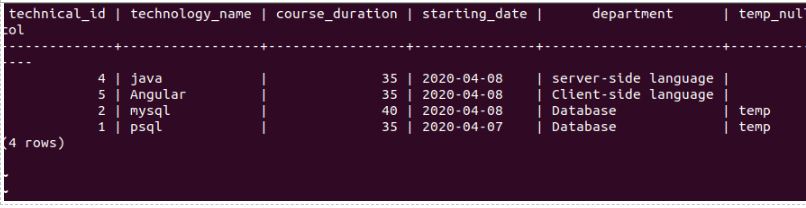
SELECT * FROM educba;Output:
We will replace the department string’s substring’ -side language’ with ‘-end technology’ using the following command.
Code:
UPDATE
educba
SET
department = REPLACE (
department,
'-side language',
'-end technology'
);Output:
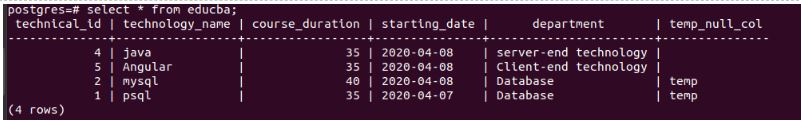
As we can see, four rows are updated, but only two of them had that substring. Hence the columns that didn’t have that substring don’t result in any error but are just skipped.
Code:
SELECT * FROM educba;Output:
In this way, we studied firstly how a single occurrence of the word can be replaced, then multiple occurrences of the word were replaced, and finally, a substring replacement and table column data substring replacement demonstration with the help of an example. Now we will see how we can replace the strings matching the regular expressions to be replaced by some other string.
The replace() Function is available and compatible with the following versions of PostgreSQL:
- PostgreSQL 9.4
- PostgreSQL 9.3
- PostgreSQL 9.2
- PostgreSQL 9.1
- PostgreSQL 9.0
- PostgreSQL 8.4
REGEXP_REPLACE Function
When we want to replace the words matching a particular regular expression to another word, we can use REGEXP_REPLACE() Function in PostgreSQL. This can be the case when replacing the old phone numbers or email ids with some default value with some new value.
Syntax:
REGEXP_REPLACE(original_string, regular_expr_pattern, new_sub_string [,option_flags])- original_string: This source string contains the words of substrings matching the regular expression that needs to be replaced.
- regular_expr_pattern: This is the regular expression pattern that will be searched for possible matched substrings to be replaced.
- new_sub_string: This is the substring with which the matched substrings will be replaced with.
- option_flags: Many flags are optional and explain the regular expression match comparison behavior. For example,’ means that the comparison should be case-insensitive, and g specifies global substitution of the substring, which means all occurrences are to be replaced.
Example of REGEXP_REPLACE Function
Given below is the example Function:
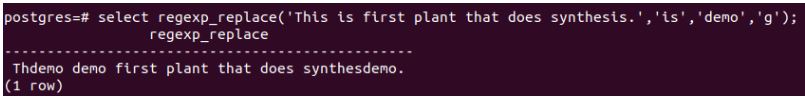
“This is the first plant that does synthesis.” we want to replace all the words containing the substring ‘is’ to the substring ‘demo’. We will use the REGEXP_REPLACE() Function, and our query statement will be as follows.
Code:
select regexp_replace('This is first plant that does synthesis.','is','demo','g');Output:
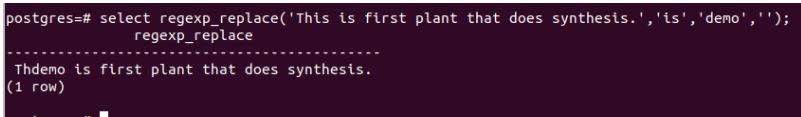
If we had not mentioned the ‘g’ flag and fired the following query.
select regexp_replace('This is first plant that does synthesis.','is','demo','');Output:
And the only first occurrence of is would have been replaced with the demo.
TRANSLATE() Function
When you need to replace more than one substring with the same substring, you can use the translate() Function in PostgreSQL.
Syntax:
TRANSLATE(original_string, set_of_characters, new_set_characters);- original_string: This source string contains the set of characters to be replaced.
- set_of_characters: This is the set of all characters in the original string you wish to replace.
- new_set_characters: This is a set of characters with which the matched characters will be replaced.
Example of TRANSLATE() Function
Given below is the example of the TRANSLATE() Function:
Code:
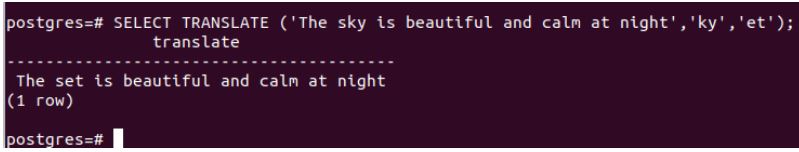
SELECT TRANSLATE ('The sky is beautiful and calm at night','ky', 'et');Output:
Conclusion – PostgreSQL replace
We saw about the methods, namely REPLACE(), REGEXP_REPLACE(), and TRANSLATE() methods, that can be used for string replacement in PostgreSQL while dealing with string manipulations.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL replace” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.