Updated May 4, 2023

Introduction to PostgreSQL Database
PostgreSQL database is an open-source database system and also an object-relational database system. It is accessed by using the psql command; the current latest version of PostgreSQL is 12; we create a database using create database statement and drop the database using the drop database statement; in PostgreSQL, we can query the database using the database SQL prompt and OS command prompt, to query using database SQL prompt we need to login into the database by using username, password, and connecting database name, If we query to the database using OS command prompt also need to provide username and password.
How to Create a Database in PostgreSQL?
We can create a database in PostgreSQL by using two methods:
Create a database statement
- The database is created using the SQL command to create database statements. Please find below syntax and example for creating a database statement.
Syntax
Create database database_name;Example
Postgres=# Create database db_testing;Output:
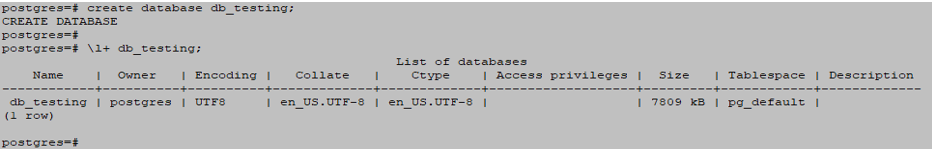
- The above syntax shows the name we used to create a new database in PostgreSQL. We can assign owner database user privileges to other users or change the user’s owner later.
- After installing, the first database is created by using initdb command.
Below are the default databases that were created at the time of installation.
- Postgres
- Template0
- Template1
- Postgres database is the administrative database of all the users in PostgreSQL. It is the default connection database of admin users.
- Template0 and template1 are the Meta database of other databases. At the time of creating a new database, these databases are used.
Create DB statement
- We can create a database using the shell prompt and the command as Createdb statement.
- Please find below the syntax and examples for the createdb statement.
- The Createdb statement connects to the database and issues create database command by using Createdb on the shell prompt.
- If we have not given any arguments at the time of database creation, it will create the database name the same as the username.
Syntax
CreatedbThe above syntax shows createdb as the command to create a database on the shell.
createdb database_nameDatabase name refers to give any name to the newly created database.
createdb –U username database_nameThe username refers to the database user name.
Example
createdb
createdb test_db
createdb –U postgres db_test
\l+ test_db;
\l+ db_test;Output:
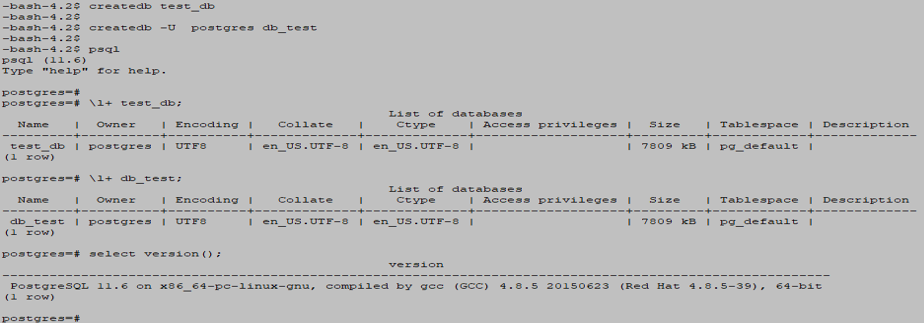
- We can also set the database owner in PostgreSQL. The database owner has all the privileges and permissions to execute database related queries.
- We can query or select the PostgreSQL database using two methods.
Please find below the methods to query the database:
- Database SQL prompt
- OS command prompt
1. Database SQL prompt
- In the Database SQL prompt, first, we need to login into the PostgreSQL database.
- We can login into the database by providing a username, password, hostname, and database name.
- Please find below the example to login to the database by providing a username and password.
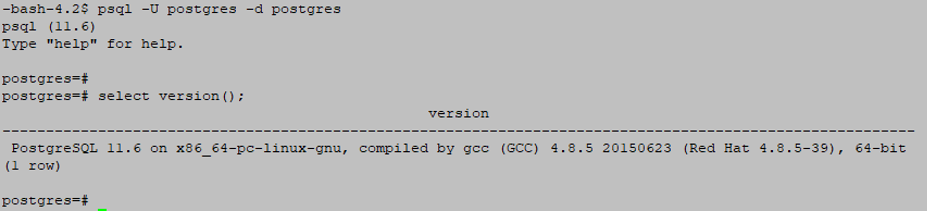
Example
psql –U postgres –d postgresOutput:
2. OS command prompt
- With the help of the OS command prompt, we may choose the PostgreSQL database
- We can select the OS prompt database by supplying the same parameter we use in the database SQL prompt.
- We must use parameters like username, password, port, hostname, etc.
- Please find below the example for the OS command prompt are as follows.
Example
psql -U postgres -d testing -c "select * from employee";
psql -U postgres -d testing -c "select version()";Output:

How to select a particular database from multiple databases?
- We can choose a particular database from multiple databases using the \l command.
- We can use the below command to choose a specific database from multiple databases in PostgreSQL.
- Mostly we have used \l db_name command to select a particular database in PostgreSQL.
- Please find below syntax and examples for the same.
Syntax
Please find below the syntax to select a particular database from multiple databases in PostgreSQL.
\l database_nameThe database name refers to the specific name of the newly created database in PostgreSQL.
\l+ database_nameIf we need a descriptive output of the database, we have used \l+ and the database name to display descriptive output.
Example
Please find below the example to select a particular database from multiple databases.
\l db_testing;
\l+ db_testing;Output:
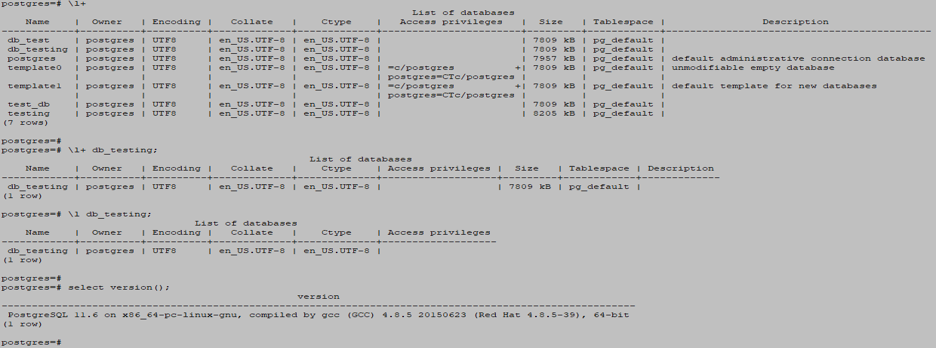
- In the above example, we have selected the db_testing database from multiple databases like db_test, Postgres, test_db, etc.
- Also, we have checked the descriptive output of the db_testing database using the \l+ db_testing command.
- This is an essential feature and commands to select a single database from multiple databases.
How to drop a database?
- We can drop the database using the drop database command in PostgreSQL. We can drop the database using login to the database and using the OS command prompt in PostgreSQL.
- If we need a database no longer, then we delete a specific database by issuing a drop database command in PostgreSQL.
- Drop database statement deletes database entries, catalogs, and data directories permanently.
- Only database owners of the database can execute the drop database command; other users do not have permission to execute the drop database command.
- Also, the admin user has permission to execute the drop statement command.
- In this dropdb program, a utility is available to drop the database. This utility allows you to remove the database. This utility executes the drop statement command behind the scene.
Please find below the syntax and example:
Syntax
drop database database_nameExample
postgres=# drop database db_testing;Output:

Conclusion
We can create a database using create database statement; also, we have to define the database owner at the time of database creation. We can drop the database by using the drop database statement; only the owner and database admin has the privilege to drop databases in PostgreSQL.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL Database” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

