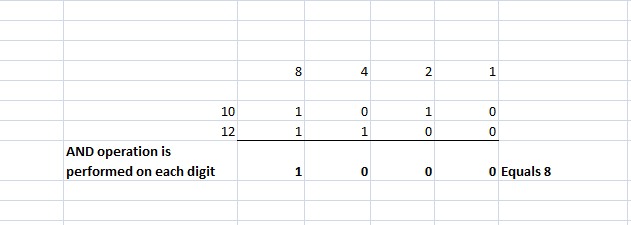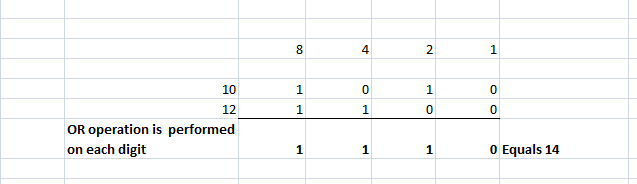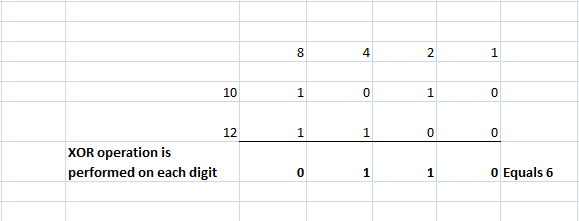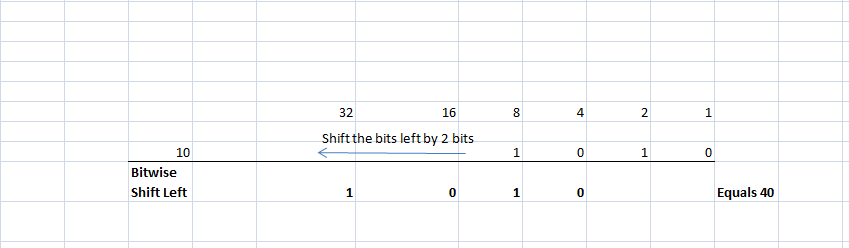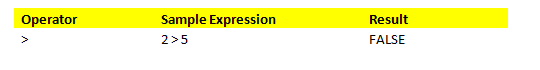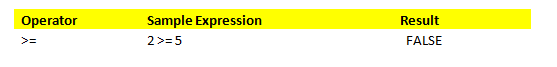Updated May 29, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL Operators
PostgreSQL Operators is a database management system and open-source software that enables easy access for the public to use for relational database purposes. Relational Database purposes are data manageability to explain it in a nutshell.
PostgreSQL Operators
Below are the different PostgreSQL Operators, which are as follows:
1. Logical Operators
In PostgreSQL, the logical operators consist of the general operators, namely, logical operators are used to perform the logical operations described below.
- OR
- AND
- NOT
a. OR Operator
| OR | The operator returns TRUE if either value of an operand is TRUE. |
- Values passed as logic can be applied in different combinations to gain desired results.
- So let us look at the truth table below.
- We can assume 0 is FALSE and 1 as TRUE. Hence 0 or 1 is 1, which is essentially TRUE.
- We can see that the OR operator returns FALSE (0) only when both X and Y are FALSE.
|
X |
Y |
X OR Y |
|
0 |
0 | 0 |
|
0 |
1 |
1 |
|
1 |
0 |
1 |
| 1 | 1 |
1 |
b. AND Operator
| AND | The operator returns TRUE only if the values of all operands are TRUE. |
- Unlike the OR operator, AND operator returns TRUE (1) only when both X and Y are TRUE.
|
X |
Y |
X AND Y |
|
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
0 |
1 |
0 |
|
1 |
0 |
0 |
|
1 |
1 | 1 |
c. NOT Operator
| NOT | This operator negates the initial value of an operand. If the operand value is TRUE, then FALSE is returned. |
Regarding the NOT operator, the logic is that the operator returns FALSE if the operand is TRUE and vice versa.
|
X |
NOT(X) |
|
0 |
1 |
| 1 |
0 |
2. Arithmetic Operators/Mathematical Operators
Arithmetic operators perform specific mathematical operations like addition, subtraction, etc. In PostgreSQL, Arithmetic operators are used to perform the Arithmetic operations as described below.
|
Operator Name |
Operators |
Functionality |
Example |
Result |
| Addition |
+ |
Adds values of operands | 10 +11 | 21 |
| Subtraction |
– |
Subtracts values of operands | 10 -11 | -1 |
| Multiplication |
* |
Performs multiplication on operands | 10 * 11 | 110 |
| Division |
/ |
Performs Division on operands | 10/5 | 2 |
| Modulo |
% |
Performs Division but returns the remainder as output | 11%10 | 1 |
| Exponentiation |
^ |
This provides the power value of the desired operand | 10^2 | 100 |
| Square Root |
| / |
Performs Square Root of an operand | |/ 16 | 4 |
| Cube Root |
| | / |
Performs Cube root of an operand | ||/64 | 4 |
| Factorial |
! |
Returns factorial of a given number (Postfix form) | 4! | 24 |
| Factorial ( with prefix operator) |
!! |
Returns factorial of a given number (Prefix form) | !! 4 | 24 |
3. Bitwise Operators
To understand Bitwise operators’ functionality, we need to know that these operators will work only on integrals and that the operator’s functionality takes place in the operand’s binary form (representation in 0s and 1s). In PostgreSQL, Bitwise operators are used to perform the Bitwise operators as described below.
|
Operator Name |
Operators | Example |
Result |
| Bitwise AND |
& |
10 & 12 | 8 |
| Bitwise OR |
| |
10 | 12 | 14 |
| Bitwise NOT |
~ |
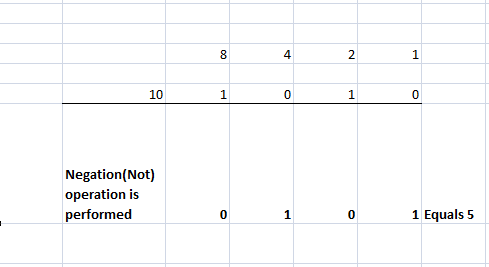
~10 | 5 |
| Bitwise XOR |
# |
10 # 12 | 6 |
| Bitwise shift left |
<< |
10 << 2 | 40 |
| Bitwise shift right |
>> |
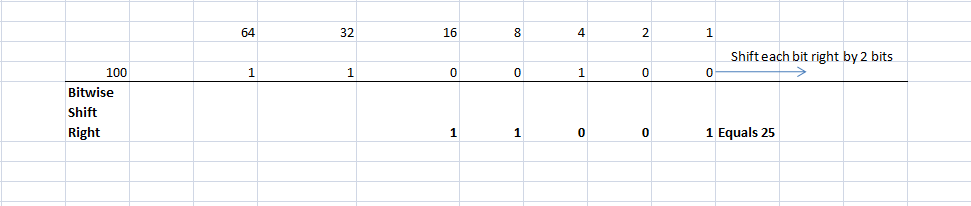
100 >> 2 | 25 |
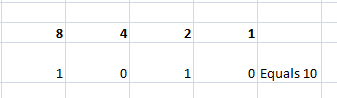
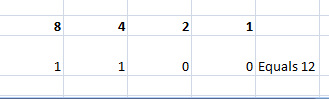
Let us take two operands, for example:
- 10 – Binary Representation is 1010.
- 12 – Binary Representation is 1100.
Refer below to how operands 10 and 12 get interpreted into their equivalent Binary form.
10 – Binary Representation is 1010
12 – Binary Representation is 1100
a. Bitwise AND Operator
This operator interprets the operands in their binary representation and performs the AND function on every digit of the operands.
b. Bitwise OR Operator
This operator interprets the operands in their binary representation and performs the OR function on every digit of the operands.
c. Bitwise Not Operator
This operator performs the negation operation on each digit of the operand. It can take only one operand at a time; hence it is known as a unary operator.
In the above example, all 0S are converted to 1S and vice versa.
d. Bitwise XOR Operator
This operator interprets the operands in their binary representation and performs the XOR function on every digit of the operands.
- XOR function returns TRUE or 1 if either one of the operands is TRUE or 1
- XOR function returns FALSE or 0 if all the operands are TRUE or all the operands are FALSE.
e. Bitwise Shift Left Operator
This operator shifts the given number’s bits in its binary representation to the left side by a specified number of bits. Let us say the specified number of bits is x, then shift each bit of 10 to the left by x bits is denoted as 10 <<x. If x is 2, then 10 << 2 is 40.
f. Bitwise Shift Right Operator
This operator shifts the bits of the given number in binary representation to the right side by a specified number of bits. Let us say the specified number of bits is x, then shift each bit of 10 to the right by x bits is denoted as 10 <<x. If x is 2, then 10 >> 2 is 25.
4. Comparison Operators
Comparison Operators interpret an expression and provide output in Boolean values. (TRUE or FALSE). In PostgreSQL, Comparison Operators perform the Comparison Operators described below.
Some of the common Comparison operators are shown below.
|
Operator |
Operator Name |
|
< |
Less than an operator |
|
> |
Greater than operator |
|
= |
Equals |
|
<> or! = |
not equals |
|
<= |
Less than or equal to the operator |
|
>= |
Greater than or equal to the operator |
a. Operator ‘<.’
This operator compares the given expression and returns TRUE if the first operand is less than the second operand in the expression, or else it returns FALSE.
b. Operator ‘>.’
This operator compares the given expression and returns TRUE if the first operand is greater than the second operand in the expression, or else it returns FALSE.
c. Operator ‘=.’
This operator compares the operands in the expression and returns TRUE if both operands are of the same value, or else it returns FALSE.
d. Operator ‘<>’ and ‘!=.’
This operator compares the operands in the expression and returns TRUE if both operands are not of the same value or return FALSE.
e. Operator ‘<=.’
This operator returns TRUE if the first operand’s value is lesser or equal to the value of the second operand.
f. Operator ‘>=.’
This operator returns TRUE if the first operand’s value is greater or equal to the value of the second operand.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “postgresql operators” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.