Updated May 29, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL
PostgreSQL is the open-source relational database software that runs on the Linux platform and functions with objects as a relational component in the database management system. It uses Structured Query Language (SQL) to access the data in the database; hence, it is also called Postgres. Some of this Database’s prominent features are that it is highly robust and reliable, the recovery process is effortless, and maintenance costs less cost and manual effort. It is developed and maintained by the PostgreSQL Global Development Group, a group of developers.
What is PostgreSQL?
It is made alive by PostgreSQL Global Development Group, a different group of many companies and individual contributors who made this possible. It is mainly run on Linux/Unix platforms.
You will find PostgreSQL, also known as Postgres. This is an object-relational database management system, And it uses SQL (Structured query language) as its primary query language. DBMS is a combination of applications, different utilities, and libraries. Over the years, there are no. of database management systems out there. The object-relational Database specifies large, shared databases.
First of all, we need to know What is the Actual term for the Database?
A database is a system in which we can store our data. Retrieve the data from it. Manipulate the data as well. Servers mainly maintain these systems in the Database. Each application has its Database.
Understanding
It is effortless to learn. I need to know how exactly it works. And the best way to get an overview is by its building blocks. How exactly it behaves.
PostgreSQL supports many data types, like My SQL, such as string, numeric, date, and time. It also supports data types for geometric shapes, images, network addresses, bit strings, text searches, JSON entries, etc.
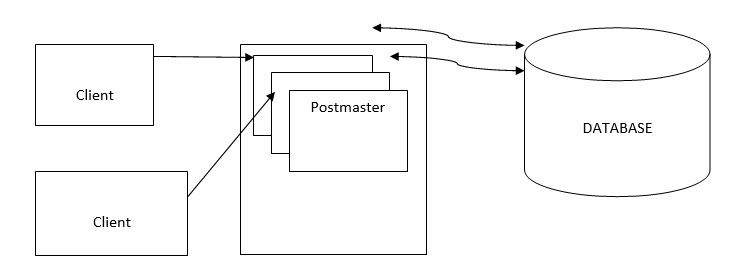
Architecture of PostgreSQL
In the following diagram, we see more than one client is requesting a database at the time. And the Database is serving these clients efficiently. This helps PostgreSQL to maintain integrity.
The Architecture is based on Client-Server Model:
Why Use PostgreSQL?
A perfect tool when it comes to integration with other tools. It handles data integrity and complex operations with ease.
- It is effortless to learn.
- Manages data in a relational database.
- It is very robust and powerful.
Key Features
- This supports the locking mechanism.
- It has high availability.
- It is free and open-source software.
- This is ACID-compliant.
- It has the capacity for fault tolerance.
- It also supports image, video, and audio storage and supports graphical data.
- Requires deficient maintenance.
- Supports Multi-version concurrency control (MVCC).
- Recovery is high.
- It has user-defined data types.
- Table inheritance.
- It runs on all operating systems.
What Makes PostgreSQL Stand Out?
It is an ancient database management system. We can integrate PostgreSQL with any programming language like Java, C, C++, etc. This feature allows defining our customized functions. The Postgre structured query language has many features that we could find in other databases.
This is an ancient database. So, we can find troubleshooting with this Database efficiently. The community base for PostgreSQL is huge.
It is flexible to work. It supports user-defined data types with primitive ones. Primitive means one which came with the language itself. Postgre Structured query language is one system that implemented multi-version concurrency control (MVCC). Like any other language, PostgreSQL has its commands. Usually, a separate database server is getting for different projects.
What is the Use of PostgreSQL?
It has the following characteristics:
- Sophisticated locking.
- View.
- Foreign key referential integrity.
- Rules.
- Inheritance.
- MVCC (Multiple version concurrency control).
- Subselects.
- Transactions.
- User-defined types.
Following are some of the New Features added to PostgreSQL
- Tablespaces.
- The point in time recovery.
- Ability to alter column types.
- Native Microsoft Windows version.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Following are the Advantages and Disadvantages:
Advantages
- Easy to use.
- Has a user-defined data type.
- Open-source.
- A lot of community support.
- Make use of Stored procedures.
- It supports ACID, i.e., Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability.
Disadvantages
- Suppose we see the architecture of Postgre (Structured query language). The above diagram creates different services for every client, which becomes a lot of memory utilization.
- If we make a comparison, PostgreSQL could be better regarding performance.
- It is less popular than other database management systems.
- This also needs more skilled professionals.
- When it comes to speed, it is not worth it as compared to other tools.
- They are making replication more complex.
- Installation is challenging for the beginner.
Conclusion
Every system has some drawbacks. Postgre Structured query language also has some. It is an ancient system, but it is still in the market and ruins in some places. If you want to learn PostgreSQL, then first start with SQL.
By learning SQL, you will have an idea of how things work. And with SQL, you are ready to tackle any database easily.
Recommended Article
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “What is PostgreSQL?” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.