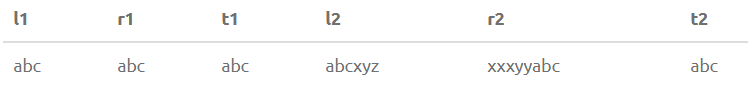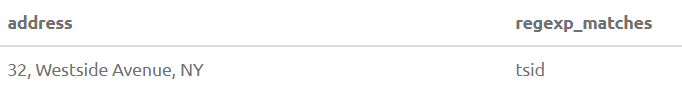Updated April 29, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL String Functions
PostgreSQL is a robust object-relational database management system that offers numerous functions and operators for the built-in data types. This enables developers to focus on solving more significant problems while relieving them from simpler tasks. One particular category of built-in functions is the PostgreSQL string functions. They handle string formatting tasks such as concatenation, displaying in a specific format, and inserting/deleting substrings which can often be tedious for developers.
PostgreSQL offers many functions not available in standard SQL functions, providing developers with a vast array of functions to leverage in solving complex problems.
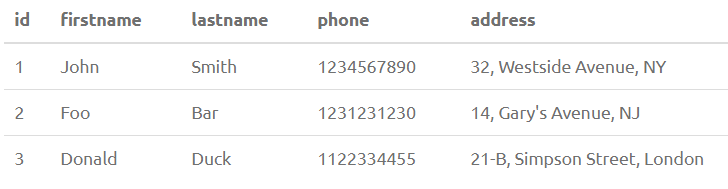
To illustrate the various PostgreSQL string functions, we need to create a database first. The following database will be referred to in all the examples.
CREATE TABLE Person(Id INT PRIMARY KEY, FirstName varchar(20), LastName varchar(20), Phone INT, Address varchar(100))Output:
Examples of String Functions in PostgreSQL
Here we will discuss how to use the string function in PostgreSQL:
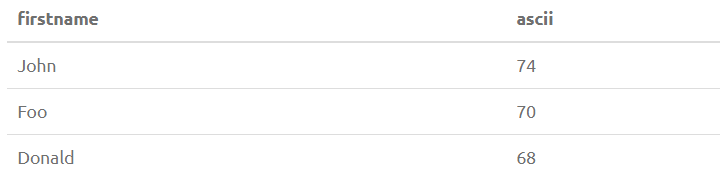
1. ASCII(str)
Returns the ASCII value of the leftmost character of the string str.
SELECT FirstName, ASCII(FirstName) from PersonOutput:
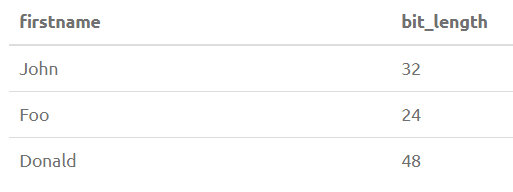
2. BIT_LENGTH(str)
Returns the length of the string str in bits.
SELECT FirstName, BIT_LENGTH(FirstName) from PersonOutput:
3. CHAR_LENGTH(str) / CHARACTER_LENGTH(str)
Returns the length of the string str in characters.
SELECT FirstName, CHAR_LENGTH(FirstName) from PersonOutput:
4. CONCAT(str1, str2, …., strn)
Returns a string formed by joining str1 to strn. NULL arguments are ignored.
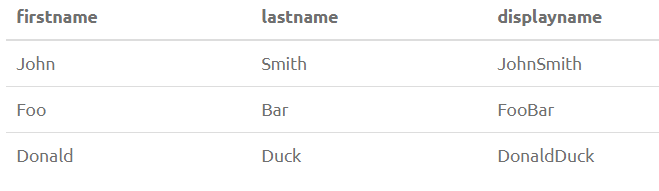
SELECT FirstName, LastName, CONCAT(FirstName, LastName) as DisplayName from PersonOutput:
5. str1 || str2 ||…|| non-str ||…|| strn
Concatenates str1, str2 to strn, and even non-string arguments.
SELECT Id || FirstName || LastName || phone || address as Concat_All from PersonOutput:
6. INITCAP(str)
Capitalizes the string, i.e., each word’s first letter is upper-cased, and the rest are lower-cased. Non-alphanumeric separators determine words.
Select INITCAP('This is a PostgreSQL example.')Output:
7. LOWER() and UPPER()
Converts a string to lower case and upper case.
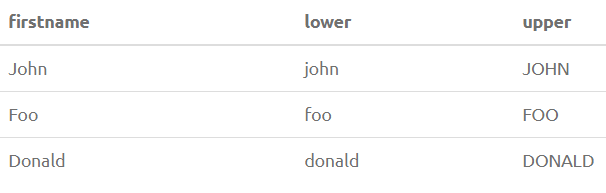
SELECT FirstName, LOWER(FirstName) as Lower, UPPER(FirstName) as Upper from PersonOutput:
8. LEFT(str, len) / RIGHT(str, len)
Returns the leftmost and rightmost len characters from the string str. When len is negative, it returns the string str except for the leftmost or rightmost len characters.
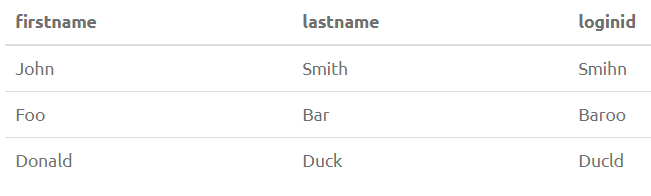
SELECT FirstName, LastName, CONCAT(LEFT(LastName, 3), RIGHT(FirstName, 2)) as LoginID from PersonOutput:
9. LENGTH(str) / LENGTH(str, encoding)
Returns the length of the string str in characters. However, it is unlike the operation of the Length function in SQL. When specified, encoding provides the length in the particular encoding.
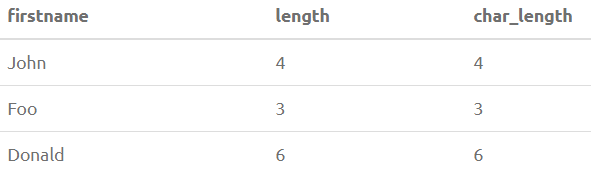
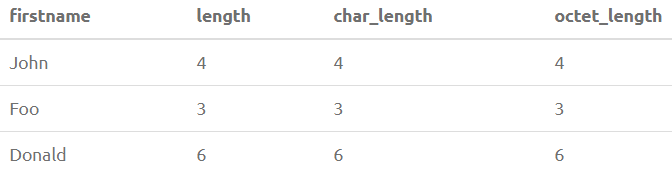
SELECT FirstName, LENGTH(FirstName), CHAR_LENGTH(FirstName) from PersonOutput:
10. OCTET_LENGTH(str)
Calculates the length of the string str in bytes.
SELECT FirstName, LENGTH(FirstName), CHAR_LENGTH(FirstName), OCTET_LENGTH(FirstName) from PersonOutput:
This is very much similar to LENGTH and CHAR_LENGTH functions. The difference comes when there are multibyte characters involved.
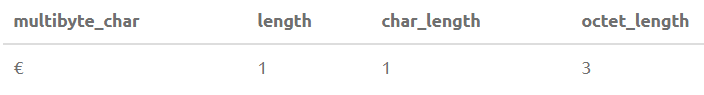
SELECT '€' as multibyte_char, LENGTH('€'), CHAR_LENGTH('€'), OCTET_LENGTH('€')Output:
This happens because Euro (€) sign occupies 3 bytes in memory.
11. LPAD(str, len, padstr) / RPAD(str, len, padstr)
Inserts sub-string from position 0 of the string padstr at the beginning and end of the string str until the resultant string is of len characters.
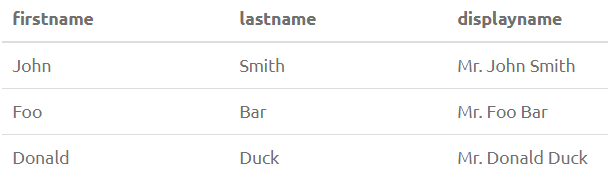
SELECT FirstName, LastName, LPAD(CONCAT_WS(' ', FirstName, LastName), CHAR_LENGTH(CONCAT_WS(' ', FirstName, LastName))+CHAR_LENGTH('Mr. '), 'Mr. ') as DisplayName from PersonOutput:
12. LTRIM(str, chars) / RTRIM(str, chars) / TRIM(str, chars)
Returns the string str after trimming all char(s) occurrences from left, right, or both ends. If chars are not specified in the arguments, spaces are trimmed.
SELECT LTRIM(' abc ') as L1, RTRIM(' abc ') as R1, TRIM(' abc ') as T1, LTRIM('xxxyyabcxyz', 'xyz') as L2, RTRIM('xxxyyabcxyz', 'xyz') as R2, TRIM('xxxyyabcxyz', 'xyz') as T2Output:
13. POSITION(substr in str) / STRPOS(str, substr)
Finds the position of the substring substr in the string str. Remember, the index starts from 1 in PostgreSQL. Returns 0 if no match is found.
SELECT Address, POSITION('Avenue' in Address) from PersonOutput:
14. QUOTE_IDENT(str) / QUOTE_LITERAL(str)
This query quotes and un-quotes the string str. Most special characters are doubled.
SELECT Address, QUOTE_IDENT(Address), QUOTE_LITERAL(Address) from PersonOutput:
15. REPLACE(str, from_str, to_str)
Replaces all occurrences of sub-string from_str with sub-string to_str in the string str. It is case-sensitive.
SELECT Address, REPLACE(Address, 's', 'SS') from PersonOutput:
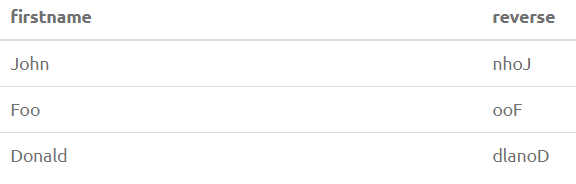
16. REVERSE(str)
Reverses the string str.
SELECT FirstName, REVERSE(FirstName) from PersonOutput:
17. REGEXP_MATCHES(str, pattern)
Returns all substrings that match the POSIX Regex pattern.
SELECT Address, REGEXP_MATCHES(Address, '.[sN]i.') from PersoOutput:
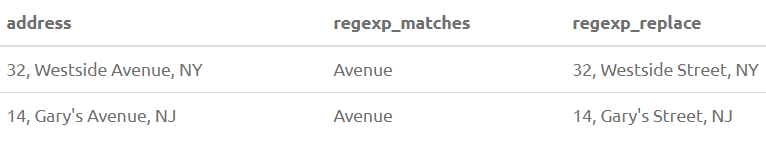
18. REGEXP_REPLACE(str, pattern, newstr)
Replaces all substrings that match the POSIX Regex pattern with the newstr.
SELECT Address, REGEXP_MATCHES(Address, '..[e][n]..'), REGEXP_REPLACE(Address, '..[e][n]..', 'Street') from PersonOutput:
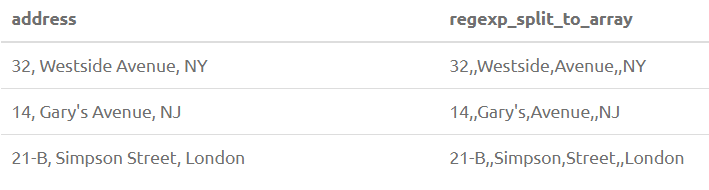
19. REGEXP_SPLIT_TO_ARRAY(str, pattern)
Splits the string str into an array of substrings separated by POSIX Regex pattern. Pattern E’\\s+’ means one or more blank spaces.
SELECT Address, REGEXP_SPLIT_TO_ARRAY(Address, E'\\s+') from PersonOutput:
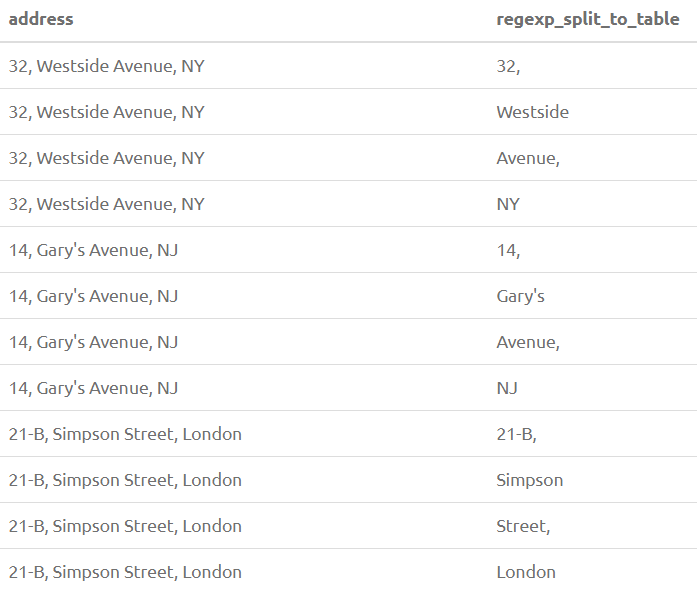
20. REGEXP_SPLIT_TO_TABLE(str, pattern)
Splits the string str into a table of substrings separated by POSIX Regex pattern.
SELECT Address, REGEXP_SPLIT_TO_TABLE(Address, E'\\s+') from PersonOutput:
21. SUBSTRING(str from pos for len)
Returns a substring from string str starting at position pos of length len.
SELECT FirstName, SUBSTRING(FirstName from 2 for 4) as a sub from PersonOutput:
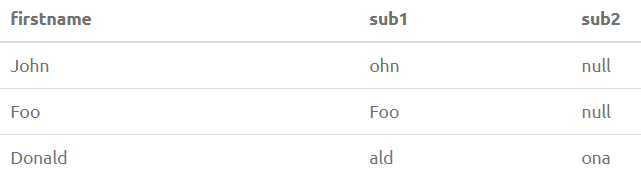
22. SUBSTRING(str from posix_pattern) / SUBSTRING(str from sql_pattern for escape)
Returns a substring from string str that matches the POSIX Regex or SQL Regex. It is recommended to get hold of Regex patterns before implementing them haphazardly.
SELECT FirstName, SUBSTRING(FirstName from '...$') as sub1, substring(FirstName from '%#"o_a#"_%' for '#') as sub2 from PersonOutput:
Conclusion
PostgreSQL, with all its built-in functions, makes it a powerful system. The inclusion of regex patterns adds more power to it. Once the art of writing Regex patterns is learned and mastered, playing with the database will be much more fun.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “postgresql string functions” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.