Updated May 16, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL Client
PostgreSQL client is defined as connect to the database server using the command, utility, or third party tool. Basically, we are using the psql utility to connect the database server from the OS interface, also, we are using the pg_admin tool to interact with the database server using the client interface. We can connect the database server using the username, password, and hostname of the database server, we can also connect the database server using client applications like pg_admin. We can connect to the database server from client by using a local host or from the remote host using psql utility or third party tool.
Syntax of PostgreSQL Client
Below is the syntax of the PostgreSQL Client:
# psql –U username –W user_passwordor
# psql –U username –W user_password –d database_nameor
# psql –U username –W user_password –d database_name –h hostnameor
# psql –U username –W user_password –d database_name –p port_noBelow are the parameter description syntax of the PostgreSQL client:
- Psql: A client utility is used to connect to the database server. We can use this utility with the username, password, and hostname. Psql is a useful and important client utility that connects to the database server.
- Username: The username is an important parameter used to connect to the database server and authenticate.
- Password: We define the password parameter as a means to authenticate the client user with a password. If the password is incorrect, the database will not authenticate the user. We need to provide a password with psql utility to connect the database server.
- Database name: This defines the database name to connect to the specified database. To connect to the database, we need to provide connect grant on database to the specified user.
- Host name: If we want to connect from another host, then we need to use this parameter in PostgreSQL. If we connect to the local host there is no need to define the host name with psql utility. The psql utility in PostgreSQL uses an optional parameter.
- Port no: We define the use of a port number when connecting to the database server. The parameter is optional, and you can use it with the psql utility in PostgreSQL.
How does PostgreSQL Client works?
Given below shows how the PostgreSQL Client works:
- Client is used to connect to the database server.
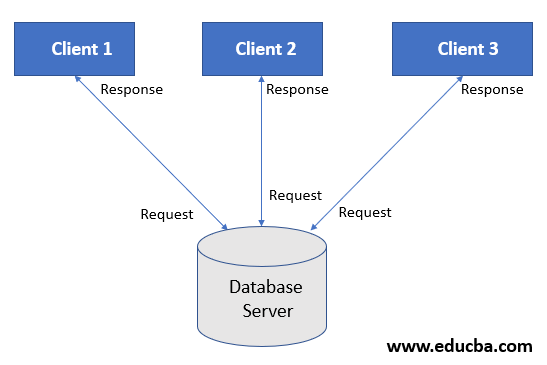
Below figure shows that client architecture in PostgreSQL.
- In PostgreSQL, the client-server architecture is basically divided into two parts: the client and the server.
- We define the client as a command execution environment, such as psql, or we use a special driver for it.
- The PostgreSQL client uses libpq libraries to communicate and connect to the database server.
- In PostgreSQL, the library that is used with each client application via the postmaster process is called Libpq. Libpq is similar to OCI, which is used in Oracle.
- Client will first request to the database server through the client utility. Request will contain the SQL query.
- After requesting the client to the database server, it will check the request from the client after checking request, it will authenticate with the database server.
- After successful authentication, it will respond to the client with his request.
- We can connect multiple client simultaneously to the server to process the client’s request.
- Users can manage the PostgreSQL database using a number of GUI applications available in PostgreSQL.
- The GUI application manages SQL queries and displays database activities in PostgreSQL.
- We can use a socket while connecting through the command line tool. If we want to connect from the application, then we are using the port no while connecting to the database server.
- We can also set up the connection with SSH tunnel in PostgreSQL. SSH tunnel is a more secure method while connecting to the database server through the client.
- We can also direct set up the connection between our local computer and remote computer.
Examples
Examples are mentioned below:
Example #1
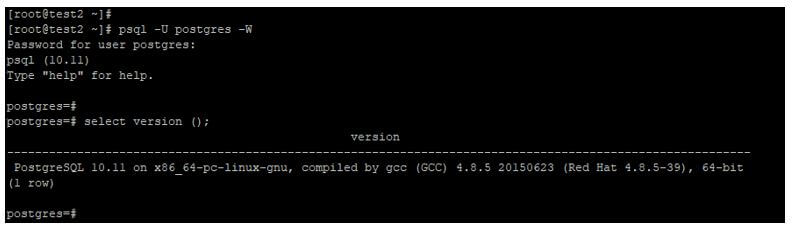
Connect from client through username and password.
Below example shows that connection from client through username and password. We have connected the database server through psql utility.
Code:
psql -U postgres –WOutput:
Example #2
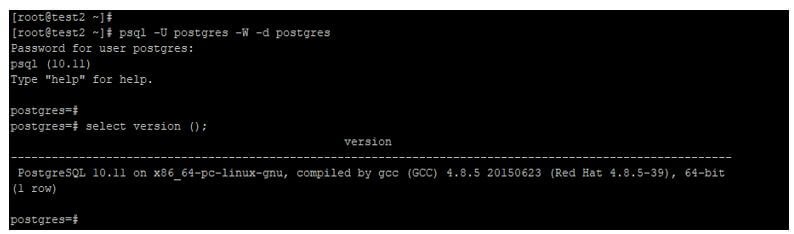
Connect from client through username, database name, and password.
Below example shows that connection from client through username, database name, and password. We have connected the database server through psql utility.
Code:
psql -U postgres –W –d postgresOutput:
Example #3
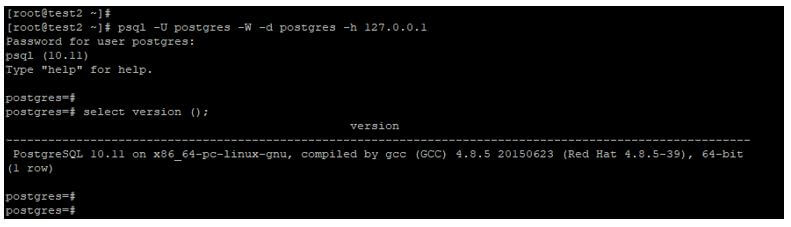
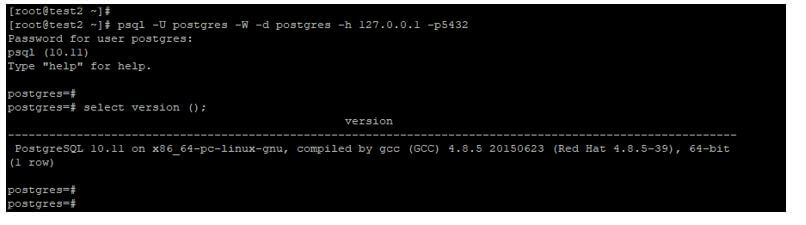
Connect from client through username, database name, hostname, and password.
Below example shows that connection from client through username, database name, hostname, and password. We have connected the database server through psql utility.
Code:
psql -U postgres –W –d postgres –h 127.0.0.1Output:
Example #4
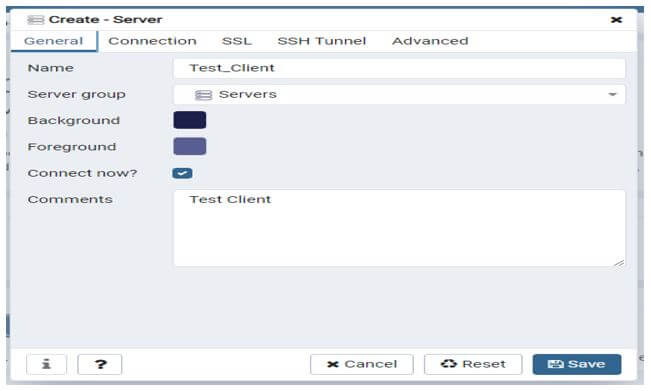
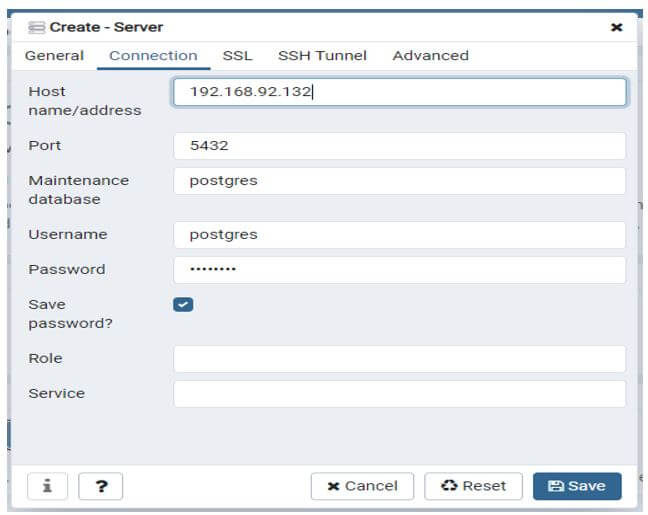
Connect from the pg_admin tool to the database server.
Below example shows that connect to the database server through the pg_admin tool. We need to provide below connection parameter while connect to the database server from pg_admin tool.
Output:
Example #5
Connect client through username, database name, hostname, port, and password.
Below example shows that connection from client through username, database name, hostname, port, and password. We have connected the database server through psql utility.
Code:
psql -U postgres –W –d postgres –h 127.0.0.1 –p5432Output:
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL Client” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.