Updated May 16, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL Import CSV
PostgreSQL import CSV is defined as load the data into the table by using the CSV file, we have used a comma-separated file (CSV) to import the data from the file into the PostgreSQL table. To import the data from the CSV file into the table, the same table needs to be present on the database also, we need the same structure of the table in which data was present in the CSV file. Import data from CSV file is a very useful and important operations in PostgreSQL for importing data from the file. We have to use the copy command to import data from CSV file.
Syntax and Parameters
Below is the syntax of the import CSV file into the PostgreSQL table.
COPY table_name (Column_name1, column_name2, …, column_nameN) from file_name (Path of file) Delimiter [ Character of delimiter which was we have used ] CSV [Header of CSV file.]COPY name_of_table from name_of_file Delimiter [ Character of delimiter which was we have used ]Below is the parameter description syntax of import CSV into the PostgreSQL table.
- Copy: This command in PostgreSQL is used to import the data from the CSV file into the table. The copy command is very useful to import the data into the PostgreSQL table.
- Table name: The table name specifies the name of the table on which we have imported the data from the CSV file.
- Column name1 to column names: We have to define column name with the copy command. The column name specifies that we have to insert or load the data from the CSV file on which column that we have specify in copy command.
- From: This keyword is used to specify the CSV file name from which we have importing the data into the table.
- Filename or path of file: This is specify that name of file from which we have imported data into the table. In PostgreSQL, the file’s absolute path needs to be specified when using the “COPY” command to define the path.
- Delimiter: This is defined as the value which was separated by a semicolon. We can use any delimiter to separate the value of a column in PostgreSQL.
- Header of CSV file: We define this as the column name of the table where we imported data from the CSV file. Data have their header to defined or import the data from a file.
How Import CSV work in PostgreSQL?
Below is the working of import CSV file into the table in PostgreSQL. We have using copy command in PostgreSQL to import the file. To import the data from the CSV file into the table, we need to follow the below things, or same table is present on the database.
1. Create a table with same structure of CSV file
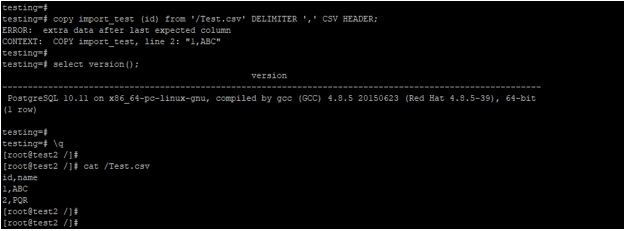
To import data from a CSV file into a table, you need to create a table with the same name and structure as the CSV file. The number and data type of the columns in the CSV file need to be the same as those specified in the PostgreSQL table. Mismatch of the column is not allowed while importing data from a CSV file. If column name and data is mismatch, then it will issue error as “ERROR: extra data after last expected column”. Below is the example in that we required the same name of column and data while importing data into the table.
Code:
copy import_test (id) from 'https://cdn.educba.com/Test.csv' DELIMITER ',' CSV HEADER;
[root@test2 /]# cat /Test.csvOutput:
2. Determine the delimiter
Basically, we have separate the values using a comma, but in some file, we have used another delimiter to separate the values. We can also separate the values using ‘|’, tabs’ \t’ or newline’ \n’. TSV file, also known as Tab-separated values, is used in PostgreSQL. The delimiter is very important while importing data from a CSV file into the table.
3. Check the data have a header or not
- Some CSV file contains the header, or some file is not contains the header. The header is nothing but the column name, which was we have defined in table.
- The header is defined in the first line of the CSV file. If the CSV file contains the header, then we need to define the header in copy command.
- There is no need to define a header when the header is not present in the CSV file.
Below example shows that we need to define a header when a CSV file contains the header.
Code:
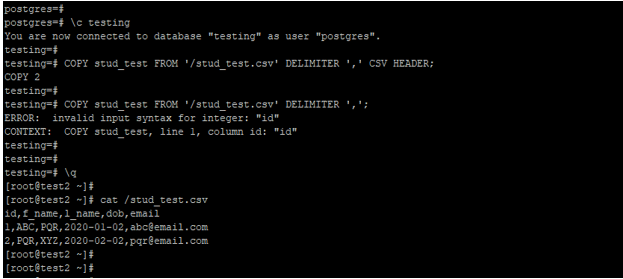
COPY stud_test FROM 'https://cdn.educba.com/stud_test.csv' DELIMITER ',' CSV HEADER;
COPY stud_test FROM 'https://cdn.educba.com/stud_test.csv' DELIMITER ',';
cat /stud_test.csvOutput:
Examples to Implement Import CSV in PostgreSQL
Below are the examples mentioned:
We have using stud_test table to describe an example of import a CSV file into a PostgreSQL table.
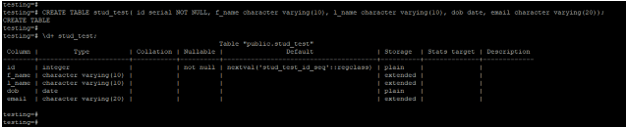
Below is the structure of the stud_test table.
Code:
CREATE TABLE stud_test( id serial NOT NULL, f_name character varying(10), l_name character varying(10), dob date, email character varying(20));
\d+ stud_test;Output:
1. Import the CSV file into a table by using the header
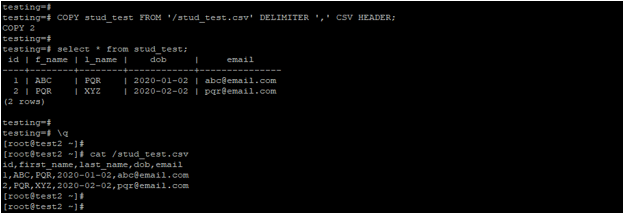
In the below example, we have import a CSV file into the table by using a header. We have used the stud_test table to import the data from the CSV file.
Code:
COPY stud_test FROM 'https://cdn.educba.com/stud_test.csv' DELIMITER ',' CSV HEADER;
select * from stud_test;
cat /stud_test.csvOutput:
2. Import CSV file into a table without using header
In the below example, we have import a CSV file into the table without using header. We have used the stud_test table to import the data from the CSV file.
Code:
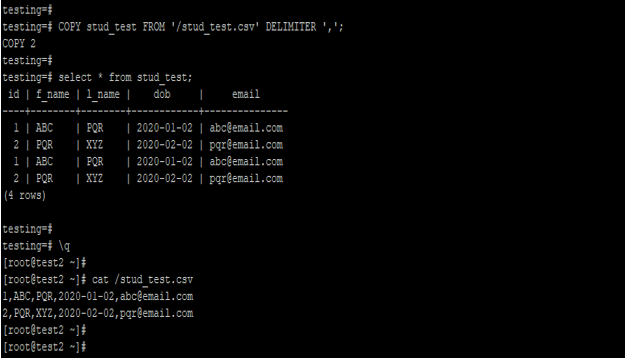
COPY stud_test FROM 'https://cdn.educba.com/stud_test.csv' DELIMITER ',';
select * from stud_test;
cat /stud_test.csvOutput:
3. Import CSV file into a table from shell prompt
In the below example, we have import CSV file into the table by using shell prompt.
Code:
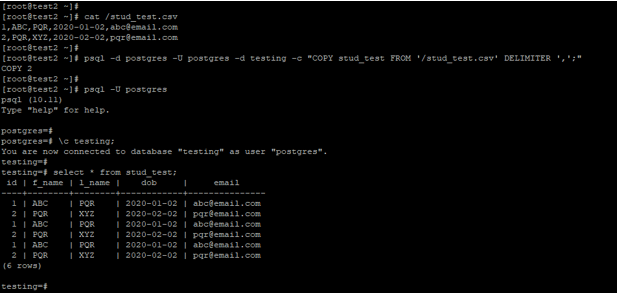
psql -d postgres -U postgres -d testing -c "COPY stud_test FROM 'https://cdn.educba.com/stud_test.csv' DELIMITER ',';"
select * from stud_test;Output:
Conclusion
We import the data from the CSV file into the table to import the data from the CSV file is faster than the normal insert. We have import the file with and without specifying the header. Also, we can use the column name with a copy command to import the data from CSV file.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL Import CSV” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.