Updated May 11, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL UNIQUE Index
The PostgreSQL UNIQUE INDEX is used when we want to ensure that the column stores unique values only. If we define the UNIQUE INDEX on the particular column, then that column can not have the same value in multiple rows. Also, we can define the UNIQUE INDEX on multiple columns to enforce them to store the combined unique value. While creating a table, we can add a UNIQUE constraint or primary key for the table, which automatically constructs a UNIQUE INDEX for a column that we have marked as a primary key of the table or the column on which we have added a UNIQUE constraint.
Syntax:
Consider the following syntax for creating the PostgreSQL UNIQUE INDEX:
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX index_name ON table_name(column_name, [...]);Explanation:
- index_name: This defines the name given to the UNIQUE INDEX.
- table_name: This defines on which table we are adding a UNIQUE INDEX.
- column_name: This defines the column or list of columns that will be covered under the UNIQUE INDEX to have unique values.
How Does UNIQUE Index Work in PostgreSQL?
1. We can add a UNIQUE INDEX on one or more columns; if we have added a UNIQUE INDEX on a single column, then that column can not have the same value in multiple rows.
2. Also, if you have added a UNIQUE INDEX on more than one column, then the combined value of all these columns should be unique and can not have the same value in multiple rows
3. The NULL value is considered the DISTINCT value, so the column with a UNIQUE INDEX applied can store multiple NULL values. Similar is applied to the multiple columns for which we have applied the UNIQUE INDEX.
4. If we have added a UNIQUE constraint or primary key for the table while creating a table, which automatically constructs a UNIQUE INDEX for a column which we have marked as a primary key of the table or the column on which we have added a UNIQUE constraint.
Examples to Implement PostgreSQL UNIQUE Index
Below are the examples of the PostgreSQL UNIQUE Index:
We will create a table named ‘student22’ to understand the UNIQUE INDEX in detail. Consider the following CREATE TABLE statement, which will create a ‘student22’ table.
Query:
CREATE TABLE student22 (
stud_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
stud_firstname VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
stud_lastname VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
stud_email VARCHAR(255) UNIQUE
);In the above statement, we have added the stud_id column as a primary key column. Also, the column stud_email is defined with the UNIQUE constraint applied to it, which will cause to create of two UNIQUE indexes for stud_id and stud_email columns.
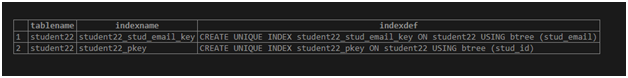
We can get the indexes of the student22 table by using the following SQL statement:
Query:
SELECT tablename, indexname, indexdef
FROM
pg_indexes
WHERE
tablename = 'student22';Output:
Example #1 – Single Column
Now we will add a column of the name ‘stud_contact’ to the ‘student22’ table by using the following statement:
Query:
ALTER TABLE student22 ADD stud_contact VARCHAR(20);The contact number for each should be unique. So we will add a UNIQUE index for the stud_contact column to ensure that all students’ contact numbers are distinct.
Consider the following SQL statement, which will add a UNIQUE index for the stud_contact column.
Query:
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX idx_student_stud_contact
ON student22(stud_contact);Now we will insert some data into the student table to validate the uniqueness of the stud_contact column.
Consider the following INSERT INTO statement for inserting a new row into the student22 table:
Query:
INSERT INTO student22
(stud_firstname, stud_lastname, stud_email, stud_contact)
VALUES
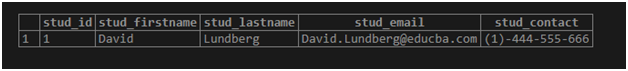
('David','Lundberg','[email protected]', '(1)-444-555-666');Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following snapshot and SQL statement.
Query:
select * from student22;Output:
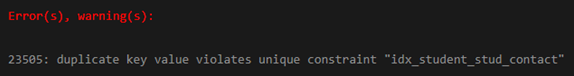
Again, consider the following INSERT INTO statement for inserting a new row into the student22 table, but this time we will add the same contact number as we have added earlier.
Query:
INSERT INTO student22
(stud_firstname, stud_lastname, stud_email, stud_contact)
VALUES
('Patrik','Brand','[email protected]', '(1)-444-555-666');Output:
Here we got an error which is because we are trying to insert the duplicate contact number in the stud_contact column.
Example #2 – Multiple Columns
Now we will add two new columns of the name ‘stud_batch’ and ‘stud_reg_no’ to the ‘student22’ table by using the following statement:
Query:
ALTER TABLE student22
ADD stud_batch VARCHAR(5),
ADD stud_reg_no VARCHAR(5);The Batch of multiple students can be the same, but each student’s registration can not be the same. To ensure the same criteria, we have to define the UNIQUE index on the columns.
‘stud_batch’ and ‘stud_reg_no’ of the ‘student22’ table.
Query:
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX idx_student_batch_regno
ON student22(stud_batch,stud_reg_no);Now we will insert some data into the student table to validate the uniqueness of the stud_batch and stud_reg_no columns.
Consider the following INSERT INTO statement for inserting a new row into the student22 table:
Query:
INSERT INTO student22
(stud_firstname, stud_lastname, stud_batch, stud_reg_no)
VALUES
('Thomas','John','A-1', '444');Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following snapshot and SQL statement.
Query:
select * from student22;Output:
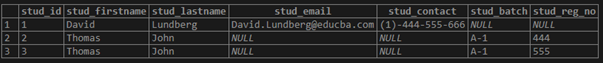
Again, consider the following INSERT INTO statement for inserting a new row into the student22 table, but this time we will add the same Batch as we have added earlier with a different stud_reg_no.
Query:
INSERT INTO student22
(stud_firstname, stud_lastname, stud_batch, stud_reg_no)
VALUES
('Thomas','John','A-1', '555');Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following snapshot and SQL statement.
Query:
select * from student22;Output:
The combination of values of stud_batch and stud_reg_no columns is unique because this INSERT INTO statement worked without any error.
Again, consider the following INSERT INTO statement for inserting a new row into the student22 table, but this time we will add the same Batch and stud_reg_no as we have added earlier.
Query:
INSERT INTO student22
(stud_firstname, stud_lastname, stud_batch, stud_reg_no)
VALUES
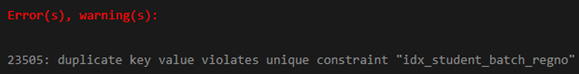
('Thomas','John','A-1', '555');Output:
Here we got an error which is because we are trying to insert the duplicate stud_batch, stud_reg_no, which already exists in the student22 table.
Conclusion
From the above article, we hope you understand how to use the PostgreSQL UNIQUE INDEX and how the PostgreSQL UNIQUE INDEX works. Also, we have added several examples of PostgreSQL UNIQUE INDEX to understand it in detail.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on the “PostgreSQL UNIQUE Index” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.