Updated May 29, 2023
Definition of PostgreSQL caching
Data caching in PostgreSQL is not suitable, or we can say not pre-allocated, and it can be calculated only and depends on the workload. The main purpose of caching in PostgreSQL is to increase the server’s performance. The caching means when we execute a query, it goes from different stages, which there is one stage we called the planning stage. In the planning stage, we select the most suitable plan for query execution. Caching is temporary memory, and it is used to increase the performance of the query and the server. Cache is allocated per query execution plan once the query is executed, then the cache vanishes.
Syntax:
explain (analyze, buffers) select * from table name order by column name limit;Explanation:
In the above syntax, we use an explanatory statement to show the performance of the database table and a query execution tool. Where analysis and buffer are used to show the details structure of the query statement, after that, we use a select statement for table selection with different parameters, such as order by clause.
How caching works in PostgreSQL?
We must install PostgreSQL in your system. It required basic knowledge of PostgreSQL. We must require a database table to perform the caching operation in PostgreSQL. Need basic knowledge about caching, which means how it is worked.
PostgreSQL process based on the system is when the PostgreSQL process requests for any access through SQL query statement at that time, PostgreSQL requests for the buffer allocation. If the memory block is available, then it directly returns the result. If a memory block is unavailable, it goes for buffer allocation to get a free block for query execution.
Examples
Let’s see a different example to understand PostgreSQL caching better as follows.
Example #1
We required a table to check the performance of the query statement to see the performance. So let’s create a table by using the following query statement.
create table empp (emp_id serial PRIMARY KEY, emp_name varchar(30), emp_dept varchar[],emp_city varchar[],emp_salary text[]);Explanation:
In the above example, we create an emp table with different attributes such as emp_id, emp_name, emp_dept, emp_city, and emp_salary with different data types, as shown in the above statement.
Now insert some records into an emp table using the following statement.
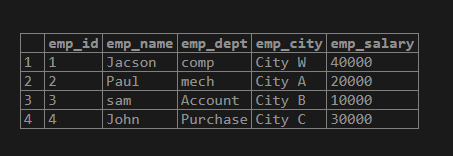
Insert into empp (emp_name, emp_dept, emp_city, emp_salary) Values ('Jacson','{"comp"}' , '{"City W"}', '{"40000"}'), ('Paul', '{"mech"}', '{"City A"}', '{"20000"}'), ('sam', '{"Account"}','{"City B"}','{"10000"}'), ('John', '{"Purchase"}', '{"City C"}','{"30000"}');
select * from empp;Explanation:
With the help of the above statement, we insert 4 records into an empp table. Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the following snapshot.
Now let’s see the performance test of the above statement by using the caching concept as follows.
Example #2
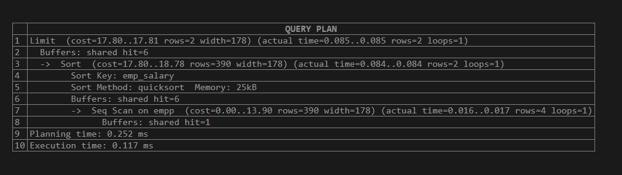
explain (analyze,buffers) select * from empp order by emp_salary limit 2;Explanation:
See in the above example, we execute a select query, which means a data manipulation query. When we execute a select statement, in which if that page is available in memory, then it is able to be written otherwise, they get the page from disk to written. When we execute the above statement, it shows the detailed structure of the select statement. Here we use buffers to analyze the select query. Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the following snapshot.
The above snapshot shows the shared hit means the cache configuration is correct. It shows the actual time, planning time, and execution time.
Let’s see what happens when we execute the same query statement as follows.
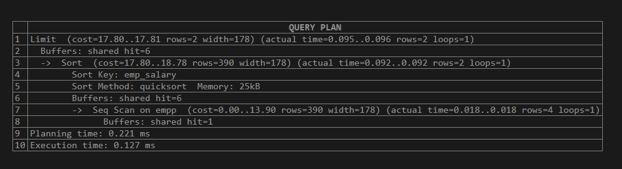
explain (analyze,buffers) select * from empp order by emp_salary limit 2;Explanation:
Here we execute the same query statement then it shows the different values of shared hit, actual time, planning time, and execution time. Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the following snapshot.
Example #3: Sequential Scan
A sequential scan means there is no index in PostgreSQL and has to fetch all records or data from disk, creating a problem for the cache to fetch the data. Using a single scan erases all data from the cache, so we handle it by employing an alternative method. Instead of using the LRU algorithm, it uses a series of buffers as follows.
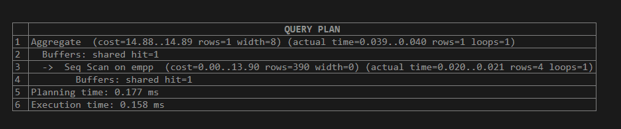
explain (analyze,buffers) select count(*) from empp;Explanation:
The above example shows a sequential buffer concept in which the shared hit is 1, which means it uses a single buffer for execution. This value may vary, that is, it depends on the query statement. Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the following snapshot.
How to Improve the performance of Caching in PostgreSQL?
When we think about caching, that means it increases the speed of operations and data retrieval speed. Let’s discuss different scenarios to increase the performance of caching as follows.
1. Bottleneck situation in the query performance
Before discussing the solution to the problem, let’s understand why queries are slow. The first reason is the performance of your system. That means when we run an application on a system at that time, we check the performance of the system. For that instance, any CPU or network bottleneck may occur that affects your process means fetching data from the database. The solution for that problem is to check the health of your system regularly and for bottleneck increase or scale up the database size.
2. Internal Cache Performance
Internal cache performance means the hit rate of the database table. Insufficient internal buffer space of the database is the main reason for the low hit rate of the database table. So in PostgreSQL, we use the shared buffer concept to avoid a low rate of database table. A shared buffer is used to manage the buffer space of a database.
Conclusion
We hope from this article, you have understood about PostgreSQL Caching. The above article taught us the basic syntax of PostgreSQL Caching. We have also learned how to implement them in PostgreSQL with different examples of each method. From this article, we have learned how we can handle PostgreSQL Caching in PostgreSQL.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL caching” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.