Updated March 28, 2023
Introduction to Natural Join in Oracle
A Natural Join in Oracle is a SQL query technique that combines row(s) from two or more Tables, View or Materialized View. A Natural Join performs join based on column(s) of the tables which are participating in a join that have the same column name and data type. To perform this join operation, the Natural Join keyword explicitly is used.
Points of Concentration:
- A Natural Join combines multi Tables, View or Materialized View to retrieve data.
- A Natural Join returns all rows that satisfy the same column name and data type condition.
- Oracle provides the Natural Join keyword to perform Natural Join.
- If the Natural Join doesn’t satisfy the same column name and data type condition then it returns a Cartesian result.
- Natural Join does not exclude duplicate record(s).
Syntax:
SQL> SELECT Column_1, Column_2, Column_n FROM Table1 NATURAL JOIN Table2 WHERE condition;
Description:
- Col_1/2/n: The column(s) or calculation as per your requirement.
- Table 1/2: As per table participation in Natural Join.
- WHERE: It’s an optional. It is used to filter the output result.
Example:
SQL> SELECT Name, Designation, Salary, State, Deptnumber FROM Employee
NATURAL JOIN Dept_Category;
Output:
Rules and Restrictions of Natural Join in Oracle
Given below are rules and regulations:
- The Natural Join does not require to pass join condition explicitly (common column condition), it finds automatically common column name and data type and performs join.
- If all participating tables, more than one column have the same name and data type then Natural Join would use them as well for joining conditions.
- The column(s) is/are used in Natural Join can’t have a column qualifier.
Examples of Natural Join in Oracle
Given below are the examples. Here we will use the below sample table (Employee & Dept_category) with 14 & 8 records.
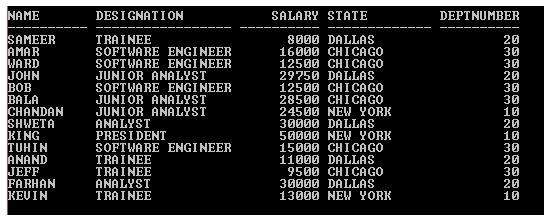
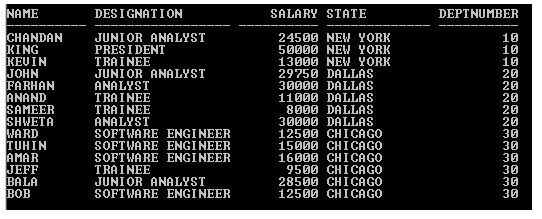
SQL> SELECT * from Employee;
Output:
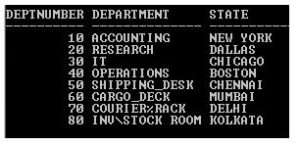
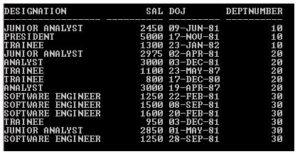
SQL> SELECT * from Dept_Category;
Output:
Example #1
Natural Join with single common column and without any condition.
SQL > SELECT Name, Designation, Salary, State, Deptnumber FROM Employee
NATURAL JOIN Dept_Category;
Output:
In the above example, Natural Join combines tables (Employee and Dept_Category) using the Deptnumber column because of only this column full filling the same column name and data type condition in both the tables.
Example #2
Natural Join with multiple common column and without any condition.
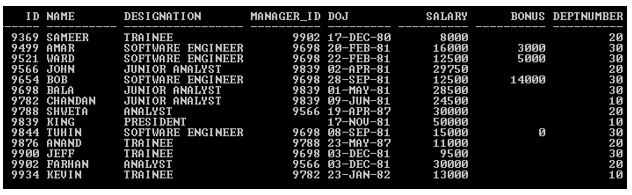
SQL> SELECT Designation, Sal, DOJ, Deptnumber FROM Emp NATURAL JOIN Employee;
Output:
In the above example, Emp and Employee tables participating for Natural Join and both the tables have two common columns (DOJ & DEPTNUMBER) and each table has 14 records and Deptnumber column’s all data matches with each other table. But output returns only 13 records. WHY?
Because in the above example there are two common columns (DOJ & DEPTNUMBER) participating as a join condition. So Deptnumber column’s data getting matched with each other table but from Emp table DOJ column has one unmatched record with other table so Natural Join exclude that record and returns 13 records.
Example #3
Natural Join without any common column.
SQL> SELECT Designation, Sal, DOJ, Deptnumber FROM Emp NATURAL JOIN Employee;
Output:
This JOIN statement returns 196 records.
But each table consists 14 records only. WHY 196 records?
Because there is no common column or same column name and data type in both the tables. Natural Join does not find any common column name and data type, so it performs join without join condition means it joins every single record from one table with every single record from another table (14* 14). That’s why it returns 196 records. This kind of operation or result set is known as a CARTESIAN product.
Example #4
Oracle Natural Join with WHERE clause.
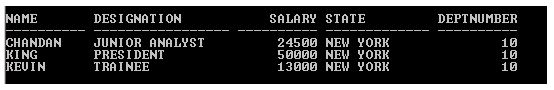
SQL > SELECT Name, Designation, Salary, State, Deptnumber FROM Employee
NATURAL JOIN Dept_Category WHERE Deptnumber =10;
Output:
In the above example, WHERE clause condition filters the result and returns only those records which are having Deptnumber is 10.
Example #5
Natural Join with Column Qualifier.
SQL > SELECT E.Name, E.Designation, E.Salary, D.State, D.Deptnumber
FROM Employee E NATURAL JOIN Dept_Category D WHERE Deptnumber =10;
Output:
In the above example, E and D is the alias name of tables respectively. The alias names are being used by columns as a qualifier to retrieve the data from that specified tables but Natural Join does not accept column qualifier and throws an error. So column qualifier can’t be a part for Natural Join operation.
Tips:
- An asterisk (*) can be used to retrieve all fields of the tables that are participating in join. But it join columns left table columns left side and right table columns right side.
- Oracle Natural Join is similar by nature to Oracle proprietary EQUI JOIN with join condition.
Conclusion
Oracle Natural Join is a join query which combines multiple Tables, View or Materialized View to retrieve data. It does not need to declare the join condition explicitly because it considers implicitly a join condition based on the same column name and data type. So, it can be used to get the records for single or multiple join conditions without explicitly declared.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Natural Join in Oracle. Here we discuss the introduction, rules, and restrictions of Natural Join in Oracle with respective examples. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –