Updated June 20, 2023
Introduction to GROUP BY in Oracle
The GROUP BY Oracle clause divides the table’s rows into groups. It is used in the SELECT statement for grouping the rows by values of column or expression. The GROUP BY clause groups the results by one or more columns’ values.
Points of Concentration
- If the group function is included in a SELECT statement, then individual result column(s) cannot be used without the GROUP BY clause.
- To ensure correct syntax, you must declare any additional non-group functional columns in the GROUP BY clause.
- Using the WHERE clause, you can pre-exclude rows before dividing them into groups.
- You cannot use Column ALIAS in the GROUP BY clause.
- By default, rows sort in ascending order of the column(s) in the GROUP BY list.
- The columns applied upon the GROUP BY clause need not be part of the SELECT list.
- In a SELECT statement, you must use the GROUP BY clause when including a group function with a non-group functional column.
Syntax
1. Syntax without Group Function
SELECT Column_1, Column_2,..., Column_N FROM Table_Name WHERE condition(s)
GROUP BY Column_Name(s) ORDER BY Column(S);
2. Syntax with Group Function
SELECT Column_1, Column_2,..., GROUP_FUN(Column) FROM Table_Name
WHERE condition(s) GROUP BY Column_Name(s) ORDER BY Column(S);
Description:
- Col_1/2/n: The column(s) or calculation as per your requirement.
- Table_Name: As per your requirement
- WHERE: It’s optional, depends on your requirement
- GROUP_FUN: AVG, SUM, MIN, MAX
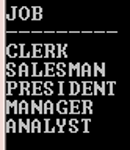
Example: Without GROUP Function
SQL> SELECT Job FROM Emp GROUP BY Job;
Output:
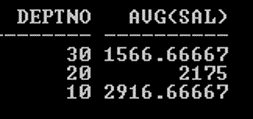
Example: With GROUP Function
SQL> SELECT Deptno, AVG (Sal) FROM Emp GROUP BY Deptno;
Output:
Explanation: The above two examples (without and with ALIAS name) clearly shows how the GROUP BY clause groups the rows based on condition.
Implementations of Oracle GROUP BY Clause with Examples
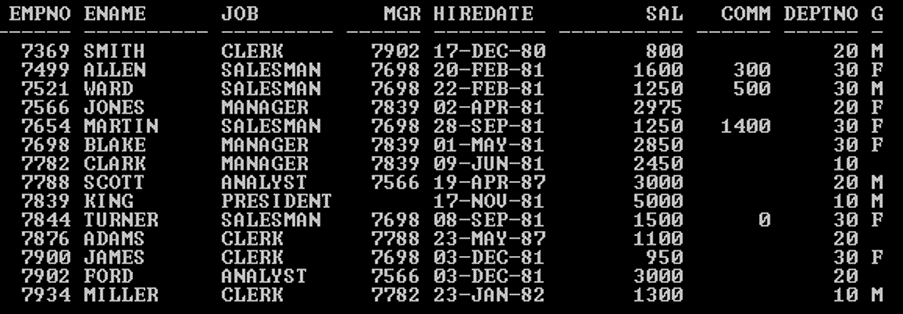
This section will show the Oracle GROUP BY Clause implementation and its behavior. We will use the sample table (Emp) below with 14 records to understand the Oracle GROUP BY Clause behavior.
SQL> SELECT * from Emp;
Output:
Example #1
GROUP BY clause with Non-GROUP Functional columns
SQL > SELECT Empno, Ename, Job, Deptno FROM Emp GROUP BY Deptno;
Output:
The above SELECT statement triggers an error because it includes four Non-GROUP Functional columns, but the GROUP BY clause has only one column.
All non-group functional columns should be included in the GROUP BY clause to prevent this error. Example below:
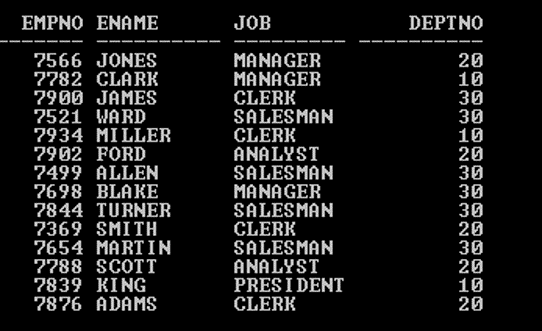
SQL > SELECT Empno, Ename, Job, Deptno FROM Emp GROUP BY Empno, Ename,Job, Deptno;
Output:
Example #2
Column ALIAS name in GROUP BY Clause
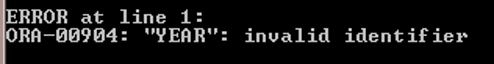
SQL> SELECT TO_CHAR (Hiredate, 'YYYY') Year FROM Emp GROUP BY Year;
Output:
The above SELECT statement triggers an “invalid identifier” error because it uses the column ALIAS name (Year) in the GROUP BY Clause. As per the rule, Column ALIAS cannot be used in the GROUP BY clause. The correct SELECT statement is below:
SQL> SELECT TO_CHAR (Hiredate, 'YYYY') Year FROM Emp GROUP BY
TO_CHAR (Hiredate, 'YYYY');
Output:
Example #3
GROUP BY Clause with GROUP Function
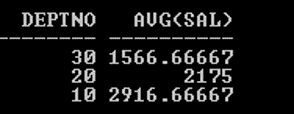
SQL> SELECT Deptno, AVG (Sal) FROM Emp GROUP BY Deptno;
Output:
In the above example, Output shows the Average salary of each Deptno after grouping the Deptno.
SQL> SELECT Deptno, Job, SUM (Sal) FROM Emp GROUP BY Deptno;
Output:
The above SELECT statement throws an error because it includes two Non-GROUP Functional columns with the GROUP functional column. Still, only one Non-GROUP Functional column is included in the GROUP BY clause.
To avoid this error, declare all non-group functional columns in the GROUP BY clause. Example below:
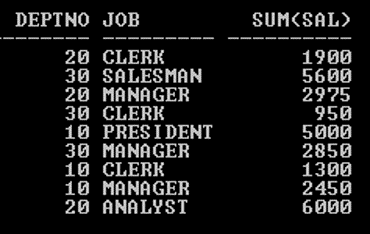
SQL> SELECT Deptno, Job, SUM (Sal) FROM Emp GROUP BY Deptno, Job;
Output:
Example #4
GROUP FUNCTIONAL column and Non-GROUP Functional column without GROUP BY Clause
SQL> SELECT Deptno, AVG (Sal) FROM Emp;
Output:
The above SELECT statement pop-ups an error because the GROUP FUNCTIONAL column is used with the Non-GROUP Functional column. As per rule Non-GROUP, the Functional column must be included in the GROUP BY clause if the GROUP FUNCTIONAL column is used.
See below the correct SELECT statement for the above scenario:
SQL> SELECT Deptno, AVG (Sal) FROM Emp GROUP BY Deptno;
Output:
Example #5
Here are a few more examples of Group-wise Summaries
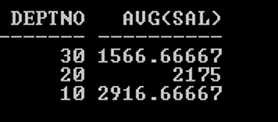
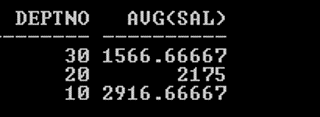
SQL> SELECT Deptno, AVG (Sal) FROM Emp GROUP BY Deptno ORDER BY
AVG (Sal);
Output:
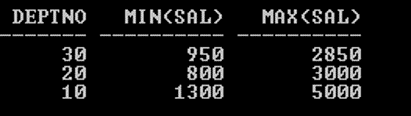
SQL> SELECT Deptno, MIN (Sal), MAX (Sal) FROM Emp GROUP BY deptno;
Output:
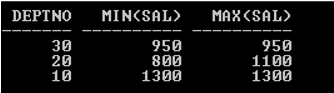
SQL> SELECT Deptno, MIN (Sal), MAX (Sal) FROM Emp WHERE Job=’CLERK’
GROUP BY deptno;
Output:
TIPS:
- Do not use the GROUP BY clause if only the GROUP FUNCTIONAL column is used.
- You can use the GROUP FUNCTIONAL column ALIAS name in the ORDER BY clause but not in the GROUP BY clause.
- GROUP FUNCTIONAL column always returns a single-row result.
Conclusion
Oracle GROUP BY Clause is an expression or keyword that groups a result set into subsets with matching values for one or more columns. If you need to group the result set or apply an aggregate or GROUP function with the Non-GROUP Functional column, the Oracle GROUP BY Clause is a good option.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to GROUP BY in Oracle. Here we discuss the introduction, points of concentration, and implementations of Oracle GROUP BY Clause with examples. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more–