Updated May 17, 2023
Introduction to MySQL Flush Privileges
The following article provides an outline for MySQL Flush Privileges. Whenever we create a user, we assign or grant some privileges to it. These privileges include permission to perform operations on the database and access to it. Users can create and grant functions such as Insert, Update, Delete, and Select to the user in MySQL Workbench. Other than this, the privilege to Grant and Revoke can also be assigned.
After you grant the privileges to the user, we need to either reload or restart the MySQL service we are using to make those changes take effect. Other than that, one more method can be used to make the granted privileges take effect without restarting the MySQL service. We can use the flush privileges command once all the granting operations are done.
Working on MySQL Flush Privileges
If the MySQL service starts without the option “–skip-grant-tables,” it will read all the grant table contents during startup. Further, suppose we grant or revoke the privileges using account-management statements indirectly. In that scenario, MySQL automatically detects any modifications made to the grant tables, and subsequently reloads them into memory. However, if you directly modify the grant tables, the changes will not take effect unless you explicitly specify to restart or reload the MySQL service.
Directly modify the grant tables by using statements like Insert, Delete, and Update. In such cases, we can command the server to reload the MySQL server by operating flush privileges. You can perform this operation by using the FLUSH PRIVILEGE command statement. Alternatively, you can use the mysqladmin flush-privileges or mysqladmin reload command to reload the MySQL service.
For the client sessions, the reloading of the grant tables takes effect as specified below:
- The privileges on the columns and tables take effect when the client’s next request is triggered.
- Whenever we use the following command of the use database_name statement, all the privileges changed on the database are taken into effect.
- Sometimes, the name o the database is cached in the memory; hence, the effect of changes may not be visible. For this, you will first have to use a different database and then use the same previous one on which you were working.
- The “FLUSH PRIVILEGES” command does not impact passwords, and any modifications made in the grant tables are specifically related to global settings. You will have to use a new session in the same connection.
Using the “–skip-grant-tables” option to start the MySQL service can be extremely risky and insecure. It bypasses the reading of grant table contents and disables the access control system, allowing any user to log in to the database and perform any operation without restrictions. To prevent this, we can flush the privileges to make the server read all the grant table contents and access control systems.
Syntax:
Using the following Flush statement, we can reload the grant tables in the memory by running the flush-privileges command.
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;Examples of MySQL Flush Privileges
Here are the examples mentioned:
We will create one user, assign specific privileges to that user, and then check whether the privileges are given and taken into effect properly from the user table.
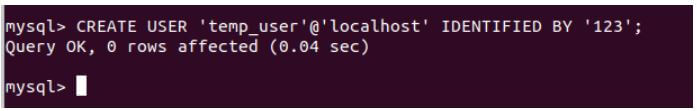
First, create a user named temp_user having password 123 by using the following CREATE USER query statement.
Code:
CREATE USER 'temp_user'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY '123';Output:
Example #1
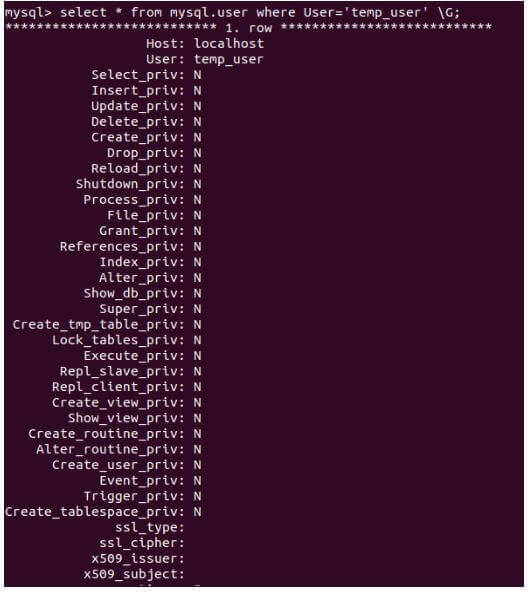
Now, let us check all the privileges assigned to the temp_user by default when it is created by querying the user table using the following statement.
Code:
select * from mysql.user where User='temp_user' \G;Output:
The privileges granted to the user “temp_user” for all columns ending with “_priv” have the value “N,” indicating that no privilege for that operation has been assigned to the user.
Example #2
Here we will grant some privileges to the temp_user table using the following GRANT query statement.
Code:
GRANT SELECT, INSERT, DELETE ON *.* TO temp_user@'localhost';We have assigned the SELECT, DELETE, and INSERT privileges on all the tables of all the databases to the temp_user.
Output:
Example #3
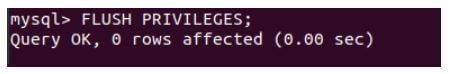
Let us check if all the privileges have been assigned after executing the following command.
Code:
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;Output:
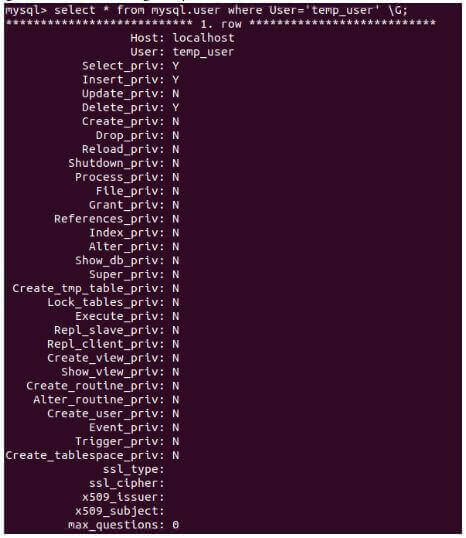
Code:
select * from mysql.user where User='temp_user' \G;Output:
Example #4
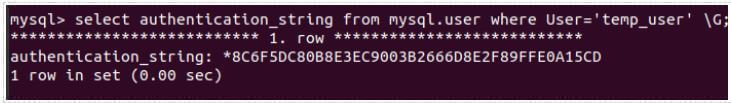
Let us check the authentication string, the encrypted password stored for temp_user, by using the following query statement.
Code:
select authentication_string from mysql.user where User='temp_user' \G;Output:
Example #5
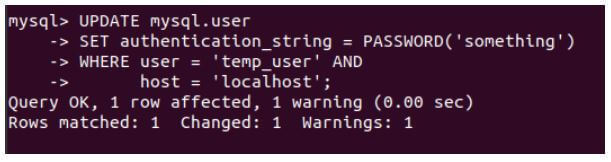
Let us alter the authentication string by changing the password using the following query statement.
Code:
UPDATE mysql.user
SET authentication_string = PASSWORD('something')
WHERE user = 'temp_user' AND
host = 'localhost';Output:
Example #6
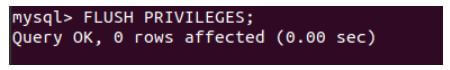
Let us flush the privileges by executing the flush command with the following output.
Code:
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;Output:
Example #7
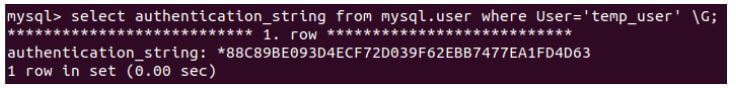
Let us now check the authentication string by retrieving it using the following query statement.
Code:
select authentication_string from mysql.user where User='temp_user' \G;Output:
We can see that the previous and the present authentication string show a substantial difference in the encrypted string stored in it.
Previous authentication string: *8C6F5DC80B8E3EC9003B2666D8E2F89FFE0A15CD
Present authentication string: *88C89BE093D4ECF72D039F62EBB7477EA1FD4D63
Conclusion
We can make the changes made in the privileges to the user or the modification in the grant tables into effect by reloading the grant tables into the memory. You can accomplish this by using the Flush Privileges command, mysqladmin flush-privileges, or mysqladmin reload command to reload the grant tables in memory. When you use the Grant command, there is no requirement to explicitly flush the privileges because MySQL automatically recognizes the changes and reloads the grant tables. This behavior remains consistent even if you modify the grant tables using Insert, Update, or Delete commands. In that case, it is necessary to reload the grant tables by executing the flush privileges command to take the changes into effect.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL Flush Privileges” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.