Updated June 6, 2023
Introduction to MySQL super Privilege
MySQL super Privilege is a GRANT statement that provides permissible privileges that allows a user account to make administrative changes and execute different operations in the database table. super Privilege in MySQL permits a MySQL user to apply admin-level operations and queries, which include KILL, PURGE BINARY LOGS, SET GLOBAL, CHANGE MASTER TO, and also mysqladmin command. MySQL grants privileges to perform operations using SQL queries and command prompts. This comprises defined privilege levels that help to regulate the level to which the privileges can be implemented with access. MySQL GRANT statement supports different privilege levels such as Global, Database, Table, Column, Stored Routine, and Proxy Types.
Syntax of MySQL super Privilege
Here is a simple syntax for utilizing super privilege in MySQL. Once the user is created, you can add this command to the database.
CREATE USER super@localhost IDENTIFIED BY 'pass_super!';GRANT SUPER ON *.* TO 'user@localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'Password_Name';After we execute the above statement, we need to remember to end the query by adding the below command:
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;- Here, the symbol *.* denotes that it is applied for all databases present in the MySQL server. user@lcoalhost defines the user created on the MySQL server using CREATE USER as similar to that of CREATE TABLE statement. Also, the Password_Name denotes the specified password set for that user when creating it on the server.
- Again, running the Flush privilege statement indicates reloading the grant tables in the database server, which enables the modifications to be effective without the need to restart or reload actions on the MySQl service option.
How does super Privilege work in MySQL?
In MySQL, the CREATE USER command creates one or multiple user accounts without privileges. This means a user account can be logged into the server but still does not have the right to perform any actions, such as to query data from database tables and select any database.
To work with the database objects, you need to grant privileges to the user account. To do this, use the GRANT statement, which enables the user account to have one or more privileges to perform operations in the MySQL server.
Following is the basic syntax for the GRANT query:
GRANT privilege [,privilege],…
ON privilegelevel
TO accountname;For example, suppose we want the SELECT privilege for table Products in the database provided to the user account achu@localhost:
GRANT SELECT
ON Products
TO achu@localhost;For privilege levels, let us see the main levels supported by MySQL as follows:
- Global Privileges: It implements all present databases in the server MySQL. We must apply the *.* structure code after the ON keyword.
- Database Privileges: It implements all available database objects comprising of indexes, tables, views, etc., using the syntax after ON as DatabaseName.*
- Table Privileges: It implements all table columns in a database.
The syntax is:
DatabaseName.TableName- Column Privileges: It implements a table column, but columns or columns should be specified for every privilege used after the GRANT keyword.
- Stored Routine Privileges: It implements stored functions as well as procedures.
- Proxy User Privileges: It applies proxy of one user for another one. All privileges of a proxy user are already delivered to the proxy user. We need to add PROXY after GRANT in the syntax ON root.
To use the GRANT query, you should always verify whether you have the necessary privileges before granting any rights. Additionally, if the read_only system variable is enabled, you must have super privilege access to execute a GRANT statement.
Example of MySQL super Privilege
Given below is the example of MySQL super Privilege:
Usually, we will build a new user account using the CREATE USER query and afterward implement the GRANT statement to allow privileges to that user account to make changes within a database server.
Suppose we are creating a user as super@localhost by the CREATE TABLE command in MySQL shown below:
Code:
CREATE USER super@localhost IDENTIFIED BY 'pass_super!';Next, let us display the privileges allocated to the super@localhost user using the SHOW GRANTS command as follows:
Code:
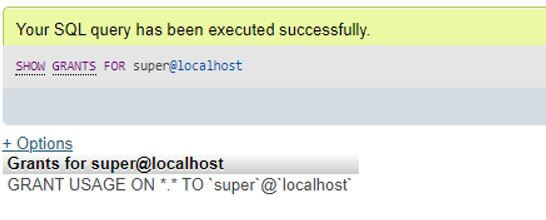
SHOW GRANTS FOR super@localhost;Output:
Here, the USAGE denotes that the user named super@localhost can log in to the database server but still holds no privileges.
In the third step, we will now provide all privileges in all available databases in the present MySQL database server to the user super@localhost.
Code:
GRANT ALL
ON achu.*
TO super@localhost;Next again, view the details through the SHOW GRANTS query statement executed as below:
Code:
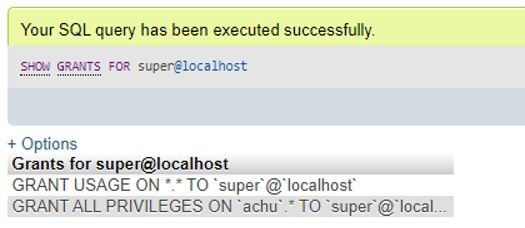
SHOW GRANTS FOR super@localhost;Output:
The result shows that the user super has all the privileges on the localhost in the server MySQL for all databases. This means that the Super privileges will allow to use of all GRANT privileges and make operations in the server. The REVOKE and GRANT statements can utilize the allowable privileges.
The super privileges in MySQL affect the operations and behaviors of the MySQL server:
- It empowers the server configuration modifications by altering global system variables like setting up a session variable; also, we need to have the super privilege.
- It permits changing the global transaction features, starting an account, and stopping replication along with Group Replication.
- It allows using statements such as CREATE SERVER, DROP SERVER, and ALTER SERVER. Also, it enables to implementation of mysqladmin debug query.
- It permits InnoDB encryption along with key rotation. In addition, it empowers the reading DES key with the help of the DES_ENCRYPT() function.
- It controls the client connections and allows execution of Version Tokens MySQL user-defined functions.
- To create or modify stored functions in MySQL, you must have super privileges enabled when binary logging is allowed.
Conclusion
Initially, we need super privilege in MySQL to run the GRANT statement query. Global-level privileges in MySQL refer to administrative privileges that enable the use of super privileges. The super privilege in MySQL helps to avoid unauthenticated access. It allows granting privileges to user accounts that are valid and managed by the admin of the MySQL database server. Thus, this is a significant factor in the security and maintenance of the MySQL server.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL super Privilege” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.