Updated May 11, 2023
Introduction to ROLLUP in MySQL
MySQL ROLLUP is a type of SQL Keyword used in the statement with GROUP BY Clause that helps to create subtotals and grand totals for the result set of columns as a summary row. The ROLLUP operator is used in MySQL with GROUP BY Statement as an extension or an advanced feature to filter the sum total for a column or a group of columns by adding additional rows.
The GROUP BY query is applied with aggregate functions like COUNT, MAX, MIN, SUM, and AVG, which groups the result rows by single or more columns. The ROLLUP SQL operator is an option to use the GROUP BY Clause to allow you to include extra fields representing the subtotals. Super-aggregate rows refer to the subtotal rows, along with the grand total row. So, we can create multiple grouping of set rows by using a single query containing both the GROUP BY Clause and ROLLUP extension in MySQL.
Syntax:
Supported by SQL Server | Oracle | MS Access
SELECT r1, r2 AggregateFunction(r3) FROM TableName GROUP BY ROLLUP (r1,r2);For MySQL, we use this syntax which is slightly different from the above:
SELECT r1, r2 AggregateFunction(r3) FROM TableName GROUP BY r1, r2 WITH ROLLUP;Since ROLLUP follows a hierarchy of input columns, so from the above syntax, when we provide (r1, r2), it assumes the hierarchy r1 > r2. ROLLUP creates a group of columns that is sensible using this hierarchy. Therefore, for generating reports in MySQL, we consider the ROLLUP clause to produce subtotals and grand totals.
How ROLLUP works in MySQL?
- You can use the ROLLUP operator as an option to retrieve the result set with calculated subtotals based on the grouped columns using GROUP BY.This produces the summarized amounts based on the table columns provided by the ROLLUP keyword in MYSQL.
- Hence, the result table formed using the ROLLUP operator collects the data from grouping sets of columns at a level of specifications and rolling them up to the main table.
- Logically, we can justify that a ROLLUP operator is a SQL modifier used with GROUP BY Clause in the statement. Thus it affects the summary output by including extra rows that determine the high level of instant operations in the table.
- You can also add the LIMIT Clause simultaneously to limit the rows in the result set with the ROLLUP clause.
- The ROLLUP is not used with ORDER BY. We can use ASC or DESC type of sorting in the GROUP BY clause using the ROLLUP operator in the SQL statement.
Examples of ROLLUP in MySQL
Given below are the examples of ROLLUP in MySQL:
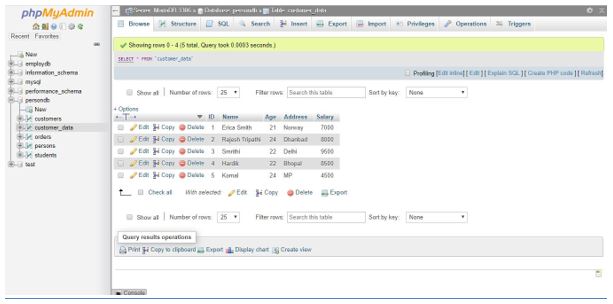
For example, we have used the Customer_Data table with columns (ID, Name, Age, Address, Salary) in the Database PersonDb.
Customer_Data table
Example #1
MySQL ROLLUP with one column.
We are executing the below SQL Query to fetch the total salary by Customer name using GROUP BY Clause and the SQL SUM () aggregate function in MySQL.
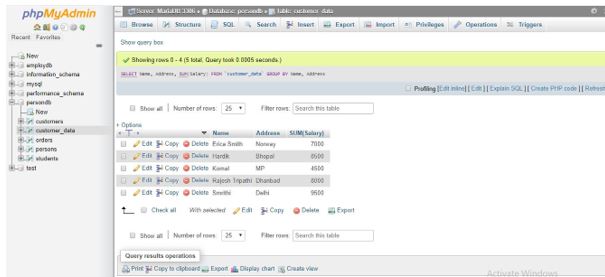
SELECT Name, SUM(Salary) FROM `customer_data` GROUP BY Name;Output:
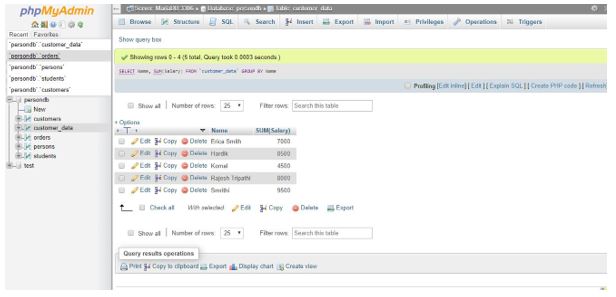
Now, let us query the following statement to retrieve the total amount in all salary columns using the ROLLUP operator to the above SQL syntax code:
SELECT Name, SUM(Salary) FROM `customer_data` GROUP BY Name WITH ROLLUP;Output:
In the above result set, you can view that the grand total line is specified by the NULL value column in the table. Here, the ROLLUP adds an extra row to display the grand total super aggregate row of all salary amounts from the table data.
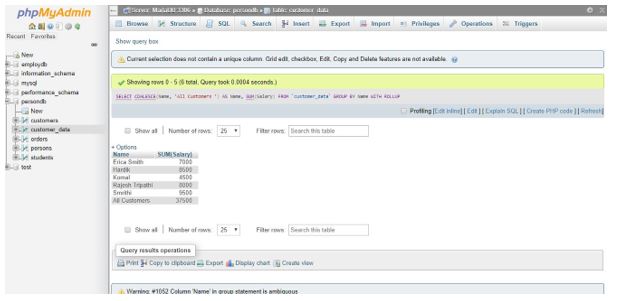
Hence, we can make the result ROLLUP row more informative to users by using SQL COALESCE() function, which is responsible for substituting the column value NULL with any other text word we want; suppose here we have used “All Customers”.
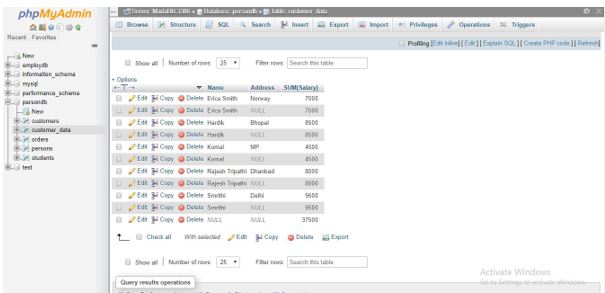
SELECT COALESCE(Name, 'All Customers ') AS Name, SUM(Salary) FROM `customer_data` GROUP BY Name WITH ROLLUP;Output:
Example #2
MySQL ROLLUP with Multiple Columns.
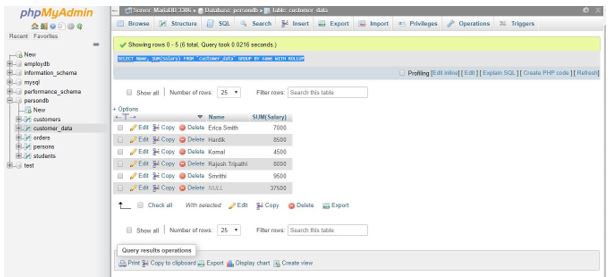
The following code calculates the Customer_Data by two columns Name and Address:
SELECT Name, Address, SUM(Salary) FROM `customer_data` GROUP BY Name, Address;Output:
Now, adding ROLLUP to the above SQL GROUP BY Statement:
SELECT Name, Address, SUM(Salary) FROM `customer_data` GROUP BY Name, Address WITH ROLLUP;Output:
The result table includes the output summary of rows not only at a single level but at two levels in the analysis process with ROLLUP.
- An extra row is summarized for every set of Address rows of a particular Name that shows the total Customer_Data salary, with the Address value in the columns defined as NULL.
- The result table has an additional row at the end, with the total amount of salary for all Name and Address columns that have NULL values.
Example #3
MySQL ROLLUP with Partial rollup.
We can also perform operations in MySQL using ROLLUP and GROUP BY clauses in a partial way rollup. Using ROLLUP helps to reduce the number of calculated subtotals.
SELECT DISTINCT Name, Address, SUM(Salary) FROM `customer_data` GROUP BY Address WITH ROLLUP;Using the ROLLUP clause, the super aggregate total is calculated only for the Address column, and not for the name columns, as clarified in the result set.
Therefore, we can analyze multiple levels of operations using only a single SQL query in MySQL.
Conclusion
Active: Developers use the ROLLUP operator in MySQL on a table to generate multiple grouping sets of columns to group with. From this, the SQL ROLLUP can also form a grand total of the columns and not just subtotals. Assume that we are using multiple columns to write the query statement for a table using the ROLLUP and GROUP BY clauses, then the SQL ROLLUP clause requires a hierarchy among these columns. Thus, the ROLLUP clause with the GROUP BY clause in MySQL helps produce a subtotal of the row each time a new column changes and finally calculates grand total at the end.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “ROLLUP in MySQL” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.