Updated May 15, 2023
Introduction to MySQL DECODE()
The MySQL DECODE() function is known to be a decryption type of function in the database for data interpretation. This MySQL DECODE function is responsible to decode an encrypted string part from the record values and then returns the original one. Also, if the input for this DECODE() function is provided as an empty encoded string, then the result processed by MySQL will be the empty string itself. Otherwise, using the DECODE() function, we can revert the original string, which is now available in an encoded form for security purposes. The DECODE() function in MySQL allows the supplementing technique of if-then-else statement logic to the MySQL queries.
Syntax
Find the below MySQL syntax for DECODE() function:
DECODE(EncryptedString, PasswordString);Explanation: From the above arrangement of the MySQL DECODE() function, we can say that the function receives two parameters as arguments to execute the decoding process on the MySQL database. The first parameter, ‘EncryptedString’, specifies the encoded value string that you want to decode. The second one, i.e., ‘PasswordString’, is the helpful password string to decode the input to produce the output string. The function retrieves and returns the original string that was encoded and stored in the database records. We use the DECODE function with SELECT MySQL Statement to execute the queries.
How does DECODE() function work in MySQL?
The DECODE() function syntax utilizes two parameters to decode an encoded value and generate the output. The first parameter is the string value that needs to be searched or compared, typically in an encrypted or cryptic form. The second parameter of a decoding function is commonly known as the “password” or “key” because it serves as the decryption key used to decrypt the encoded string.
This function performs to compare the argument expression specified to every search value line by line. In this processing, if the argument is found identical to a search, then the MySQL database displays the equivalent result. If the match does not exist, then the function returns to default. If the default is, by chance, omitted, then the MySQL server outputs NULL.
DECODE() function Arguments
The DECODE() function arguments can be as follows:
- Numeric Form: In this parameter value type, we can include a Number, Binary_Float, or Binary_Double. Suppose the function’s first pair of the search result is a number. In that case, MySQL matches all the search result values. The initial argument value to find its maximum numeric antecedence also implicitly converts the remaining parameters to the same data type. The function generates and returns the result in the specified data type.
- Character Form: In this form, the search and other arguments are specified as character types, and the MySQL DECODE function matches them using non-padded evaluation semantics. This form can include the inputs in any data type, such as VARCHAR2, VARCHAR, NCHAR, CHAR, or NVARCHAR2. Whatever the data type of the first search argument, the result data type character data type will be similar to it.
- When the first data type argument is in CHAR form or a NULL value, the server results change the output value to the VARCHAR2 data type.
- Since the DECODE function follows the if-the-else type of logical loop technique, it uses a short series of evaluations like it examines search values just before matching it to the argument relatively than to all search results. Suppose the preceding search is identical to the argument; then the execution is completed.
- According to the first search value, the data type of arguments will be converted, and the result will be displayed in the same data type in MySQL DECODE() function.
- The highest number of constituents that a DECODE() function can include is 255.
Examples to Implement MySQL DECODE()
We will now discuss how it works on the encoded data part:
Example #1
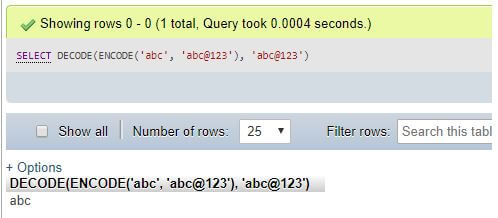
Executing MySQL DECODE() function using a string
Code:
SELECT DECODE(ENCODE('abc','abc@123'),'abc@123')Output:
Example #2
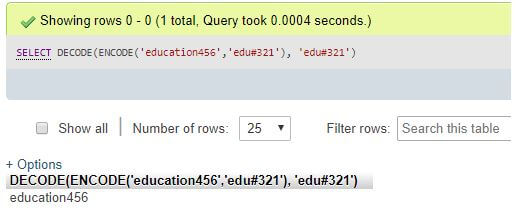
Executing using a combination of characters and numbers
Code:
SELECT DECODE(ENCODE('education456','edu#321'), 'edu#321');Output:
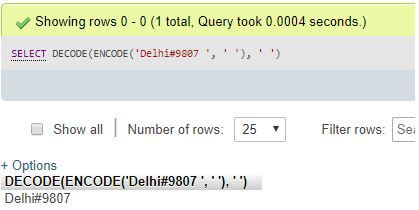
Code:
SELECT DECODE(ENCODE('Delhi#9807',''), '');Output:
Explanation: In WAMP phpMyAdmin, if you want to leave the password empty or unset, you can pass an empty string (”) as the second argument in the DECODE() function. However, if you have set a password for the local or online database server, you need to provide the password string as the second argument in the DECODE() function.
Example #3
Executing using a NULL string value which returns the length of the same string after the process of compression
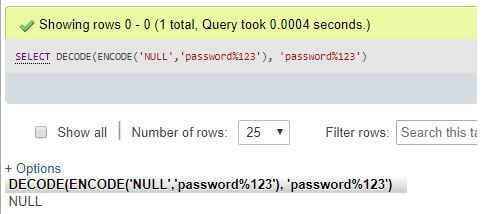
Code:
SELECT DECODE (ENCODE('NULL','password%123'),' password%123');Output:
Explanation: In the above examples, it is clear that the function ENCODE has encrypted the arguments using the passwords specified. Then, using the MySQL DECODE() function, we can now receive the original string or the function’s first argument with the same password’s help. If a character string is passed through the function, then the function returns a character data type result. In the case of combining both characters and numeric, the result is also in the same format. Again, the DECODE function produces a NULL value for NULL input.
Example #4
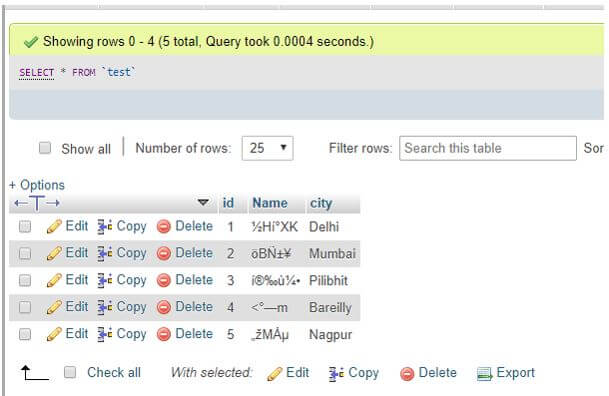
MySQL DECODE() function with table columns
Consider a sample table as ‘Test’ with fields ID, Name, and City where the Name column has encoded values. We have some data rows inserted into it. We have the table view as follows:
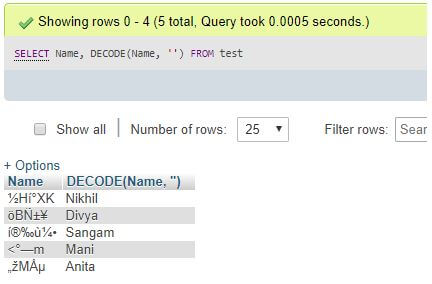
To execute the DECODE() function on a table column, such as “Name,” you can use the following query statement with arguments:
Code:
SELECT Name, DECODE(Name,'') FROM test;Output:
Explanation: The code snippet provided demonstrates the application of the DECODE() function to the table column ‘Name’. As a result of the query execution, the decrypted data rows corresponding to the encoded ‘Name’ values have been retrieved from the database.
Conclusion
If the DECODE() function finds a match during execution, it retrieves the original string. However, if there are no matches, it outputs a default value. In cases where a default value is not specified, MySQL provides a NULL value as the result. This DECODE() function is useful to undo the encrypted formula and receive the original data whenever necessary.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL DECODE()” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.