Updated May 30, 2023
Introduction of MySQL Concat
MySQL Concat function is used when dealing with string in a database that can be in any format, column values, variables, or literal values in the string that helps to append two or more such string values to each other to create a new string value that is returned by the function that is the resultant value consisting all the string values passed to it in appended format and forming one large string. In this article, we will learn how to use the MySQL Concat function to concatenate two or more string values, study its syntax and work and implement a few examples that will demonstrate the usage of the Concat function in MySQL.
Syntax and Working of Concat Function:
The syntax of the Concat function in MySQL is as defined below:
CONCAT(string_expression1,string_expression2, ... );We can provide as many parameters as we want to concatenate using the Concat function. The string expressions can be any of the constant or literal string values, variables having string values, columns that store the string values with datatype varchar, or any string value specified in single or double quotes. If the Concat function is used without specifying any parameter value, it will result in an error. The minimum one parameter is a must for using the Concat function. Passing a NULL value to the Concat function in any of the parameters gives out the resultant value as NULL itself, irrespective of what other values are passed as parameters.
Examples of MySQL Concat
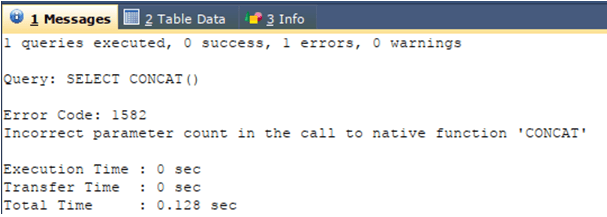
Let us first try to execute the MySQL Concat function without passing any parameters and see the output which is arisen. We will execute the following query statement –
SELECT CONCAT();The execution of the above query statement gives the following output –
We can observe from the output that an error is raised, saying that an incorrect number of parameters were supplied to the Concat function.
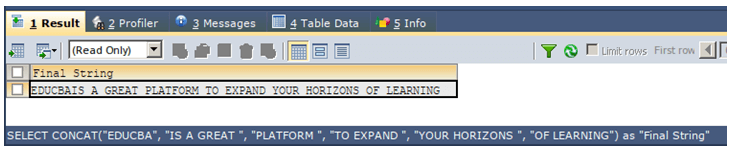
Now, we will concatenate the string values “EDUCBA”, “IS A GREAT “, “PLATFORM “, “TO EXPAND “, “YOUR HORIZONS” and “OF LEARNING” using the Concat function in MySQL. For this, we will use the following query statement –
SELECT CONCAT("EDUCBA", "IS A GREAT ", "PLATFORM ", "TO EXPAND ", "YOUR HORIZONS ", "OF LEARNING") AS "Final String";The execution of the above query statement gives the following output:
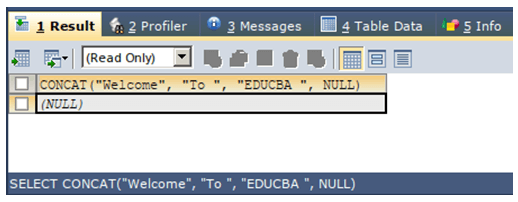
Let us try concatenating the strings with a NULL value as one of its parameters in the Concat function. We will try concatenating “Welcome”, “To “, “EDUCBA” and NULL parameters using the following query –
SELECT CONCAT("Welcome", "To ", "EDUCBA ", NULL);The execution of the above query statement gives the following output as NULL because even a single NULL parameter can result in the output string being NULL:
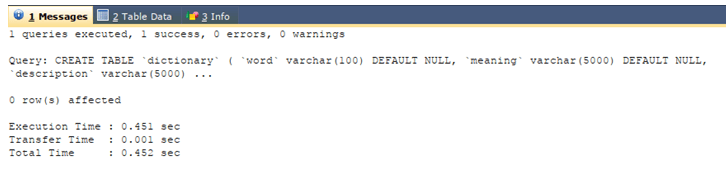
We can even concatenate the values stored inside the variables and column values. Let us create a dictionary table containing three columns: word, description, and meaning. We will use the following table to create the table:
CREATE TABLE 'dictionary' (
'word' varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
'meaning' varchar(5000) DEFAULT NULL,
'description' varchar(5000) DEFAULT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1;The execution of the above query statement gives the following output:
Let us insert some records in the table using the following query statement:
INSERT INTO 'dictionary' ('word', 'meaning', 'description') VALUES
('antonym', 'a word that means the opposite of another word', 'an Alternative name'),
('connotation', 'an additional idea or emotion that a word suggests to you', 'emotions attached to words' ),
('etymology', 'the study of the origins of words; the origins of a particular word', 'the study of the origins'),
('lexicography', 'the job or skill of writing dictionaries', 'writing dictionaries'),
('polysemy','the fact that some words can have more than one meaning', 'multiple meaning words'),
('thesaurus', 'a reference tool which shows groups of words that have similar meanings', 'representation of groups of words that have similar meanings'),
('knack', 'an acquired or natural skill at doing something.', 'natural skill'),
('flair', 'stylishness and originality.', 'originality'),
('panache', 'a tuft or plume of feathers', 'feather collection');The execution of the above query statement shows the following output:
Let us retrieve the inserted records:
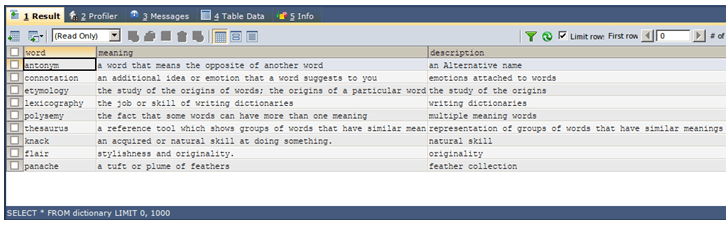
SELECT * FROM dictionary;Gives the following output:
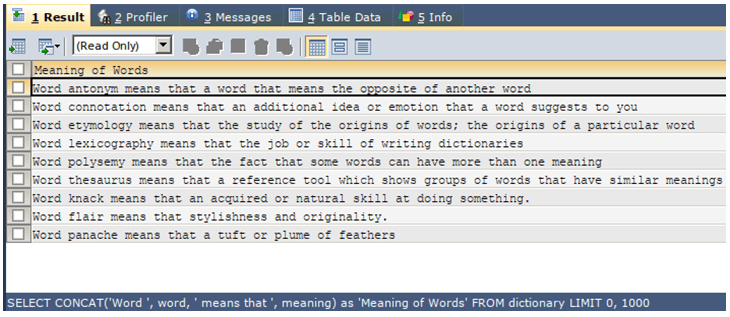
Now, we have to concatenate the column values such that the resultant string will have the strings in the format Word “word column string” means that “meaning string”. We can use the Concat function to do so in the following query statement:
SELECT CONCAT('Word ', word, ' means that ', meaning) AS 'Meaning of Words' FROM dictionary;The execution of the above query statement gives the following output with expected strings:
An alternative way of concatenating strings in MySQL:
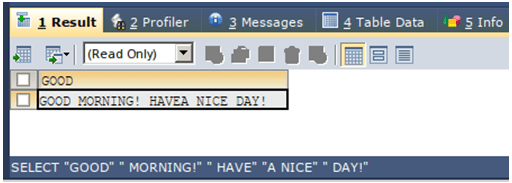
In MySQL, you can easily concatenate strings by specifying them within single or double quotes and separating them with spaces. This automatically results in a single concatenated string that appends all the selected strings, separated by spaces. Consider a simple example where we want to concatenate the string values “GOOD”,” MORNING!”,” HAVE”, “A NICE” and” DAY!”. We can use the simple SELECT statement to retrieve the concatenated string for this. We will use the following query statement to concatenate the strings in MySQL:
SELECT "GOOD"" MORNING!"" HAVE""A NICE"" DAY!";The execution of the above query statement gives the following output after execution:
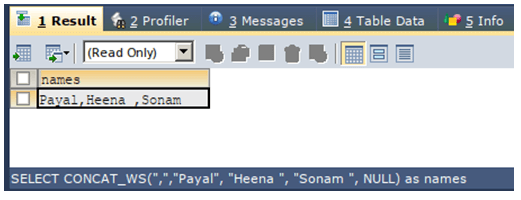
MySQL offers the CONCAT_WS() function as an alternative to using CONCAT() and regular SELECT statements. CONCAT_WS() allows us to specify a separator and conveniently ignores any NULL values passed as parameters. The syntax is the same as the concat function, with the first parameter being the separator. Consider example –
SELECT CONCAT_WS(",","Payal", "Heena ", "Sonam ", NULL) AS NAMES;Where the comma is the separator that gives the following output:
Conclusion
We can concatenate the string in MySQL by using simple SELECT statements or CONCAT and CONCAT_WS functions available in MySQL. We need to specify at least one parameter to the Concat function and be careful that none of the parameters should have a NULL value.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL Concat” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.