Updated May 11, 2023
Introduction to MySQL IN Operator
MySQL IN Operator retrieves the result set by checking whether a value from the set of literal values provided by the subquery is matched. This operator helps to determine the specific value if available in the result of the subquery using the WHERE clause. If a particular value is present in the list of values provided to match a conditional expression, it fetches the set of columns from the table.
Thus, like other MySQL operators, the MySQL IN operator allows comparing a value matching from the set of column values returned by a subquery statement. If we want to get the rows from the Database table where a particular value should be present in a list of values available through a conditional query, then we use the MySQL IN operator. We extract the rows with matching values in the list of values in IN operator function from a particular value of the column given using the WHERE keyword in MySQL.
Syntax:
We have the following SQL syntax statement to illustrate the IN operator working and query in MySQL:
SELECT * FROM TableName WHERE (ColumnA) IN (SELECT query statement);OR
SELECT ColumnA, ColumnB,.., FROM TableName WHERE (ColumnA or any expressional condition) IN ('ValueA', 'ValueB',…..);Explaining the above syntax in brief:
- We must provide any column value as ColumnA or use any expression with IN operator in the WHERE clause query.
- We must differentiate the values in the IN operator list with a comma (,).
- You can provide any subquery statement that uses the SELECT clause in MySQL with the IN keyword to filter the values from other tables, and then run the statement to get the required set of result rows from the table.
- The result of IN operator will be one of the column values or the subquery expression result value matches any values in the list. If it does not match, then the result of IN operator will be 0.
How does IN Operator Work in MySQL?
As per the above syntax, MySQL IN operator provides an equal argument value. Use the IN Keyword; We combine it with the WHERE clause. When this happens, the query executed only affects the records whose values match the list of values in the IN Keyword. IN keyword in MySQL helps to minimize the use of the OR clause.
Suppose we have all the constant values in the list; in MySQL, we perform the following operational steps:
- Firstly, it examines whether the values are the same data type as the column. Also, we evaluate the expression or subquery results.
- Next, we sort the values in a proper sequence.
- Then, the SQL statement searches for the value based on the Binary Search Algorithm, which enables the query using the IN operator with a list of constant values to execute quickly.
- Otherwise, based on the rules in MySQL, type conversion can take place to process the query.
Examples of implementing IN operator in MySQL
Let us discuss the IN operator using examples and learn the code to write the SQL query.
Example #1 – within, NOT IN and OR
We named the tables ‘Customers’ and ‘Employees’ and are currently using them. Below is the SQL statement using IN operator in the Customers table.
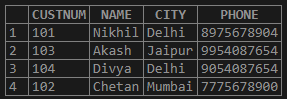
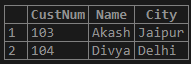
Customers Table:
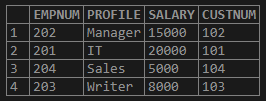
Employees Table:
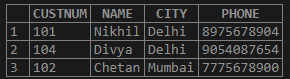
SELECT * FROM Customers WHERE City IN ('Delhi', 'Mumbai');The above query with IN operator will fetch all the records from the table where the customers are from the cities provided in the IN keyword: Delhi and Mumbai.
Output:
If we use the OR operator in the query above, then the result will be the same as above:
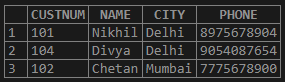
SELECT * FROM Customers WHERE City = 'Delhi' OR City = 'Mumbai';Output:
But if we have multiple values in the list, we need to separate each value with OR operators, and the statement will be constructed very long. Therefore, MySQL introduced the IN operator to avoid such issues and make the SQL syntax more proper and readable. So, the IN keywords have helped to shorten the statement by listing values together, separated by commas.
If we want to obtain the result set that does not match the values in the list, we use the following query with the NOT IN operator in MySQL:
Query:
SELECT * FROM Customers WHERE City NOT IN ('Delhi', 'Mumbai');Output:
You can see from the result above that the NOT IN operator has fetched the rows of customers from the table that does not belong or are related to the cities provided in the list: Delhi and Mumbai.
Example #2 – With Subquery
Generally, the IN operator is used with an inner query or subquery. It is done so because instead of passing a list of literal values with IN keyword, we can use a subquery that fetches the list of values from one or multiple tables and provides them as input to IN operator to match the value in the outer query and produce the result from the SQL statement.
In the following query, we have taken both tables Customers (CustNum, Name, City, Phone) and Employees (EmpNum, Profile, CustNum, Salary) to filter the result set from both the tables in MySQL:
Query:
SELECT CustNum,Name, City FROM Customers WHERE CustNum IN (SELECT CustNum FROM Employees where EmpNum > 202 ) ORDER BY CustNum;Output:
Here, the IN Operator has provided the result rows from Customers using a subquery where the values of the CustNum column, including the employees whose salary is greater than 5000, are the output of the subquery from Employees.
Conclusion
- Remember that as per the above IN operator syntax, if ColumnA value is not present in the table or the subquery expression provides a NULL value, or if any values in the list are NULL, then the condition does not give proper comparability of values, and thus, the result of IN operator will be NULL.
- If we want a result that does not match the values in the list of values, we can use the NOT IN operator instead of IN.
- Hence, along with the WHERE clause, we can use IN operator in MySQL in other SQL queries or statements like UPDATE and DELETE.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL IN Operator” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.