Updated May 11, 2023
Introduction to ANY in MySQL
ANY is a MySQL operator that returns a true value if any of the Subquery conditions in MySQL is fulfilled when the SQL query is executed. However, ALL SQL operator works related to ANY operator, but it returns true if all the Subquery values are satisfied by the condition in MySQL. MySQL introduces special characters or words that help perform a specified operation or more. We can use the SQL operators and operands to generate a SQL statement code to contain a particular condition or execute specific operations. Hence, like other operators, developers also use the ANY operator in MySQL to govern a provisional expression in a SQL statement query and produce a result set with true values that fulfill the benchmarks.
Syntax
Here is the elementary syntax of the ANY operator used in MySQL:
SELECT Column1 [Column2,..] FROM TableA WHERE Column2 Operator ANY (SELECT Column2 FROM TableB WHERE condition);We can use the All SQL operator with the below query:
SELECT Column1 [Column2,..] FROM TableA WHERE Column2 Operator ALL (SELECT Column2 FROM TableB WHERE condition);Remember that the SQL operator used here should be a typical comparison operator that is commonly used in MySQL, such as <, >, =, !=, <>, <=, >=.
How does ANY Operator work in MySQL?
Generally, in MySQL operation with ANY and comparison operator, we have the following syntax:
Operand ComparisonOperator ANY (Subquery);- Since ANY operator should return true if the condition is true so, the ANY SQL keyword should track a comparison operator and if a comparison is valid for ANY of the values provided in the column by the result of the subquery.
- For illustration, let us consider the succeeding statement:
SELECT K1 FROM Q1 WHERE K1 > ANY (SELECT K1 FROM Q2);- Suppose a field row exists in the Q1 table with value (11), then the ANY operator returns TRUE from the expression if there exist values in table Q2 at least one less than 11, for example (30, 12, 8). Here, the condition will be fulfilled because, in Q2, a value of 8 is available, a smaller amount than 11 in Q1 so the ANY keyword will result in a TRUE value.
- But supposing Q2 comprises (30,12,31), then no values of subquery will be less than the Q1 value, and thus the ANY operator will show FALSE as the conditional expression is not satisfied. Also, if Q2 holds NULL values like (NULL, NULL, NULL), then the expression will be unknown.
- The keyword IN in MySQL works as a code-named (alias) for = ANY when used with a Subquery in the query statement. Hence, we can say that the below two SQL statements are identical in MySQL;
Code:
SELECT K1 FROM Q1 WHERE K1 = ANY (SELECT K1 FROM Q2);
SELECT K1 FROM Q1 WHERE K1 IN (SELECT K1 FROM Q2);- But we cannot say that IN SQL operator and = ANY operator keywords are synonyms when we use a list of expressions because IN takes the list of expressions and = ANY cannot.
- Also, NOT IN cannot be an alias or designated name for <> ANY operator but can be used for <> ALL.
- MySQL gives the keyword SOME as an alias to the ANY keyword, making the two SQL code declarations equivalent.
Code:
SELECT K1 FROM Q1 WHERE K1 <> ANY (SELECT K1 FROM Q2);
SELECT K1 FROM Q1 WHERE K1 <> SOME (SELECT K1 FROM Q2);- Given that the table contains only one column, we can use table query in a scalar IN, ANY, and SOME subquery condition. Understand if Q2 in the above table has only one column, then the above SQL statements can be re-written as follows:
Code:
SELECT K1 FROM Q1 WHERE K1 > ANY (Table Q2);// (SELECT K1 FROM Q2) is substituted with Table Q2
Code:
SELECT K1 FROM Q1 WHERE K1 = ANY (Table Q2);
SELECT K1 FROM Q1 WHERE K1 IN (Table Q2);
SELECT K1 FROM Q1 WHERE K1 <> ANY (Table Q2);
SELECT K1 FROM Q1 WHERE K1 <> SOME (Table Q2);- Remember <> operator defines the true meaning of SQL syntax, indicating that nearly some values are not equal to a condition but not all values.
Examples to Implement ANY in MySQL
Let us show some examples and take some tables named ‘Customers’ and ‘Orders’ to execute SQL queries using ANY keyword:
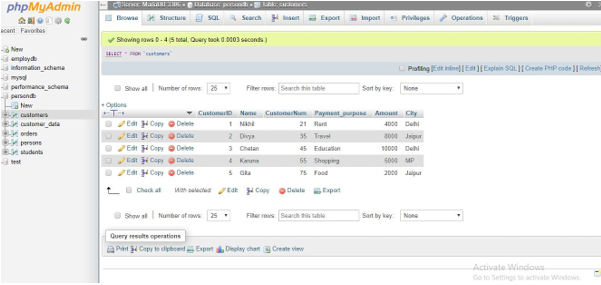
1. Customers Table
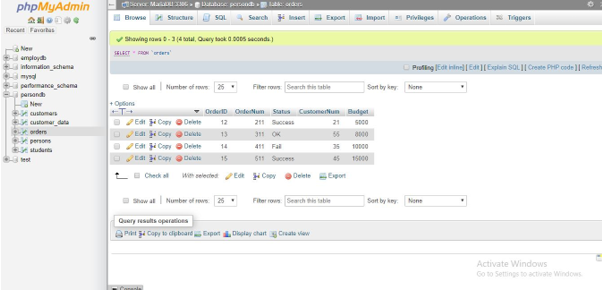
2. Orders Table
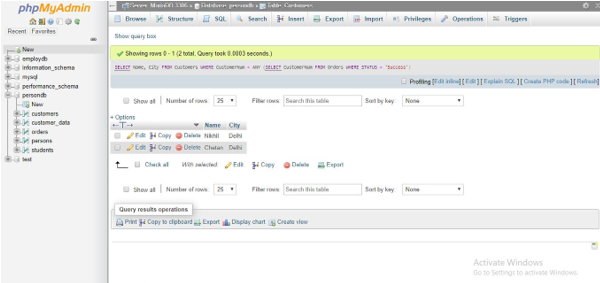
1. ANY with = operator
Code:
SELECT Name, City FROM Customers WHERE CustomerNum = ANY (SELECT CustomerNum FROM Orders WHERE STATUS = 'Success');Output:
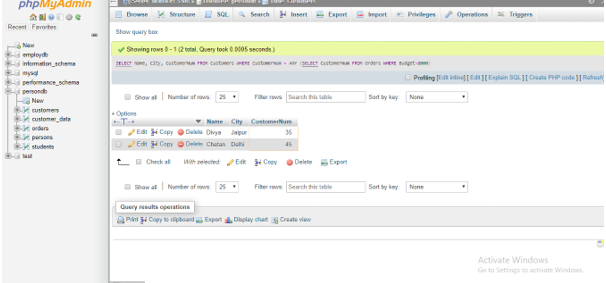
2. ANY with > operator
Code:
SELECT Name, City, CustomerNum FROM Customers WHERE CustomerNum = ANY (SELECT CustomerNum FROM Orders WHERE Budget>8000);Output:
Advantages of using ANY operator in MySQL
- ANY is a logical operator in MySQL that returns the Boolean value due to the SQL query. Developers use it to select any or some tuples of the SELECT statement.
- The ANY operator allows comparing the value of a table to each value in the result list or rows provided by the subquery condition. After this, the ANY keyword finds any value that matches at least one value or row of the inner query. Then, it gives TRUE as a result.
- Thus, in MySQL, the ANY operator should be preceded by comparison operators. So, the ANY operator returns TRUE if any of the inner queries execute to satisfy the condition.
- The ANY keyword is useful to provide the result, a distinct column value from a table that matches or has any record in another table.
- You can perform many different types of comparison using ANY operator with SELECT and WHERE keywords and out a condition to match and provide the required result from a combination of two tables.
- It is helpful to get the result if any value in one table satisfies a specific condition that shows the value that matches.
Conclusion
The ANY operator in MySQL filters the result set from SQL syntax only if any values meet the condition; otherwise, it shows false. By comparing subquery results and operands in the SQL expression, developers also use the ANY keyword along with comparison operators in MySQL to achieve a specific result. I hope you like the article and learned some new points.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “ANY in MySQL” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.