Updated February 28, 2023
Introduction to MongoDB Unique
MongoDB’s Unique Constraint makes certain that the fields indexed in it, do not store duplicate values for the same field, i.e., making sure the uniqueness of fields. By default, MongoDB enforces this unique constraint on the “_id” field, while inserting new data. One of the major responsibilities is to ensure no duplicate data has been stored in a single key. We also have restrictions here, like MongoDB will be unable to establish a unique index on any specific field, in case if the collection somehow has already stored any data that would breach the feature of unique constraint for the index.
Syntax:
Now that we have understood what Unique Constraint in MongoDB, let us learn the standard syntax to write this Unique method.
db.collection_name.createIndex( {field_name : 1} , {unqiue : true} )
Explanation: Now, as you can see in the above syntax, we have created a simple index, which means the data stored in the collection will be indexed and adding the argument with “{unqiue: true}” implements the unique constraint.
How UNIQUE Constraint works in MongoDB?
The Unique Index allows the insertion and storing of the values in a document into a collection IF there is no other document in the same collection with the same index key and value. The unique constraint can be implemented on compound indexes. This helps MongoDB to implement uniqueness when combining the index key values. Unique Constraint over separate multiple documents is possible in MongoDB, and it is an essential function in avoiding storing of same values for the indexed key in a different document.
Unique Constraint in MongoDB will allow only a single document with the same value for the indexed key. If we attempt to insert the same value for a single indexed key, it will result in an error.
Query #1
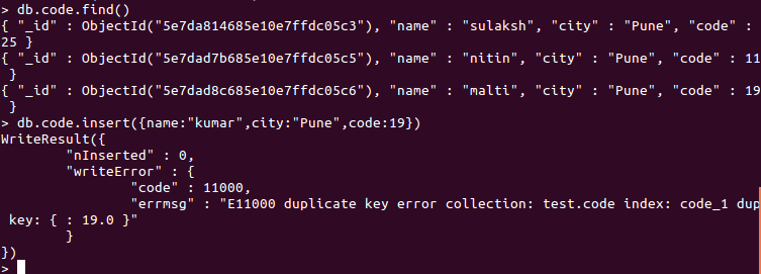
db.code.find()
This returns every document in the collection.
Query #2
db.code.insert( { name:”kumar”, city:“Pune”, code:19 } )
This is an attempt to insert a record with the same code.
Code:
db.code.find()
Output:
Explanation: Here, we have implemented the unique index for “code” key, and so when we try to store a document with existing code, it results in “duplicate key error”.
Unique Constraint for Null Value
When we store any document, we store values for the respective keys, and it is stored as per indexing. But in case, if we attempt to store a document that has no specific value or data for a key, for any uncertain key, the document will be stored, and the empty value will be stored as a null value in that document. In MongoDB, only on the document is allowed to be stored with a single index field missing.
Examples to Implement UNIQUE Constraint in MongoDB
Implementing Unique Contraint on separate documents to not store the same value for the indexes key, in two different documents.
Example #1
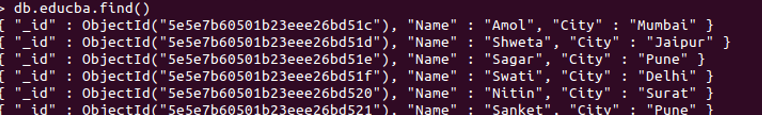
We will attempt to insert and store documents with duplicate values. We have a collection named educba, which we will check with find method: db.educba.find()
Code:
db.educba.find()
Output:
As you can see in the above image, we have a collection named educba, and the document has one default unique “_id” and two more keys. We will now implement the unique constraint on the “Name”, which will make it unique, duplicate insertion proof.
Code:
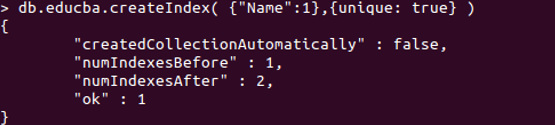
db.educba.createIndex( { “Name” : 1 } , { unique : true } )
Output:
Using >db.educba.createIndex( { “Name”:1 ,{ unique: true} ) we have implemented the unique constraint of the Name key. In return message we have “ok” and other details. Now let us attempt to insert a single new document and then reinsert it with the same value. Refer to the below screenshot for the proper output.
Code:
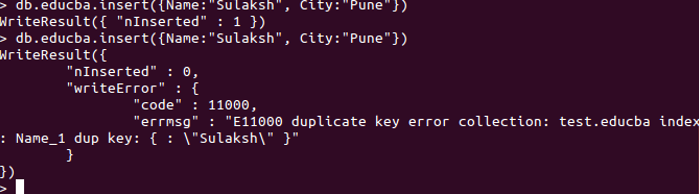
db.educba.insert({ Name : "Sulaksh" , City : "Pune" })
Output:
First Query:db.educba.insert({ Name : "Sulaksh" , City : "Pune" })
The above query will be successfully inserted. Then we attempted to insert the same query, i.e. same document with the same values, but it resulted in an error that states, “terms”: “E11000 duplicate key error collection: test.educba index: Name_1 dup key: { : \”Sulaksh\” }””. This makes our unique constraint applied over the Name field successfully.
Example #2
We will now implement the unique value constraint on Key, which holds Email Values. We will update our documents to add another field with emails. We will then add another index on the field of emails, in order not to store the same email id for multiple documents.
Code:
db.educba.createIndex( {email : 1},{unique : true} )
Output:
We will not attempt to insert a document with a different name but an email id that already exists in another document. Expectations are that the insertion operation will not work and through us an error of duplicate value. We have another document with a slightly different name: Sanket1, for the test purpose, and now we will attempt to update the document with an email: [email protected].
Code:
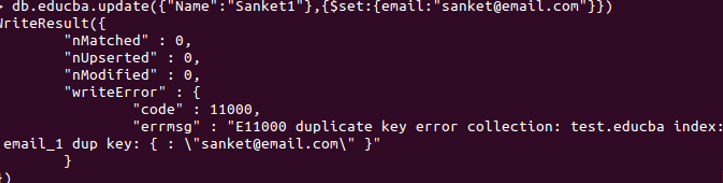
db.educba.update( { “Name” : ”Sanket1” } , { $set : {email : “[email protected]” }})
Above query will aim to search a record with Name: Sanket1 and will update the record with adding an email id to the document, here $set will add a field for the document.
Output:
As you can see in the above screenshot, when we attempted to update a record with the different Name field, the email was the same as one existing document. It threw us a write error, which means an error occurred while writing the document. The error states “duplicate key error collection: test. educba index: email_1 dup key”. The error points to the issue and makes things clear for us to understand. Like in our case, the email with the value of “[email protected]” is duplicated, already stored, so it will not store again due to unique indexing on the email field. In case you want to know, I’ve used the update with $get to add another field for existing records.
Use Case for this example: Is the New User Registration where we have to ensure that a single mail id is not used to create multiple accounts.
Conclusion
Implementing Unique Constraint will restrict the database from storing duplicate values for the same indexed key to wrap it up. This feature helps in storing documents with uniqueness. We learned and understood the syntax followed by the working of it. Then we implemented the unique constraint with example and understood the same along with screenshots, respectively.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to MongoDB Unique. Here we discuss an introduction, how does Unique works and examples for better understanding. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –