Updated March 27, 2023
Introduction to MongoDB Collection
We have a table in the relational database management system. In MongoDB, we have a collection to store N number of records that are documented. Collection stores N number of documents. MongoDB accepts unstructured data. Document stores data which is not in structure format because MongoDB is a schema-less database. We don’t need to define column and datatype while creating a collection. Collection name starts with name or namespace, and it can have any numbers. The collection name should not exceed 128 characters. By using (.), the collection gets organized into groups. We can create any number of collections in the database. We should first create a database to store the collection value.
How does Collection Methods work in MongoDB?
1. We first need a MongoDB database to create a collection.
USE<"database name">
2. Mention Collection name and insert a record into it.
collection_name.create(<document>)
3. Collection Gets Created.
4. We can view any number of collections with command.
show collections
Syntax
1. To create a collection
db.collection_name(field:value)
2. To delete collection
collection_name.drop()
Examples to Implement MongoDB Collection
Below are the examples of implementing MongoDB Collection:
A) Create a Collection
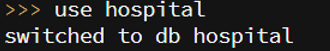
1. We have created a database named hospital.
Code:
use hospital
Output:
2. We have created a collection named the patient.
Code:
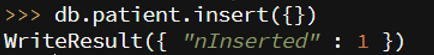
db.patient.insert({})
Output:
- If we don’t enter any value inside (), then an error will appear. Error: no object passed to insert!
3. We have inserted a record for the patient with field: value pair.
Code:
db.patient.insert({name:'akash',age:23,reason:'fever'})
- Be careful while creating record because if we don’t use ( ‘ ‘) for the string, then an error will appear.
- “nInserted”:1 means record inserted successfully.
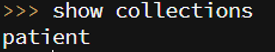
4. To show the list of collections.
Code:
show collections
Output:
5. We have inserted multiple records into the patient collection.
Code:
db.patient.insert({name:'megha',age:24,reason:'fever'},{name:'rohit',age:25,reason:'cuff'})
Output:
6. We have inserted the record into the patient history.
Code:
db.patienthistory.insert({name:'rupali',age:34,experience:12})
Output:
B) Delete Collection (drop the collection)
We can delete the collection from the database. Select the database from which you want to delete the collection.
- USE <database name>
- Verify if the collection is present or not with <show collections>.
- Apply drop command with a collection.
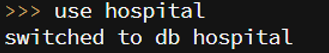
1. We have used the hospital database.
Code:
use hospital
Output:
Code:
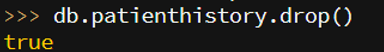
db.patienthistory.drop()
Output:
- We get the true message which means collection deleted successfully.
- If the false message is displayed, then the collection is not deleted yet.
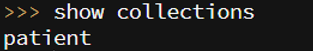
2. We have checked the collection list. We can observe that patient history is not present.
Code:
show collections
Output:
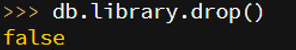
3. If we try to delete the non-existing collection, then the false message is displayed.
Code:
db.library.drop()
Output:
1. Find ()
1. This command will display data from collection means documents/records inserted into the collection.
Syntax:
db.collection_name.find()
Code:
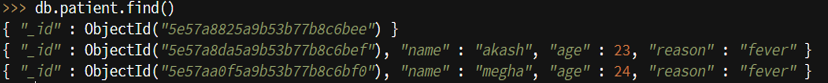
db.patient.find()
- _id – it is defined for each document by default if we do not mention it while creating a document.
- We have inserted name, age and reason for each patient.
- We can observe that no data is present in the first record because we have created a document without field: value pair.
Output:
2. We have created a document with a collection with no record.
Syntax:
collection_name.insert({})
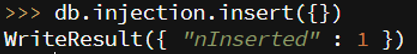
Code:
db.injection.insert({})
Output:
2. Filtering collection
If we have a huge dataset and want to find a particular value or fetch certain records, then find () will help us.
Syntax:
db.collection_name.find({field:value})
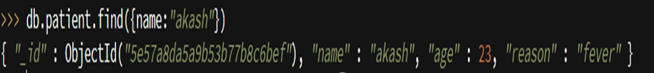
Code:
db.patient.find({name:"akash"})
Output: It has fetched all the details of Akash from the patient collection.
3. Formatting the result
We can observe in the above image, and filtering has displayed the result in one single line. The above-displayed document has less field: value pair, so it is easy to read, but if the document contains the huge number of the field: value pair, then it isn’t easy to read. We can format the result that is fetched document will be displayed in vertical format.
Syntax:
db.collection_name.find({field:value}).pretty()
Code:
db.patient.find({name:"akash"}).pretty()
Output:
4. OR condition
This command will fetch a record from two or more conditions. Suppose we have mentioned two conditions then if one condition is not satisfied, then the second condition will check and the result gets displayed.
Syntax:
db.collection_name.({$or:[{field:value},{field:{$lt:value}}]})
Code:
db.patient.find({ $or:[{reason:"cuff"},{age:{$lt:23}}]})
Output:
$lt means age is less than 23. From the above image, we can understand that there are two conditions. One reason is cough and age is less than 23. This command has checked for the reason as a cuff, but it did not find age less than 23. So only one condition is matched, and the result is displayed.
- In the result section, we can see reason as the cough is displayed even if age is not less than 23.
- We have fetched results with the pretty() command, now it is easy to understand for us while reading it.
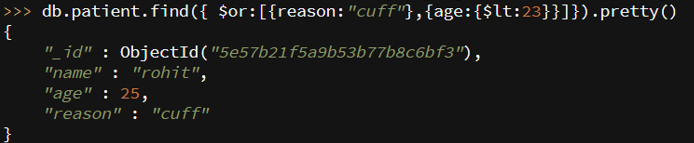
Code:
db.patient.find({ $or:[{reason:"cuff"},{age:{$lt:23}}]}).pretty()
Output:
5. AND condition
1. One or more conditions should be matched.
Syntax:
db.collection_name.find({field:value,field:{value}})
Code:
db.patient.find({reason:"cuff",age:{$lt:23}})
Output:
2. We can observe in the above image no result is displayed because one condition is false. The first condition is a cough, and the second condition is age less than 23. In the above example, the second condition failed, and we get no result.
We are going to change the command. We will change the age of <40.
Code:
db.patient.find({reason:"cuff",age:{$lt:40}})
Output:
We can observe in the above image, and the result is displayed because reason as cuff and age <40 conditions are matched.
6. findOne()
It will display the first record by default.
Syntax:
collection_name.findOne()
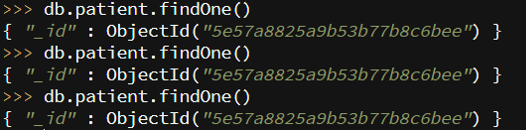
Code:
db.patient.findOne()
Output: The result shows _id only because we have not inserted any field: value while creating a document.
Output: If we run this command N number of times, the same result will appear.
7. _id
If we do not assign any value to an id, then the system generates id automatically. If we assign value to id while creating the record, then id will be displayed when we fetch the result.
Syntax:
db.collection_name.insert({_id:1,field:value,field:value,…})
Code:
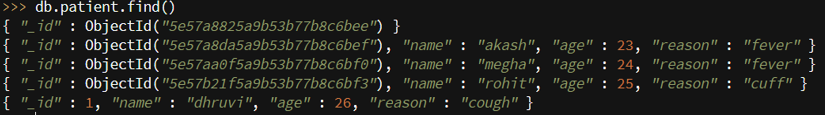
db.patient.insert({_id:1,name:"dhruvi",age:26,reason:"cough"})
Output:
Code:
db.patient.find()
Output:
Conclusion
We have learned about the collection, database, and document in MongoDB. Syntax of collection, database, and document. To create a database “USE” command should be used when we create a collection inside the database, and the document gets created inside the collection. We can perform addition, deletion, and updating of documents inside the collection. Information about the database is presented in certain collections, and it is grouped in system namespace as (dbname.system.*).
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to MongoDB Collection. Here we discuss basic concept, methods, and examples of MongoDB collections with proper codes and outputs. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –