Updated February 27, 2023
Introduction to MongoDB Features
MongoDB, being one of the most widely used NoSQL databases, provides a wide range of features and functionalities. These features are the reason why MongoDB is easy to use and adapted by major companies. We will learn about these features, with proper explanation and syntax, and example queries wherever required. MongoDB is a Document-based, Cross-Platform Database Program. It implements JSON like documents. Latest Stable version is, 4.2.5, released on 26th March 2020.
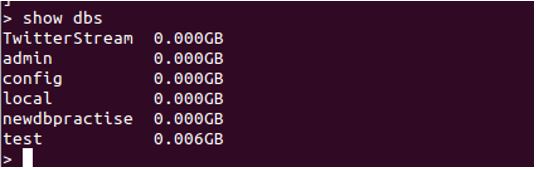
Below is a simple query returning the list of collections in the Database.
Code:
show dbs
show DBS will list every collection or table present in the DB.
Data is stored in the form of JSON Document in MongoDB’s Collection. Every collection has documented, and every document has multiple key-value pairs. The key “_id” is involuntary set default primary key and initially indexed.
MongoDB Features
Let us now define and understand each feature :
1. Ad Hoc Queries Support
Basically, when we are in the Database Design phase, we have no idea of what queries might be executed. So, when we say, MongoDB supports Ad Hoc Queries, it means that the MongoDB supports queries that were not known while establishing a structure for the database. This is an amazing feature that makes MongoDB stand out. Ad hoc queries function in a way to better the performance and are real-time.
2. Indexing
One of the most important features for a Database is Indexing, which results in improvements. We can index any field in MongoDB. Creating indexes helps in faster search results. Indexing is possible with any field or key, in a document.
Code:
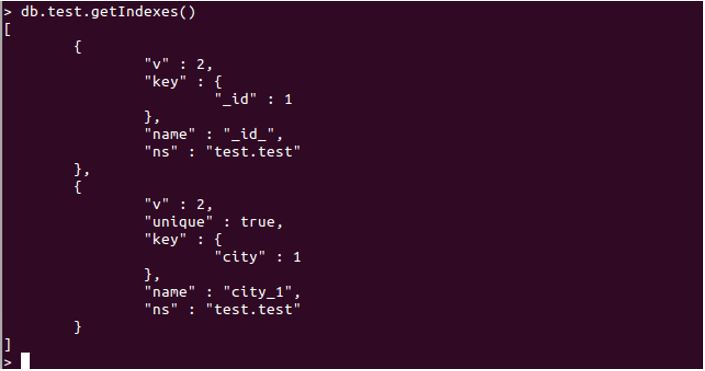
db.test.getIndexes()
The above query will return every index that has been created for the “test” collection. Refer to the below-attached screenshot.
Output:
In the above sample, we see two indexes. The first one is created on “_id” which is default and created automatically. At the same time, the second one is with the “city” key.
3. Replication
Simply speaking, replication is a process of, distributing the data on multiple servers and keeping everything synchronized. Primary Node and Secondary Nodes are introduced here.
Working: Whenever a primary node, with the data, is down or experiences failure, the secondary node will be the working primary node, making it possible for the data to be available.
This feature is important regarding Data Storage and Backup, as it allows us to recover and restore, in case of failure in hardware or services. Thanks to this replication, that data is made available with multiple copies on different locations. Time is saved, and no operation is halted due to this amazing feature.
4. Schema-less Database
One of the most primarily discussed features of MongoDB is, it being Schemaless. Meaning that there can be multiple documents in a collection, with different keys, and these keys might not be found in other documents. This is the major reason behind MongoDB’s flexibility, with data.
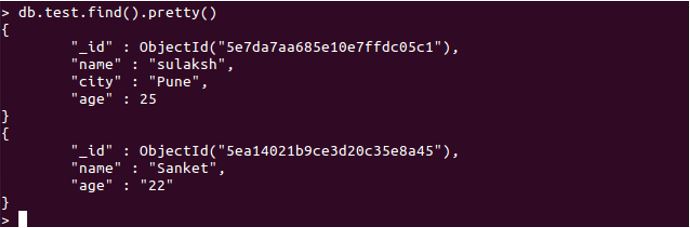
We can have multiple documents or records in a single, same collection, but with different key values pairs. Check the below-attached screenshot for reference.
Code:
db.test.find().pretty()
Output:
In the above example, you can see we have two documents. Both documents have slightly different keys. In the second record, we don’t have the city key, and yet it does not affect. This is made possible with a schema-less feature.
5. Document Oriented
Being Document Oriented is a great feature that helps MongoDB stand out among others. We have tables and rows columns structure for SQL, we have fields in key values pair, with MongoDB.
Code:
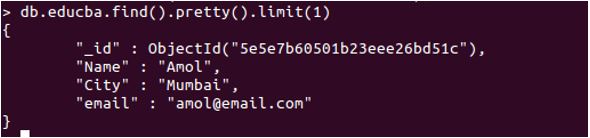
db.educba.find().pretty().limit(1)
Output:
In the above Document, we have four key values, where _id is default and set automatically—this the basic structure of a document-based database.
6. Aggregation Pipeline
Aggregation Framework is one of the most efficient features offered by MongoDB. Simply speaking it is a process of creating a pipeline of multiple operations and getting a final result, filtered.
Code:
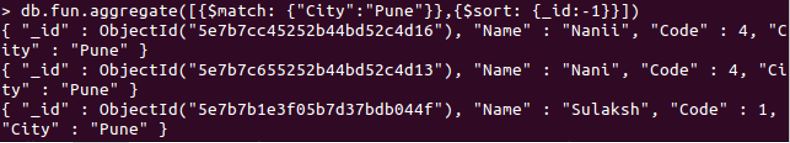
db.fun.aggregate([{$match: {"City":"Pune"}},{$sort: {_id:-1}}])
The above query will return documents that have Pune as their City, and it will print the sorted result. Refer the below-attached screenshot.
Output:
Aggregation pipelines can be created as per needs. The end result must be thought carefully while building the pipeline.
7. GridFS
When a file exceeds the BSON document limit of 16 MB, it is divided into multiple small chunks and stored separately in various documents. These chunks have a size of 255KB, excluding the last chunk. GridFS, which stands for Grid File System, use two separate collections. One collection is used to store the larger file’s chunks, while the second collection is used to store the metadata. When we execute a query for this file, the GridFS will collect and return all the chunks together. GridFS also implements the Indexing, which allows the query execution for returning the file easier.
8. Sharding
When we are encountered with large datasets, we can implement the Sharding of Data. Meaning, the large datasets are split and shared across multiple machines. The massive data can cause unexpected problems, but the implementation of sharding can be useful. Sharding is the process of database partitioning and spreading across multiple machines, while the replication is the process of making multiple copies of the database. The data is distributed over multiple collections, and these collections are known as “Shards”.
9. High Performance
MongoDB is open-source, is one the highest performing database. With the implementation of replication and indexing, query execution and data fetching are faster. With developing multiple applications, the need to check the performance is mandatory. Database Profiling, which collects the complete data for every operation that is executed against the MongoDB instance. The output provided by the DB Profiler can help us understand the queries and operations that are being inefficient.
Conclusion
Document oriented and schema-less structure makes the MongoDB one of the preferable choice. Many other features like Aggregation pipeline, Sharding, Replication, etc. help the database query results faster with better performance. Load Balancing is done with these features results in better performance. All these features make the MongoDB one of the better choice for Big Data Application and Real-Time Applications.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to MongoDB Features. Here we discuss an introduction to MongoDB Features, top 10 features with explanation in detail. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –