Updated February 28, 2023
Introduction to MongoDB Geospatial
MongoDB, which is a NoSQL Database, allows storing of Geospatial Data in the form of multiple GeoJSON types. Geospatial Feature of MongoDB makes it easy to store Geographical data into a database. So, basically, you can store the geospatial type data in the MongoDB in the form of GeoJSON objects. The GeoJSON is a simple representation of geographical features, also supporting non-spatial attributes, respectively. GeoJSON is based on JavaScript Object Notation and is an open standard format.
Syntax
"<field> : { type : <GeoJSON type> , coordinates : <coordinates> }"
Explanation: <field> represents the name of the field, ex. Location: type is the key to which values could be different, ex—”Point” Type, which is commonly used. Finally, coordinates are the key which holds the longitude and latitude or other numeric details of the location. Now, let us understand the simple syntax with an example.
Code:
use geo
db.geo.insert( { "Name": "Geo" } )
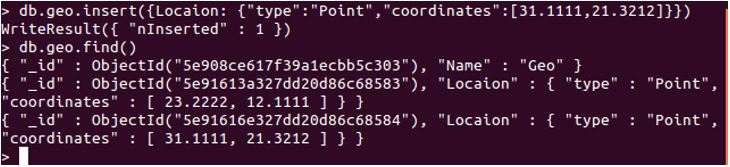
db.geo.insert( { Location : {"type":"Point","coordinates": [ 23.2222, 12.1111 ] } } )
db.geo.insert( { Location : {"type":"Point","coordinates": [ 31.1111, 21.3212 ] } } )
db.geo.find()
Output:
Explanation: Here, we are attempting to insert a single record in geo collection, which is a location and has a GeoJSON type as Point, followed by the coordinates. Check the below screenshot for proper execution:
Now that we have understood what Geospatial in MongoDB is let us look into operators available for Geospatial operations and understand them.
MongoDB Geospatial Operators
Operators in Geospatial for MongoDB can be divided into two parts which are Query Selectors and Geometry Specifiers. We will now understand each of there types, along with queries and examples. The Geometry Specifiers are used with the Query selectors so that we will learn these together. When we attempt any query selector, we have to specify a geometry specifier.
MongoDB Geospatial Query Selectors
MongoDB provides four query selectors. These are operators used when we need to search or specify some data. For example, $near operator is used to return geo objects around the point. Following are the found query selectors:
$geoIntersects
Using the $geometry operator, geoIntersects operator specifies the GeoJSON Object. The 2dsphere and 2d indexes support these geoIntersect queries. With the following example, we will implement a simple $geoIntersect operator:
Code:
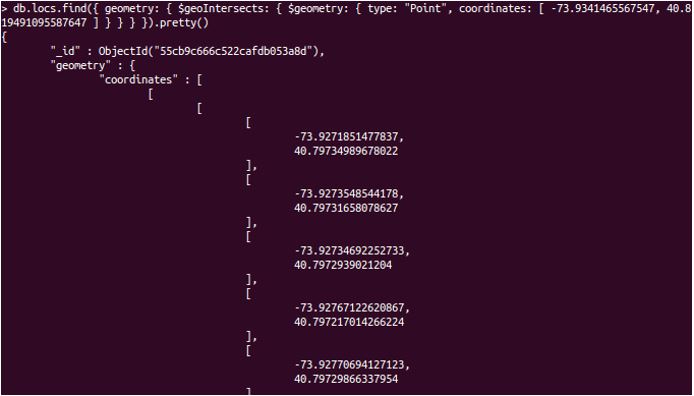
db.locs.find({ geometry: { $geoIntersects: { $geometry: { type: "Point", coordinates: [ -73.9341465567547, 40.819491095587647 ] } } } })
Output:
Explanation: we have our locs collection with 195 documents. We have specified the coordinates and will attempt to find the neighbourhood of a user. These return values might not make sense on the terminal, but it provides useful data when passed as raw data to a graphical representation.
Geometry Specifier For the use of Geospatial
Geometry Specifier used here is $geometry For the use of Geospatial Query Operators like $geoWithin, $geoIntersects, $near, and $nearSphere, $geometry is used. “EPSG:4326” is used as default CRS – coordinate reference system.
$geoWithin
This query selects the geometers which are bounded within the GeoJSON geometry. The 2dsphere and 2d indexes support $ geoWithin.
Code:
{
<location field>: { $geoWithin: {
$geometry: { type: <"Polygon" or "MultiPolygon"> , coordinates: [ <coordinates> ] } } }
}
Let us now understand $geoWithin with a proper example:
Code:
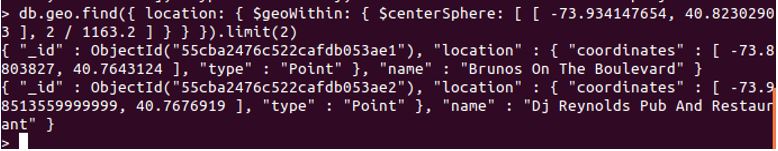
db.geo.find({ location: { $geoWithin: { $centerSphere: [ [ -73.934147654, 40.82302903 ], 2 / 1163.2 ] } } }).limit(2)
Output:
Explanation: We will attempt to find documents, using $geoWithin, which will return documents between the coordinates mentioned respectively. Refer the screenshot.
$near
This is also supported by both indexes and is used to return the geospatial object near a specific point. This returns a stored document by nearest to farthest from a point.
Code:
{
<location field>: { $near: {
$geometry: { type: "Point" , coordinates: [ <longitude> , <latitude> ] },
$maxDistance: <distance in meters>, $minDistance: <distance in meters> } }
}
We will now implement $near with an example and see its working.
Code:
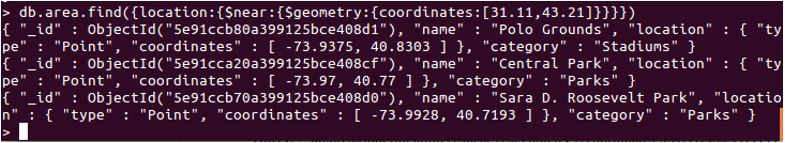
db.area.find({location :{$near :{$geometry :{coordinates :[31.11,43.21]}}}})
Output:
Explanation: This query will return several documents with coordinates nearby the mentioned ones.
$nearSphere
This query returns the documents from a collection, which lies nearest to farthest. MongoDB uses spherical geometry to calculate the distance. Geospatial index is required with $nearSphere.
Code:
{
$nearSphere: { $geometry: { type : "Point", coordinates : [ <longitude>, <latitude> ]
},
$minDistance: <distance in meters>, $maxDistance: <distance in meters> }
}
Code:
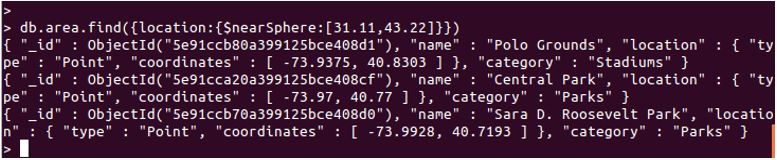
db.area.find({location :{$nearSphere :[31.11,43.22]}})
Output:
Explanation: This query will return several documents which match with the coordinates provided. Refer the below-attached screenshot for proper output. Let us now understand the geometry specifiers. We have already learned $geometry, remaining will be $center, $maxDistance, $minDistance, $polygon and $box.
$center
for $geoWithin query, $center specifies a circle. This operator DOES NOT return an object of GeoJSON.
Code:
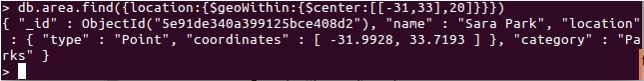
db.area.find({location:{$geoWithin:{$center:[[-31,33],20]}}})
Output:
Explanation: Here, we have used the $center query with $geoWithin. Refer the screenshot.
$minDistance
Below we have a simple example of $minDistance.
Code:
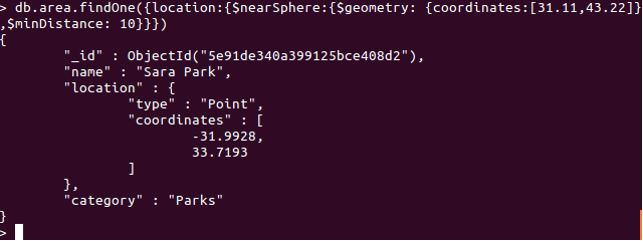
db.area.findOne({location :{$nearSphere :{$geometry : {coordinates :[31.11,43.22]},$minDistance: 10}}})
Output:
$polygon
Used with $geoWithin, returns documents which fall between the bound of a polygon. Does NOT query GeoJSON. Without a geospatial index, $polygon can be used, but queries can be executed faster with geospatial index rather than unindexed. Supported only with 2d geospatial index.
$box
which attempts to specify a rectangle for $geoWithin, and when used in a query, it finds the documents with coordinates falling between the rectangle. $box is supported only with 2d geospatial index. Using Flat Geometry, this query calculates the distance.
Conclusion
MongoDB Geospatial is used to store geographical data, like location coordinates. Multiple types of GeoJSON are supported. There are two types of queries, which are Query Selectors and Geometry Specifiers. MongoDB supports 7 types of GeoJSON Objects, Point being the most common one. We learned and understood each operator along with example and code, respectively.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to MongoDB Geospatial. Here we discuss an introduction to MongoDB Geospatial, appropriate syntax, operators, and examples. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –