Updated February 28, 2023
Introduction to MongoDB Limit()
The limit() function for MongoDB is used to limit the number of documents that are fetched with the find function. This Limit function only takes a single argument which is a simple numeric value.MongoDB is a NoSQL Database, and it is the first choice, provides a range of functions to handle the data. Instead of Databases, we have Collections in MongoDB and Documents instead of Tables. Find is a simple query to return every document in the collection, similar to select query from SQL. The limit is such one function used to limit the number of documents that are reflected upon executing find query.When we fetch documents from the MongoDB collection, we use the find function, and it fetches every document present in the collection. Now, the requirement could be of a limited number of documents instead of a whole bunch. And that can be achieved using the limit function, where the number of returned documents can be limited to a specific needs.
Syntax:
db.collection_name.find().limit(int);
The above syntax starts with the keyword, db, followed by the collection name with the documents stored in. The find() function is just the same as a select query in SQL, which returns the MongoDB documents. When we add limit function, the output will be limited to the number passed as an argument.
How Limit() Function works in MongoDB?
- Basically, every time a query is executed on MongoDB, the server returns the results in batches. There is a limit to the amount of the data that must be fetched and must not exceed the maximum BSON document size. MongoDB’s limit function has the ability to restrict the number of records or documents that have been fetched.
- Find function is used to return every document present in the collection, which is time-consuming and returns a lot of unnecessary data. When the limit function is used along with find, it will limit the documents that are to be returned.
- We can pass multiple types of integer values as a parameter for limit function, be it a positive number, a negative one, or a zero or simple a null, nothing value. The returning result will be based on the parameter passed.
- When we pass a positive value, the cursor is left open. It can receive further query results, which will result in the cursor being continuously iterated and will only end itself when it is completely exhausted.
- The limit function comes with advantages like it saves query time while performance can be maximized. Other than that, it also averts the MongoDB by not fetching documents that are not required. When we use limit, we notify the server that we need a single record and must bot look for more than that. Implementation of the limit will enhance the process. So, simply speaking, it will stop the process once it reaches the limit.
Examples of MongoDB Limit()
Given below are the examples:
Example #1 – Find Function
Simple find function, upon executing the find with db.collection_name.find() syntax, it will return every document present in the collection.
Code:
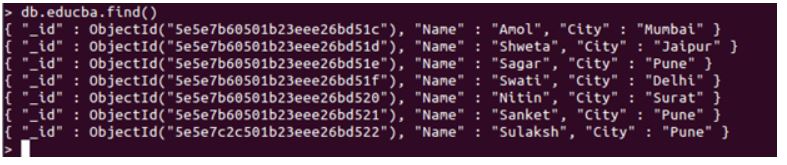
db.educba.find()
Output:
Referring to the above image, we have simply executed a find query which returns every record present in the collection, which in the long run can be an issue for performance and is responsible for fetching data which might not be needed. When we have a requirement, we are free to limit these results for better performance, and that’s where the limit function of MongoDB jumps in.
Example #2 – Limit Function
Now, let’s limit these results, using the limit function. Notice that along with find function; we have added a limit function by the end.
Code:
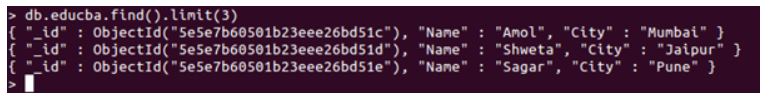
db.collection_name.find().limit(int)
db.collection_name.find().limit(3)
Output:
Now, as you can see, using the limit function at the end of normal find query, the results returning are being limited. We have passed an integer value as a parameter, which is 3 and that restricts our results to be 3.
Example #3 – Zero Value
Here, we have seen that whatever integer value we pass as parameter with limit, that number of records are fetched, but what when we pass nothing or NULL or a zero.
Code:
db.collection_name.find().limit(0)
db.collection_name.find().limit()
Output:
Referring to the above image, we have passed both, zero and a null value as a parameter with limit function. Clearly, there is no difference between passing a zero or a null, empty value in a limit.
Example #4 – Negative Values
Now, that we have demonstrated how a limit function handles various integer values, let us see how it works with negative integer value as a parameter.
When a negative value is passed in as a parameter for limit function, the query will fetch the records, the database here will return the number of records while ending the cursor. So basically, when we pass a negative value, results are fetched all as a single batch. And there are no further operations or results fetched for the same query; it ends with a single batch.
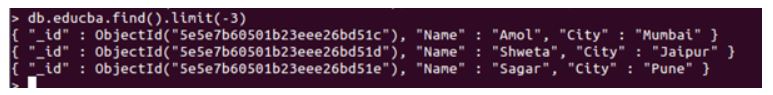
Code:
db.collection_name.find().limit(-3)
Output:
As you can see, we have passed a negative value as a parameter, and the results are just as positive. But, the major advantages here is, the cursor will end itself. Earlier, we have understood the results in MongoDB are fetched in batches, and in the same way, the cursor will be terminated in case of a negative value.
Other than on shell, MongoDB Limit function is used to perform pagination on various applications. It works best when we need to display a limited number of items on a single page, and limiting makes it easy. Various programming languages supports MongoDB limit and many other functions. MongoDB API is available for better usage and easy access.
Conclusion
MongoDB provides a wide range of functions to play with the Document based data in Collections. The limit is one of the most used functions, allowing the user to make sure that the results are limited as per requirement and enhance performance. MongoDB functions can be used with almost every programming language and perform various operations using MongoDB API for the respective language.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to MongoDB Limit(). Here we discuss the introduction, how to limit() function works in MongoDB? and examples. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –