Updated June 30, 2023
Introduction to Lock in C#
The lock construct in C# ensures that no other thread can enter the section of code where a thread is already executing. It makes the other thread attempting to enter the code section wait or block until the executing thread completes its execution. Using a lock is a faster and more convenient way to handle threads in multithreading programming.
Syntax
lock(object_name) statement_blockWhere,
- The object_name represents the name of the object on which the lock must be acquired.
- The statement_block refers to the block of code that will be executed once the lock is successfully acquired on a particular thread.
How does Lock work in C#?
- Whenever there is a need for the thread to execute in a section of code without the interruption of any other thread, we make use of a lock to make sure only one thread can access that section of code at a time.
- When a thread acquires a lock in a specific section of code, it causes any other threads attempting to access that section of code to wait or be blocked.
- Using a lock is a faster and more convenient way to handle the threads in multithreading programming.
Examples to Implement Lock in C#
Find the examples below.
Example #1
C# program to demonstrate the lock to block the execution of another thread while a thread is already executing in the critical section of the code:
Code:
using System;
using System.Threading;
//a namespace called program is defined
namespace program
{
//a class called check is defined
class check
{
//an object that defines a lock is created
static readonly object lockname = new object();
//a method called display is created in which the lock is used to make any other threads trying to access the method wait or block until thread that is already executing completes its execution
static void display()
{
//keyword lock is used to lock the object
lock (lockname)
{
for (int a = 1; a <= 3; a++)
{
//the output is displayed synchronously in a row by one thread followed by another thread because we have used lock on display method
Console.WriteLine("The value to be printed is: {0}", a);
}
}
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//an instance of the thread is created and the corresponding thread is executed on the display method
Thread firstthread = new Thread(display);
//an instance of the thread is created and the corresponding thread is executed on the display method
Thread secondthread = new Thread(display);
firstthread.Start();
secondthread.Start();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
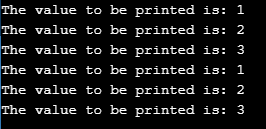
}Output:
Explanation: In the above program, the program defines a namespace called “program”. It then defines a class named “check.” This method utilizes the lock to make any other threads attempting to access it wait or block until the currently executing thread finishes its execution. The snapshot above displays the output.
Example #2
C# program to demonstrate the lock to block the execution of another thread while a thread is already executing in the critical section of the code:
Code:
using System;
using System.Threading;
//a namespace called program is defined
namespace program
{
//a class called check is defined
class check
{
//an object that defines a lock is created
static readonly object lockname = new object();
//a method called display is created in which the lock is used to make any other threads trying to access the method wait or block until thread that is already executing completes its execution
static void display()
{
//keyword lock is used to lock the object
lock (lockname)
{
for (int a = 1; a <= 3; a++)
{
//the output is displayed synchronously in a row by one thread followed by another thread because we have used lock on display method
Console.WriteLine("The first three lines are printed by first thread and the second three lines are printed by the second thread");
}
}
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//an instance of the thread is created and the corresponding thread is executed on the display method
Thread firstthread = new Thread(display);
//an instance of the thread is created and the corresponding thread is executed on the display method
Thread secondthread = new Thread(display);
firstthread.Start();
secondthread.Start();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}Output:
Explanation: The program defines a namespace called “program” and then defines a class called “check.” It creates an object that represents a lock. It uses the keyword “lock” to lock the previously created object.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we understand the concept of lock-in C# through definition, syntax, and working of the lock through programming examples and their outputs.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Lock in C#. Here we discuss an introduction to Lock in C#, syntax, and how it works with examples to understand better. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –