Updated March 21, 2023
Differences Between Kafka vs Spark
Kafka vs Spark is the comparison of two popular technologies that are related to big data processing are known for fast and real-time or streaming data processing capabilities. Kafka is an open-source tool that generally works with the publish-subscribe model and is used as intermediate for the streaming data pipeline. Spark is a known framework in the big data domain that is well known for high volume and fast unstructured data analysis. The basic storage components in Kafka is known as the topic for producer and consumer events. whereas Spark used Resilient distributed dataset structure (RDD) and Data frames for processing the data sets.
Kafka
Kafka is an open-source stream processing platform developed by the Apache. It is a mediator between source and destination for a real-time streaming process where we can persist the data for a specific time period. Kafka is a distributed messaging system. Where we can use that persisted data for the real-time process. It runs as a service on one or more servers. The Kafka stores stream of records in categories called topics. Each stream record consists of key, value, and timestamp.
To Start Kafka Server
>bin/Kafka-server-start.sh config/server.properties
Following are the main component of Kafka
Source: This will trigger when a new CDC (Change Data Capture) or new insert occurs at the source. For that, we have to define a key column to identify the change.
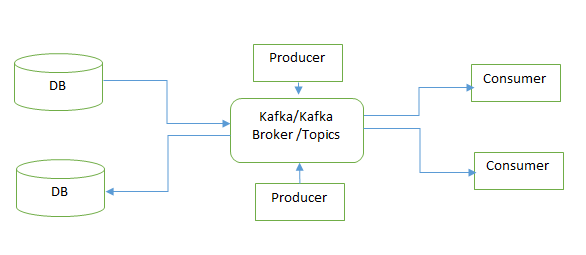
Broker: Which is responsible for holding data. Each Broker holds no of partition.
Topic: It categorizes the data. Topics in Kafka are always subscribed by multiple consumers that subscribe to the data written to it.
To Create a Topic
> bin/kafka-topics.sh --create --zookeeper localhost:2181 --replication-factor 1 --partitions 1 --topic test
And to see the topic list
> bin/kafka-topics.sh --list --zookeeper localhost:2181
Partition: Topics are further splited into partition for parallel processing.
Producer: Producer is responsible for publishing the data. It will push the data to the topics of their choice. The producer will choose which record to assign to which partition within the topic.
Kafka has commanded to produce a message to a topic.
> bin/Kafka-console-producer.sh --broker-list localhost:9092 --topic test
Hi Good Morning.
This is a test message.
Consumer: Consumers will consume data from topics. A consumer will be a label with their consumer group. If the same topic has multiple consumers from different consumer group then each copy has been sent to each group of consumers.
You can sink with multiple sources to persist the data. Kafka has commanded to consume messages to a topic.
> bin/Kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic test --from-beginning
Hi Good Morning.
This is a test message.
Flume: We can use flume Kafka Sink. In which, As soon as any CDC (Change Data Capture) or New insert flume will trigger the record and push the data to Kafka topic. For that, we have to set the channel.
Same as flume Kafka Sink we can have HDFS, JDBC source, and sink.
Kafka has better throughput and has features like built-in partitioning, replication, and fault-tolerance which makes it the best solution for huge scale message or stream processing applications
Spark
Apache Spark is an open-source cluster-computing framework. Originally developed at the University of California, Berkeley’s Amp Lab, the Spark codebase was later donated to the Apache Software Foundation. Spark provides an interface for programming entire clusters with implicit data parallelism and fault tolerance.
When Hadoop was introduced, Map-Reduce was the base execution engine for any Job task. In the Map-Reduce execution (Read – Write) process happened on an actual hard drive. This is the reason for the more time and space consumption at the time of execution.
Apache Spark is an open-source platform. Improves execution quality than the Map-Reduce process. It’s an open platform where you can use several program languages like Java, Python, Scala, R. Spark provides in-memory execution that is 100X faster than MapReduce. This uses the RDD definition. RDD is a robust distributed data set that allows you to store data on memory in a transparent manner and to retain it on disk only as required. This is where the time to access data from memory instead of the disk is through.
Spark is the platform where we can hold the data in Data Frame and process it. Application developer, Data Scientist, Data Analyst can use the Spark to process the huge amount of data within a minimum period of time. We can use a feature like interactive, iterative, analysis of data in Spark.
Spark streaming is one more feature where we can process the data in real-time. The banking domain need to track the real-time transaction to offer the best deal to the customer, tracking suspicious transactions. Spark streaming is most popular in younger Hadoop generation. Spark is a lightweight API easy to develop which will help a developer to rapidly work on streaming projects. Spark streaming will easily recover lost data and will be able to deliver exactly once the architecture is in place. And without any extra coding efforts We can work on real-time spark streaming and historical batch data at the same time (Lambda Architecture).
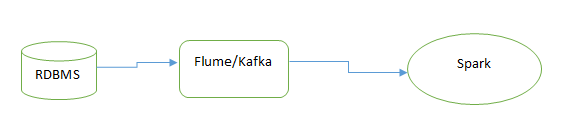
In Spark streaming, we can use multiple tools like a flume, Kafka, RDBMS as source or sink.
Or we can directly stream from RDBMS to Spark.
We can run a spark on top of HDFS or without HDFS. That’s why everybody talks about its replacement of Hadoop. HDFS is a base file system for Hadoop. We can use HDFS as a source or target destination.
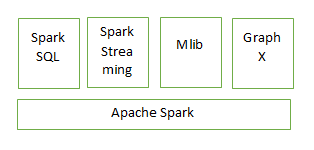
Using Spark SQL use basic SQL queries to process the data. This spark provides better features like Mlib (Machine Learning Library ) for a data scientist to predictions.
Head to Head comparison between Kafka and Spark (Infographics)
Below is the top 5 comparison between Kafka and Spark:
Key Difference Between Kafka and Spark
Let us discuss some of the major difference between Kafka and Spark:
- Kafka is a Message broker. Spark is the open-source platform.
- Kafka has Producer, Consumer, Topic to work with data. Where Spark provides platform pull the data, hold it, process and push from source to target.
- Kafka provides real-time streaming, window process. Where Spark allows for both real-time stream and batch process.
- In Kafka, we cannot perform a transformation. Where In Spark we perform ETL
- Kafka does not support any programming language to transform the data. Where spark supports multiple programming languages and libraries.
- So Kafka is used for real-time streaming as Channel or mediator between source and target. Where Spark uses for a real-time stream, batch process and ETL also.
Features of Kafka vs Spark
Some key features are listed below.
- Data Flow: Kafka vs Spark provide real-time data streaming from source to target. Kafka just Flow the data to the topic, Spark is procedural data flow.
- Data Processing: We cannot perform any transformation on data wherein Spark we can transform the data.
- Data Persistent: Kafka persists data to some time as defined in the configuration. We have to use a data frame or dataset object to persist the data.
- ETL Transformation: Using Spark we can perform ETL, Where Kafka does not provide ETL.
- Memory Management: Spark uses RDD to store data in a distributed manner (i.e cache, local space) where Kafka store data in Topic i.e in a buffer memory.
Kafka and Spark Comparison Table
Below is the topmost comparison between Kafka and Spark.
| Feature Criteria | Apache Spark | Kafka |
| Speed | 100 times faster than Hadoop | Decent speed |
| Processing | Real-time & Batch processing | Real-time / Window processing only |
| Difficulty | Easy to learn because of high-level modules | Easy to configure |
| Recovery | Allows recovery of partitions using Cache and RDD | Fault-tolerant/Replication |
| Interactivity | Has interactive modes | No Interactive mode/Consume the data |
Conclusion
We can use Kafka as a message broker. It can persist the data for a particular period of time. Using Kafka we can perform real-time window operations. But we can’t perform ETL transformation in Kafka. Using Spark we can persist data in the data object and perform end-to-end ETL transformations.
So it’s the best solution if we use Kafka as a real-time streaming platform for Spark.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the top difference between Kafka vs Spark. Here we have discussed Kafka vs Spark head to head comparison, key difference along with infographics and comparison table. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –