Updated March 23, 2023
Difference Between RabbitMQ vs Kafka
RabbitMQ is a traditional message broker with a variety of message protocols being implemented. To implement the Advance Message Queue Protocol (AMQP), RabbitMQ was initially developed. AMQP standardizes messaging with the help of Producers, brokers, and Consumers. In this topic, we are going to learn about RabbitMQ vs Kafka.
Apache Kafka is a messaging system that allows you to publish and subscribe to streams of messages that are based on topics and partition. In this way, it is similar to products such as ActiveMQ, RabbitMQ. But even with these similarities, Kafka has a range of fundamental differences from traditional messaging systems that make it different completely.
RabbitMQ
It’s a message broker; it accepts and sends messages. It is just similar to post office where mails are received, stored and transmitted to the recipient in the same way RabbitMQ accepts, stores and forwards binary data blobs (messages).
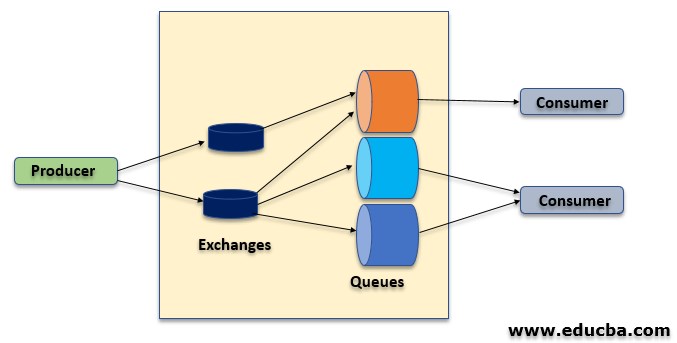
This figure demonstrates basic message consumption with the following components as discussed below
- Producer: The producer sends a message to the queue but never uses queue directly instead it uses exchange. Publishing a message means that the producer sends a message to exchange and exchange forwards the message to the queue.
- Exchange: An exchange is responsible for routing the messages with links and routing keys to various queues. A binding is a relation between an exchange and a queue.
- Queue: It is a buffer that stores messages.
- Consumer: Consuming a message means that the consumer picks up a message from a queue and consumes it.
Kafka
Kafka is a publish-subscribe messaging system. With streaming technologies such as Kafka, you can actually process new data as it is generated in your cluster, you might save it to HDFS, or you can save it to HBase or some other database, so you can actually process it in real-time as it comes in, you can do all that with streaming.
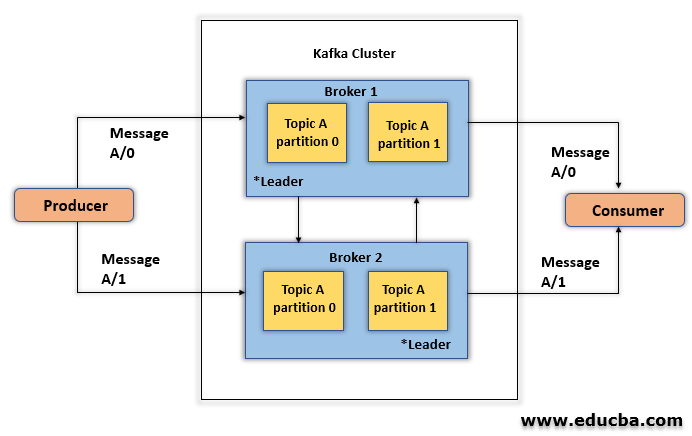
There are few simple terminologies about Kafka that should be understood.
- Producers: Producer publishes the message to a topic.
- Broker: Broker is a cluster made up of one or more servers in Kafka. The broker receives messages from the producer, assigns them to offset and commits the message.
- Topics: Messages are divided into topics. Topics are broken down into a number of partitions where they index and store messages that receive an incremental Id named offset.
- Consumers: Consumers subscribe to various topics and read data from brokers. They read data in consumer groups. The consumer always keeps track of which messages it has consumed by keeping track of the offset of messages.
Head to Head Comparison Between RabbitMQ vs Kafka (Infographics)
Below are the top 8 differences between RabbitMQ vs Kafka
Key Differences of RabbitMQ and Kafka
Here are the Key differences mention below
1. Payload
- RabbitMQ: It may have a large payload, for an instance creating an order may have 45 different attributes.
- Apache Kafka: Payload is very small in Kafka and its key-value pairs are sent across the stream.
2. Data Flow
- RabbitMQ: It has a distinct bounded flow of data, in other words, messages are created, sent, and received by the recipient of the consumer of the message.
- Apache Kafka: It has an unbounded continuous flow of data, in other words, these key-value pairs are continuously streamed to the topic.
3. Throughput
- RabbitMQ: RabbitMQ gives a throughput of up to 4K -10K messages/sec.
- Apache Kafka: With Kafka, one could get a throughput of up to 1 million messages/sec as Kafka leverages sequential disk I / O power and needs less hardware, which results in high throughput with only a small number of nodes.
4. Data Usage
- RabbitMQ: It’s good for transactional data, what I meant by transactional data is user requests, order formation, placement of an order, these are forms of transactional items.
- Apache Kafka: Kafka is really good for operational information, i.e. data are essentially about our process operations, i.e. statistics data for different
kinds of auditing, logging. This kind of data tells about the safety and activities that are going on with the system.
5. Message Retention
- RabbitMQ: RabbitMQ sends the message to the consumer and the message is removed from the queue once it has been processed and the acknowledgment has arrived.
- Apache Kafka: Because Kafka is a log, there are always messages, you can monitor this by setting a retention policy for messages.
E.g. 7 days retention
6. Design
RabbitMQ: It uses a smart broker / dumb consumer model that focuses on consistently delivering messages to consumers that consume at approximately the same pace as the broker keeps track of consumer status.
Apache Kafka: Kafka uses a dumb broker / smart consumer. Kafka does not attempt to monitor the messages each user has read and retain only unread messages; rather, Kafka preserves all messages for a certain amount of time, and consumers are responsible for monitoring their position in each log (consumer state).
7. Topology
- RabbitMQ: It has Exchange queue topology, where the producer sends a message to an exchange that is then routed to different queue bindings that consumers can consume.
- Apache Kafka: Kafka only supports the publish-subscribe type of topology. This is where the producer sends a message across the stream to a topic within Kafka that is then consumed by a different consumer group.
RabbitMQ vs Kafka Comparison Table
Let’s see some more differences between RabbitMQ vs Kafka through a comparison table for clear understanding:
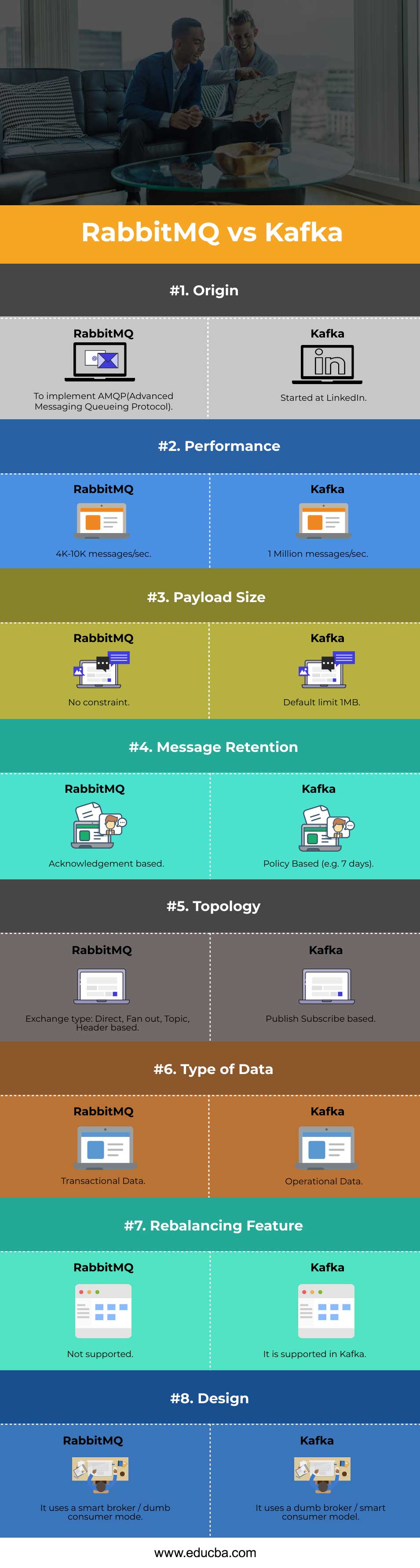
| Comparison Points | RabbitMQ | Kafka |
| Origin | To implement AMQP(Advanced Messaging Queuing Protocol) | Started at LinkedIn |
| Performance | 4K-10K messages/sec | 1 Million messages/sec |
| Payload Size | No constraint | Default limit 1MB |
| Message Retention | Acknowledgment based | Policy-Based (e.g. 7 days) |
| Topology | Exchange type: Direct, Fan out, Topic, Header based | Publish-Subscribe based |
| Type of Data | Transactional Data | Operational Data |
| Rebalancing Feature | Not supported | It is supported in Kafka |
| Design | It uses a smart broker / dumb consumer model | It uses a dumb broker / smart consumer model |
Conclusion
RabbitMQ is ideal for simple use cases, you have certain advantages with low data traffic such as priority queue and flexible routing options.
Also, if you need a commit log or multiple consumers, you can use Kafka for massive data and high throughput because RabbitMQ can’t help you with it.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to RabbitMQ vs Kafka. Here we discuss the RabbitMQ vs Kafka key differences with infographics and comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –