Updated March 17, 2023
Introduction to Kafka Producer Example
The following article provides an outline for Kafka Producer Example. The Kafka producer is defined as the Kafka can get data from the producer, and the producer can only have to describe the topic name and one broker to connect to, and then Kafka will ultimately care to beat the data to the correct brokers; producers can accept the acknowledgment of writing the data and select a key to convey a message. If a key is sent, then the producer has the assurance that all messages for the particular key will go to paired partition every time so that it can take guarantee ordering for a specific key.
Overview of Kafka Producer
The producer in Kafka is an application that can be the origin of the data flow in which it can create tokens or messages and bring them out to one or more topics in the cluster of Kafka; the Producer API, which is from Kafka, can assist to group the messages or tokens and carry them to the Kafka server, functionally the Kafka is very simple than the consumer because it does not require a group for co-ordination and the producer partitioner can plot every message to the topic partition. The producer can dispatch a request to the chief of that partition; the Kafka producer can dispatch the records to the topics. The records are occasionally mentioned in the messages, in which the producer can able to select which partition to convey the record to per topic, the producer can able to convey records round-robin, and the producer can execute systems priority which depends on the conveying of the record to the definite partitions.
The main section of the Kafka producer API is the ‘KafkaProducer’ class which can have the option to attach a Kafka broker in its constructor by using some methods, in which the Kafka producer class can divide the send method for dispatching the message non-simultaneously to the Kafka, the ProducerRecord() method can control the buffer of the records which can be held back for dispatching, and Callback() is another method which can be called as a user-supplied callback method.
Using Kafka Producer Example
Let us see the use of Kafka producer in detail:
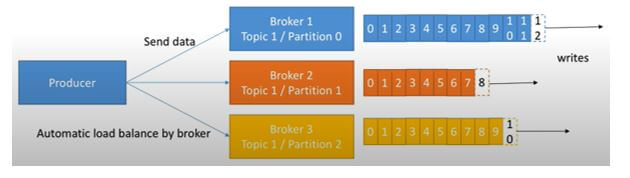
When the producer sends data to Kafka that has been converted into Brokers such as Broker 1, Broker 2, Broker 3 … etc., by partitioning it into Partitions 1, partition 2, and Partition 3, respectively, can use the automatic load balancing by a broker. It can be written as 1, 2, 3, …., etc.
Let us see a scenario for creating a Kafka producer in which a producer can define a prod_id_1 so data of that id will dispatch to partition one under Broker 1. Data of the prod_id_2 will dispatch to partition two under Broker 2, in which the data will not distribute to every partition after reflecting the key; we have to proceed with a list of Kafka brokers; we also need to define a ‘client. id’, which can recognize this producer client; we can also convey messages with the help of ids.
Aiming to interpret the data to the Kafka cluster, the producer may have other options for selecting the acknowledgment, which means that the producer can obtain authentication for interpreting the data.
- acks=0: It means that the producer can dispatch the data to the broker but does not hold back for the appreciation, and in such case, there is the possibility of a loss of data because if we have not authenticated the data, that has been dispatched successfully to the broker.
- acks=1: It means that the producer will hold back from the chief’s confession, the chief will ask the broker whether it gets strongly accepted the data, and then it will give back the response to the producer; in such case, there may be finite data loss.
- acks=all: In this case, the acceptance can be done by both chief and their followers; when they successfully admit the data, it means that the data is productively accepted, and there is no chance of losing it.
Kafka Producer Example
Given below is the example of a Kafka Producer:
Code:
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.Testback;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.KafkaProducer;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.ProducerRecord;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.RecordMetadata;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
public class SProd extends Thread {
private final KafkaProd<Integer, String> producer;
private final String subject;
private final Boolean isAsync;
public static final String KAFKA_SERVER_URL = "localhost";
public static final int KAF_SERVER_PORT = 9092;
public static final String CLIENT_ID = "SProd";
public SProd(String topic, Boolean isAsync) {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.put("bootstrap.servers", KAFKA_SERVER_URL + ":" + KAFKA_SERVER_PORT);
properties.put("client.id", CLIENT_ID);
properties.put("key.serializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.IntegerSerializer");
properties.put("value.serializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer");
producer = new KafkaProducer<>(properties);
this.subject = subject;
this.isAsync = isAsync;
}
public void run() {
int smsNo = 1;
while (true) {
String smsStr = "SMS_" + smsNo;
long startTime = System.presentTimeMillis();
if (isAsync) {
prod.send(new ProducerRecord<>(subject,
smsNo,
smsStr), new TestCallBack(beginTime, smsNo, smsStr));
} else {
try {
prod.send(new ProducerRecord<>(topic,
smsNo,
smsStr)).get();
System.out.println("Sent sms: (" + smsNo + ", " + smsStr + ")");
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
++smsNo;
}
}
}
class TestCallBack implements Callback {
private final long beginTime;
private final int key;
private final String sms;
public TestCallBack(long beginTime, int key, String sms) {
this.beginTime = beginTime;
this.key = key;
this.sms = sms;
}
public void onCompletion(RecordMetadata metadata, Exception exception) {
long proceedTime = System.presentTimeMillis() - beginTime;
if (metadata != null) {
System.out.println(
"sms(" + key + ", " + sms + ") sent to partition(" + metadata.partition() +
"), " +
"offset(" + metadata.offset() + ") in " + proceedTime + " ms");
} else {
exception.printStackTrace();
}
}
}Output:
Conclusion
In this article, we conclude that the Kafka producer can send data to Kafka through brokers by automatic load balancing to ensure the data will be sent to the particular Kafka by defining the topic name; we have also seen the example of creating the producer.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Kafka Producer Example. Here we discuss the introduction using the Kafka producer example and example. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –