Updated July 4, 2023
Difference Between iSCSI and NFS
iSCSI, or Internet Small Computer System Interface, is a block transport layer protocol that works mainly on a block-level protocol interface. Block protocol can also directly access the storage and control the data flow inwards or outwards through a protocol SCSI. Kerberos highly encrypts the Source and Target data at the iSCSI Initiator (source) level and decrypts them once they reach the iSCSI Target (destination) level. When utilizing the iSCSI interface, sharing data between two hops in parallel is impossible. iSCSI is only appropriate for transferring data between a Local Area Network (LAN) or a Wide Area Network (WAN) because of its fast data access capability.
Advantages of iSCSI
- It aims to use a session between the client and the server to communicate the stream between the two (client and server).
- iSCSI supports multiple connections in a session.
- It supports an advanced method of error recovery using connection allegiance switching between the servers.
Sun Microsystems created the Network File System (NFS) in 1984. Machines connected to the same network can share data using the NFS protocol, which enables distributed file systems. It is similar to accessing the remote machine’s data to access the local storage data. The NFS Service handles parallel access among multiple clients by utilizing resource locking. NFS also allows the admin to plug into a portion of the file system on the server that other users or clients can use in the network-based interface on the user’s respective privileges.
NFS Versions
Following are the different versions of NFS:
1. NFSv3: With the increase in the versions, the versions are improvised with enhancements. NFSv3 includes:
- Support 64-bit file size to handle data or files larger than 2GB.
- The server supports multiple writes, thereby increasing write performance.
- High-level authentication is supported.
2. NFSv4: version 4 includes high-performance enhancements and high-level file security. It also provides protocol support for cluster deployments to parallel access the files among different servers. Some of the key features of NFSv4 are:
- It integrates a number of protocols like NFS, NLM, and NSM into a single protocol to access files across the firewalls.
- High-level authentication is supported using the GSS API.
Head-to-Head Comparison Between iSCSI and NFS (Infographics)
Below are the top 7 differences between ISCSI vs NFS:
Key Difference Between iSCSI vs NFS
NFS and iSCSI are pretty much different from each other. Let us look at the key differences:
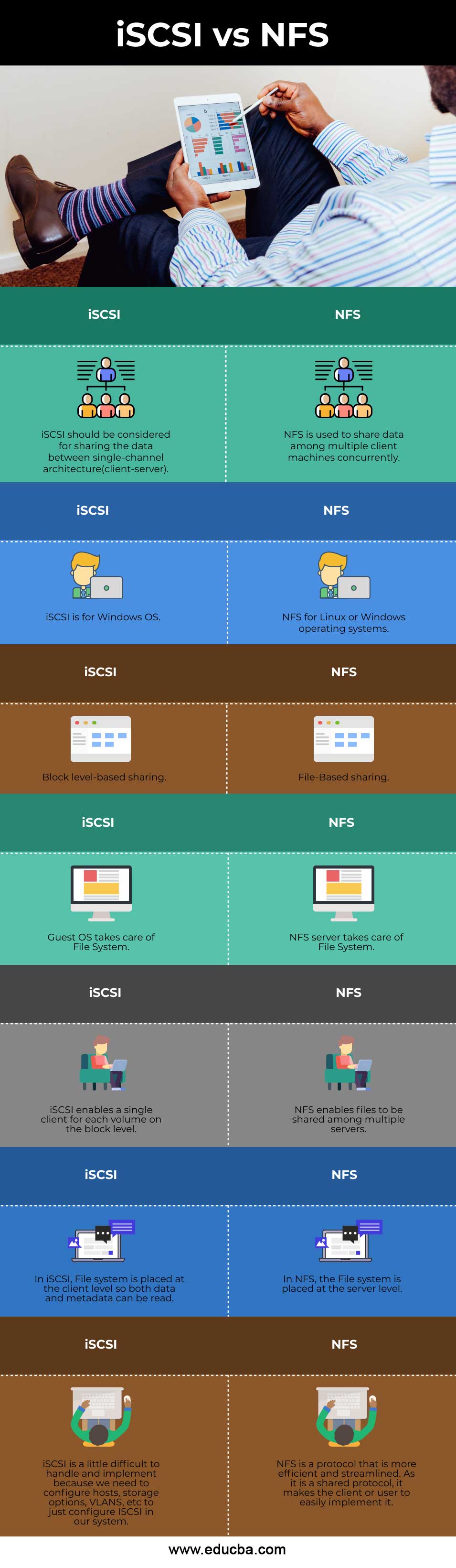
- Definition: NFS is used to share data among multiple machines within the server. It is a file-sharing protocol. ISCSI is considered to share the data between the client and the server. It is a single-channel architecture to share files.
- Operating System: NFS works on Linux and Windows OS, whereas ISCSI works on Windows OS.
- Protocols: NFS is mainly a file-sharing protocol, while ISCSI is a block-level-based protocol.
- File System: The file system is handled in NFS at the server level. Guest OS takes care of the file system.
- File Read Option: The client cannot read the data and metadata as the data in NFS is placed at the server level. This option of reading the data and metadata is handled in ISCSI as the data is placed at the client level.
- Efficiency: NFS is more efficient as it is a shared protocol and thus can be easily implemented by the users. ISCSI is a little difficult to handle as we need to configure host parameters to implement it.
Comparison Table of iSCSI vs NFS
Let’s discuss the topmost comparison between iSCSI vs NFS:
|
iSCSI |
NFS |
| iSCSI should be considered for sharing the data between single-channel architecture(client-server). | Multiple client machines can share data concurrently through NFS. |
| iSCSI is for Windows OS. | NFS for Linux or Windows operating systems. |
| Block level-based sharing. | File-Based sharing. |
| Guest OS takes care of File System. | The NFS server takes care of File System. |
| iSCSI enables a single client for each volume on the block level. | Multiple servers can share files using NFS. |
| In iSCSI, the File system is placed at the client level, so data and metadata can be read. | In NFS, the File system is placed at the server level. |
| iSCSI is a little difficult to handle and implement because we need to configure hosts, storage options, VLANS, etc., to configure ISCSI in our system. | NFS is a protocol that is more efficient and streamlined. As it is a shared protocol, the client or user can implement it easily. |
Features of iSCSI vs NFS
Given below are the features of ISCSI vs NFS:
Features of iSCSI
- IP Routing: One of the important advantages of ISCSI is that it uses TCP/IP Protocol. TCP/IP allows long-distance IP routing without external gateway hardware. It also provides high flexibility and a huge storage network environment.
- Security: The network uses the Internet Security Protocol to protect IP traffic by verifying the identity of each data packet and encrypting it as it travels.
- Storage Array: iSCSI targets a large storage array. The arrays can exist as either free software-based solutions or commercial products. It usually provides unique iSCSI targets for several clients or users.
- Standard Ethernet: iSCSI uses Standard Ethernet, and because of this, it does not require expensive components to be built for this protocol.
Features of NFS
- Remote Procedural Call (RPC): RPC is available for both the servers – NFS and Client for NFS. This service replaces the Transport Device Interface for better support and best scalability.
- Kerberization Options: NFS is a kerborized file system interface. We also get additional Kerberos privacy like Krb5p to support the existing Kerberos options like krb5 and krb5i.
- Mount Volume Point: This lets you access large volumes mounted under NFS4.1 V.
- Multiple Port Extensions: This feature supports RPC ports that are firewall-friendly and easy usage by the clients.
- Firewall Friendly: The advantage of NFSv4 is that it uses only one TCP Port -2049 to run the services, simplifying the usage of protocols across the firewalls.
Which one to use – NFS or iSCSI?
After analyzing the information above, we conclude that the NFS Protocol surpasses iSCSI. Whether you use small, large, or medium files, NFS works seamlessly and effectively compared to iSCSI. From the storage point of view, NFS will be the first choice, and then iSCSI will be coming next to NFS.
Except for the situation where we need to boot from SAN or run any Hyper-V, NFS is always a better choice from the developer’s point of view.
- NFS Security Level: NFS service supports Kerberos v5 client-server interface. For Kerberos V5 authentication, the mount and share commands have been altered in NFS Version 3. The Solaris 2.6 version release has been improvised to make the file system accessible through the server’s firewalls. The NFS Version 4 fully integrates all the necessary security measures to facilitate the mounting of the protocol.
- iSCSI Security Level: The main security risk in iSCSI SANs is that hackers can transmit the storage data over the system or the server. With ACLs (Access Control Lists), storage admins can take precautions to lock the user privileges information.
Conclusion
With the above discussions, it is clear that the usage of NFS is much better than iSCSI. Unless we need to boot from SAN or run any Hyper-V files, we are always free to use NFS. Finally, it is based on your requirements; you can use iSCSI or NFS. We compared both File Systems, considering all their pros and cons.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to iSCSI vs NFS. Here we discuss the key differences and features with infographics and comparison tables. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –


