Updated April 1, 2023
Introduction
There are two versions of the Internet Protocol: IPv4 and IPv6. IPv4 was introduced in 1983 and helps identify systems in a network using a 32-bit address that stores several addresses. IPv4 is the primary Internet Protocol that controls the majority of Internet traffic. IPv6 was developed in 1994 and is considered the next generation Internet Protocol, with a 128-bit address space. Unlike IPv4, which uses periods as delimiters, IPv6 uses colons for this purpose. Configuration is a requirement in IPv4 to connect to other systems, whereas IPv6 does not require any configuration. The rest of the article explores the differences in detail between IPv4 vs IPv6.
IPv4
IPv4 is one of the core protocols used in standard internetworking methods on the internet. It is a connectionless protocol that has uses in packet-switched networks. It uses a 32-bit address format, which allows for a maximum of 2 to the power of 32 unique IP addresses. IPv4 addresses are typically formatted as four 8-bit fields.
IPv6
IPv6 became a draft standard in 1998 and was later established as an Internet Standard in 2017. It is represented as eight groups of four hexadecimal digits, separated by colons. IPv6 also implements hierarchical address allocation methods, which enhance routing capabilities and increase the limit of routing tables. Some important characteristics of IPv6 are:
- Provides support for storing an enormous number of IP addresses, making it a preferred choice for communication between neighboring nodes.
- Provides extensive support for both stateful and stateless configurations.
- Enhances the hierarchical addressing infrastructure.
Head To Head Comparison (Infographics): IPv4 vs IPv6
Below are the top 8 differences between IPv4 vs IPv6:
Key Differences: IPv4 vs IPv6
- Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) is the fourth version of the Internet Protocol (IP) and was first introduced in 1981. Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) is the latest version of the Internet Protocol (IP), which became a draft standard in 1998 and was established as an Internet Standard in 2017.
- IPv6 offers better end-to-end connectivity than IPv4.
- IPv4 addresses are 32-bit, while IPv6 addresses are 128-bit.
- IPv6 offers an unlimited number of IP addresses, while IPv4 offers five classes of IP addresses (A to E).
- IPv6 provides much better Multicast and Anycast abilities than IPv4.
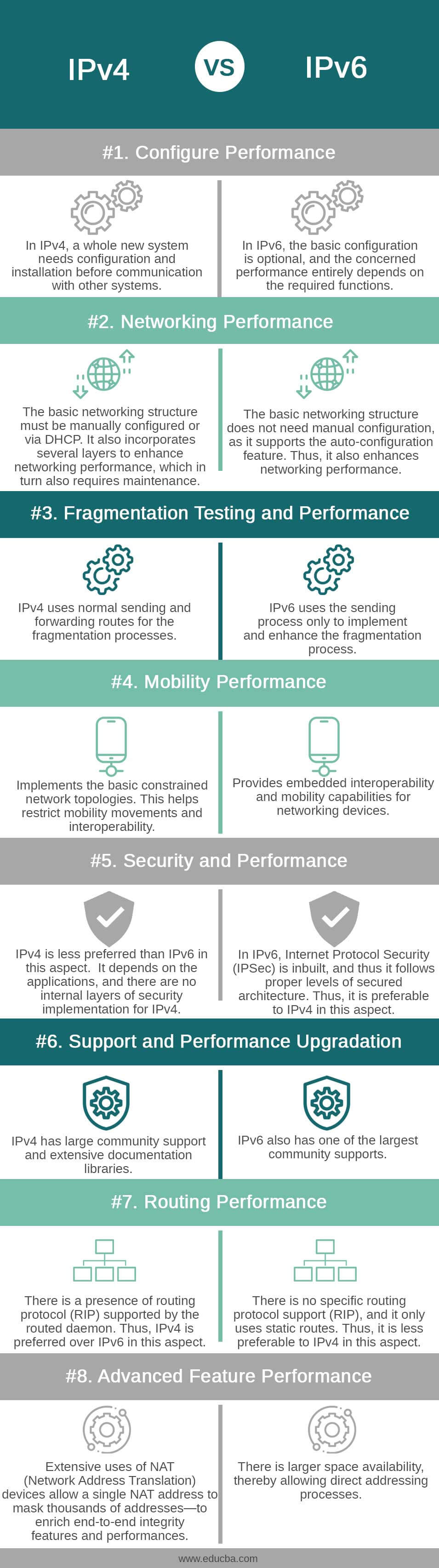
Comparison Table: IPv4 and IPv6
|
Basis of Comparison |
IPv4 |
IPv6 |
| Configure Performance | In IPv4, a whole new system needs configuration and installation before communication with other systems. | In IPv6, the basic configuration is optional, and the concerned performance entirely depends on the required functions. |
| Networking Performance | The basic networking structure must be manually configured or via DHCP. It also incorporates several layers to enhance networking performance, which in turn also requires maintenance. | The basic networking structure does not need manual configuration, as it supports the auto-configuration feature. Thus, it also enhances networking performance. |
| Fragmentation Testing and Performance | IPv4 uses normal sending and forwarding routes for the fragmentation processes. | IPv6 uses the sending process only to implement and enhance the fragmentation process. |
| Mobility Performance | Implements the basic constrained network topologies. This helps restrict mobility movements and interoperability. | Provides embedded interoperability and mobility capabilities for networking devices. |
| Security and Performance | IPv4 is less preferred than IPv6 in this aspect. It depends on the applications, and there are no internal layers of security implementation for IPv4. | In IPv6, Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) is inbuilt, and thus it follows proper levels of secured architecture. Thus, it is preferable to IPv4 in this aspect. |
| Support and Performance Upgradation | IPv4 has large community support and extensive documentation libraries. | IPv6 also has one of the largest community supports. |
| Routing Performance | There is a presence of routing protocol (RIP) supported by the routed daemon. Thus, IPv4 is preferred over IPv6 in this aspect. | There is no specific routing protocol support (RIP), and it only uses static routes. Thus, it is less preferable to IPv4 in this aspect. |
| Advanced Feature performance | Extensive uses of NAT (Network Address Translation) devices allow a single NAT address to mask thousands of addresses—to enrich end-to-end integrity features and performances. | There is larger space availability, thereby allowing direct addressing processes. |
Conclusion
After evaluating various factors, it is clear that each has its own advantages and limitations. Therefore, before selecting one over the other, it is important to thoroughly understand and analyze the fundamental features of both IPv4 and IPv6. Based on the specific project requirements, time constraints, and other relevant considerations, one can choose either protocol to achieve the desired objectives.
Recommended Articles
Here are some further comparison articles for expanding understanding: