Updated June 21, 2023
What is Android?
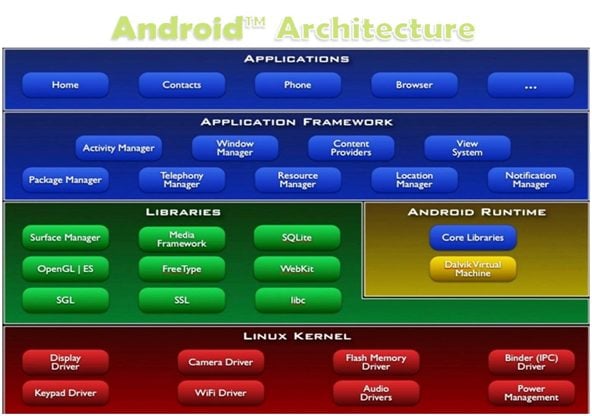
Android is a Linux-based mobile operating system that Google developed. It was aimed to be designed primarily for touchscreen devices such as smartphones and tablets. The initial version of Android was released on September 23, 2008, while the latest release was on August 6, 2018, while I was writing this introduction to Android post. It is called Android “9 Pie”.
Image Source: https://www.elprocus.com/
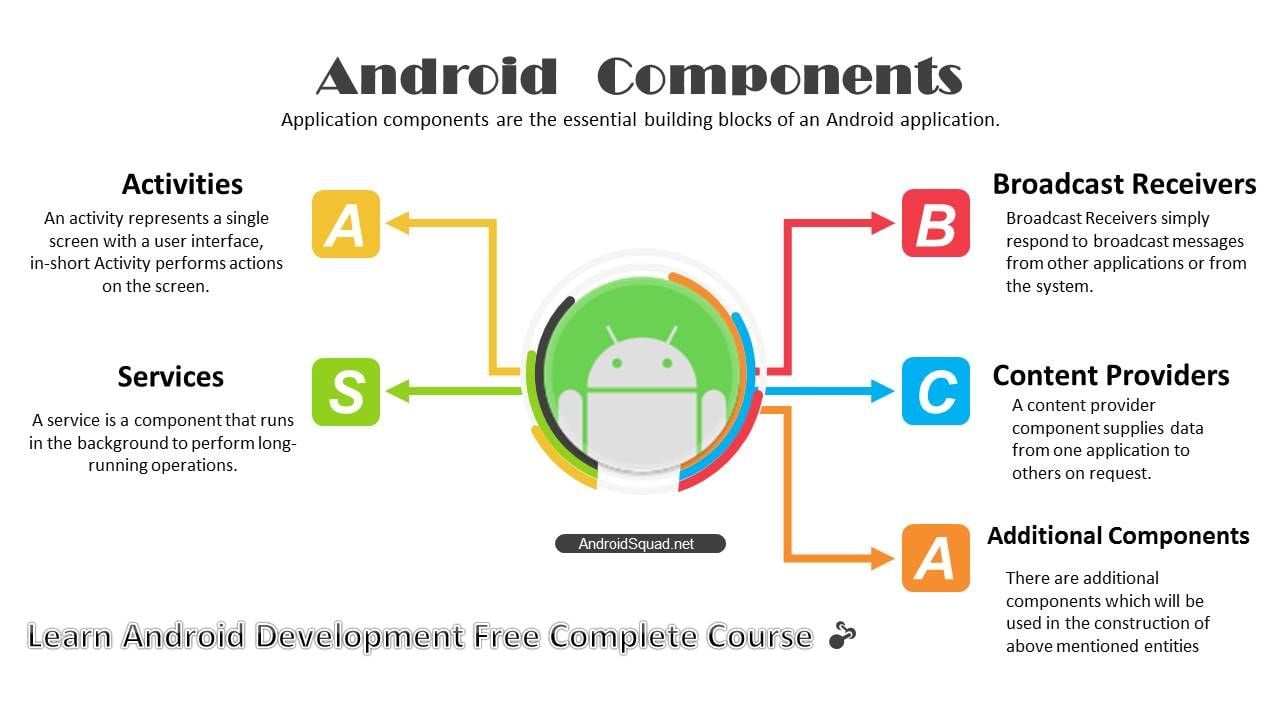
Main Components of Android
Image Source: https://www.google.co.in/imgres
The main components of any Android application are the following:
- Activities
- Services
- Content Providers
- Intent and broadcast receivers
- Widgets and Notifications
1. Activities
We can call the Activity the presentation layer of an Android application. Simply put, an Activity represents the screen on your Android application with its user interface. An application, for instance, an Email App, can have many activities, such as opening an email, composing an email, and replying to an email – these all are different activities. So every Android application has more than one activity. When we start a new activity (like replying to an email), the previous activity is pushed to the back stack, and it gets stopped until the new activity is finished; however, if we push the back button while ongoing activity, the current activity gets dissolved and is popped out of the stack and previous activity resumes.
2. Services
The other important component of an Android application is the service. It performs running operations (long or short) in the background for the activity you perform on your screen. For example, a push notification from an email. It is possible that the service still runs while you have terminated the application or you are not using it currently. For example, when you get an email, you get the notification while you are still not using the application currently.
3. Content Providers
Content Providers manage and encapsulate the application Data (Object Oriented Feature). This provides the data from one processor of an application to another one. The data might be stored in a Database, a file system, or any other storage management system. Android devices include several native Content Providers that expose useful databases such as the media store and contacts.
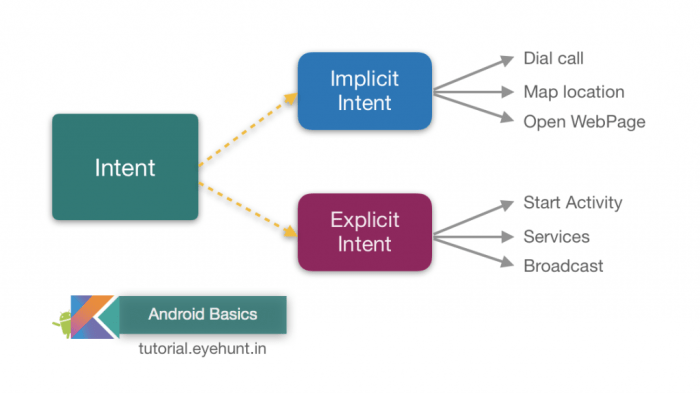
4. Intent and Broadcast Receivers
Android Intents are the means of communication that acts as a facilitator when the exchange of message occurs between different components within the same application or from one application to another. To start any service, we must intend to perform this task. Intents are of two types:
Image Source: https://bit.ly/2XKfzRX
- Implicit Intents: It does not declare the service’s name to start but the action to perform.
- Explicit Intents: It specifies the exact activity to which intent should be given.
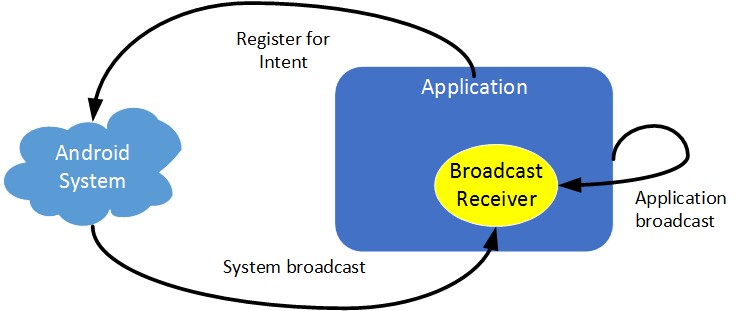
Broadcast Receivers enable your application to listen for intents matching your criteria. As an example, applications can start the broadcasts to let other applications know that little data has been downloaded to the device and is available for them to use. There are two types of broadcast:
- Normal Broadcast: They are entirely asynchronous, and all broadcast receivers are run in an undefined order.
- Ordered Broadcast: They are synchronous and delivered to one receiver at a time.
Image Source: https://www.google.co.in/imgres
5. Widgets and Notifications
Widgets display your app’s exciting or new content in the consolidated form on a mobile or tablet home screen. The user can do different activities like moving and resizing widgets.
‘There are four types of widgets:
- Information Widget – This widget displays only vital information to the users. E.g., the clock on the home screen.
- Collection Widget – This widget displays multiple pieces of information of the same type and allows you to select any of them to open. For example, when you open an email application, you see multiple emails.
- Control Widget – This widget displays frequently used functions. For example, the music app widget allows users to play music outside an application.
- Hybrid Widget – This widget combines the information from above all three widgets.
Notifications allow informing users of any events that have occurred. E.g., we use what’s app application, and when a message comes, we get a notification.
Characteristics of Android
As we have already learned about the introduction to Android, Let’s see the characteristics of Android:
- Android can run multiple applications at the same time.
- Android widgets let you display almost any feature on the home screen.
- Android supports multiple keyboards, and it is super easy to install them.
- Android supports Video Graphics Array, 2D, and 3D graphics.
- Android also supports Java applications.
- One can change settings quite faster when Android is running on the phone
- The very good app market
- Most Android devices support NFC, allowing electronic devices to interact easily across short distances.
Applications of Android
In the above section, we have seen the basic introduction to Android. Now we are going ahead with the application of Android:
Android applications are software applications which are running on the Android platform. We have already seen the Android application components previously as composed of one or more application components like activities, services, content providers, and broadcast receivers. Android apps are written in the Java programming language and use Java core libraries. Developers may download the Software Development Kit (SDK) from the Android website for Android app development. The SDK includes tools, sample code, and relevant documents for creating Android apps.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Android
Given below are the advantages and disadvantages mentioned:
Advantages:
- Android is owned by Google, one of the most trusted and reputed organizations globally. It is also an open source, and it is entirely free.
- It works on almost all devices and is flexible.
- Some widgets enable you to have a quick do to your work.
- We can run multiple tasks at the same time, which hence enables multitasking.
- Google Play Store is a giant application hub offering users millions of apps. It has way more applications than any other OS platform.
- They have multiple features as compared to other operating systems.
- Android is more customizable.
Disadvantages:
- Android advertisements most frequently occur on popular free Android applications, which are kind of annoying to users.
- Android OS is considered one of the most battery-consuming operating systems. In the Android operating system, plenty of process runs in the background, which results in the quick draining of the battery.
- Often Android applications come with low security.
- If mobile RAM is less and the user opens up a few applications, it hangs.
- It usually needs more code for development.
- An application that contains the virus is also present in the Android Market.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Introduction to Android. Here we have discussed the main components, applications, characteristics, along with the advantages and disadvantages of Android. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –