Updated June 7, 2023
Introduction to Intelligent Agents
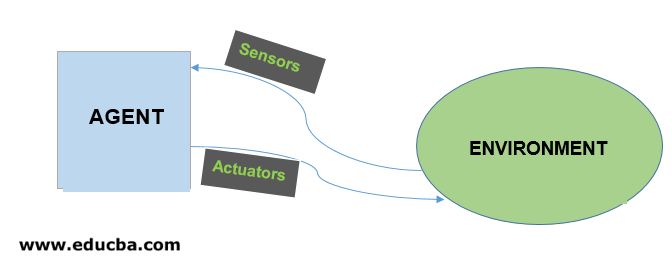
Intelligent Agents can be any entity or object like human beings, software, or machines. These agents can make decisions based on the inputs from the environment using its sensors and act on the environment using actuators. AI-Enabled agents collect input from the environment using sensors like cameras, microphones, or other sensing devices. Then, the agents perform some real-time computation on the input and deliver output using actuators like screens or speakers. These agents have abilities like Real-Time problem-solving, Error or Success rate analysis, and information retrieval.
Three Forms of Intelligent Agent
Intelligent Agent can come in any of the three forms, such as:-
- Human-Agent
- Robotic Agent
- Software Agent
These three forms are described below:
1. Human-Agent: A Human-Agent use Eyes, Nose, Tongue, and other sensory organs as sensors to percept information from the environment and uses limbs and vocal tract as actuators to perform an action based on the information
2. Robotic Agent: Robotics Agent uses cameras and infrared radars as sensors to record information from the Environment. It uses reflex motors as actuators to deliver output back to the environment.
3. Software Agent: Software Agents use keypad strokes, audio commands as input sensors, and display screens as actuators.
For Example– AI-based smart assistants like Siri and Alexa. They use voice sensors to request the user’s request and search for the relevant information in secondary sources without human intervention, and actuators like their voice or text module relay information to the environment.
Types and Rules of Intelligent Agents
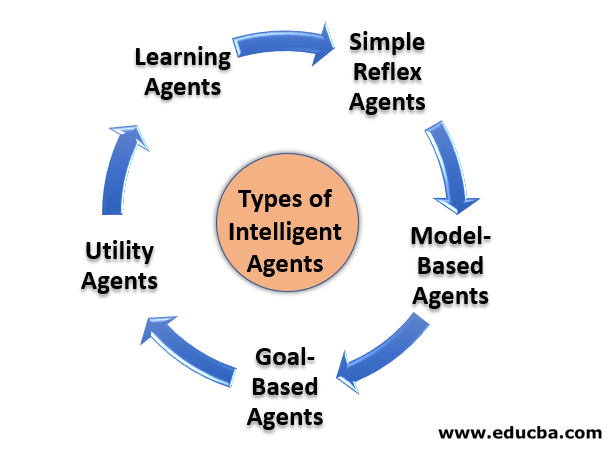
These Agents are classified into five types based on their capability range and extent of intelligence.
1. Simple Reflex Agents
They are the basic form of agents and function only in the current state. They have very low intelligence capability as they can’t store past state. These types of agents respond to events based on pre-defined rules, which are pre-programmed. They perform well only when the environment is fully observable. Thus, these agents are helpful only in a limited number of cases, like a smart thermostat. Simple Reflex Agents hold a static table from where they fetch all the pre-defined rules for acting.
2. Model-Based Agents
It is an advanced version of the Simple Reflex agent. Like Simple Reflex Agents, it can also respond to events based on pre-defined conditions; on top of that, it can store the internal state (past information) based on previous events. Model-Based Agents update the internal state at each step. These internal states aid agents in handling the partially observable environment. It relies on both the internal state and current percept to perform any action. However, it is almost impossible to find the exact state when dealing with a partially observable environment.
3. Goal-Based Agents
These agents’ actions depend on the distance from their goal (Desired Situation). The actions are intended to reduce the distance between the current and desired states. To attain its goal, it uses the search and planning algorithm. One drawback of Goal-Based Agents is that they don’t always select the most optimized path to reach the final goal. This shortfall can be overcome by using Utility Agent described below.
4. Utility Agents
The action taken by these agents depends on the end objective, so they are called Utility Agents. Utility Agents are used when there are multiple solutions to a problem, and the best possible alternative has to be chosen. The alternative chosen is based on each state’s utility. Then, they perform a cost-benefit analysis of each solution and select one to achieve the minimum cost goal.
5. Learning Agents
Learning Agents have learning abilities to learn from their past experiences. These agents can start from scratch and, over time, acquire significant knowledge from their environment. The learning agents have four major components which enable them to learn from their experience.
- Critic: The Critic evaluates how well the agent performs vis-à-vis the set performance benchmark.
- Learning Elements: It takes input from the Critic and helps the Agent improve performance by learning from the environment.
- Performance Element: This component decides on the action to improve performance.
- Problem Generator: The problem Generator takes input from other components and suggests actions resulting in a better experience.
Rules
There are a few rules agents must follow to be termed Intelligent Agents.
Rule 1: The Agent must be able to percept information from the environment using its sensors.
Rule 2: The inputs or observations collected from the environment should be used to make decisions.
Rule 3: The decision so made from the observation should result in some tangible action.
Rule 4: The action taken should be rational.
Structure of Intelligent Agent
The Intelligent Agent structure combines Agent Function, Architecture, and Agent Program.
Agent = Architecture + Agent Program
The three entities are described below.
1. Architecture: Architecture is the machinery on which the agent executes its action. It is essentially a device with embedded actuators and sensors. Example: Autonomous cars, which have various motion and GPS sensors attached to them and actuators based on the inputs, aid in actual driving.
2. Agent Function: Agent Function helps in mapping all the information it has gathered from the environment into action
3. Agent Program: The Agent Program performs the execution of the Agent Function. The execution happens on top of Agent Architecture and produces the desired function.
Conclusion
The end goal of any agent is to perform tasks that otherwise have to be performed by humans. Thus, agents act like intelligent assistants who can enable the automation of repetitive tasks, help in data summarization, learn from the environment, and make recommendations for the right course of action, which will help reach the goal state. Intelligent agents are in immense use today and will only expand.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Intelligent Agents. Here we discuss the three forms, types, rules, and structure of Intelligent Agent. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –