Updated March 17, 2023
How to Install SQL Server?
The following article provides an outline for How to Install SQL Server. SQL server can be installed by Downloading SQL server from Microsoft.com site where various version is available and launching the appropriate installer once the download is completed. There are three editions for the installation type: Basic, Custom, and Download media; it is always recommended to select custom type as it helps to select the features from the list we wish to install.
How to Download Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio 2017 (SSMS)
SSMS is a tool used to configure, monitor, and administer instances of SQL and SSMS use for data-tier components to monitor, deploy, and upgrade it for the applications and even the important use to build and run scripts and queries.
Now download the Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio 2017 from:
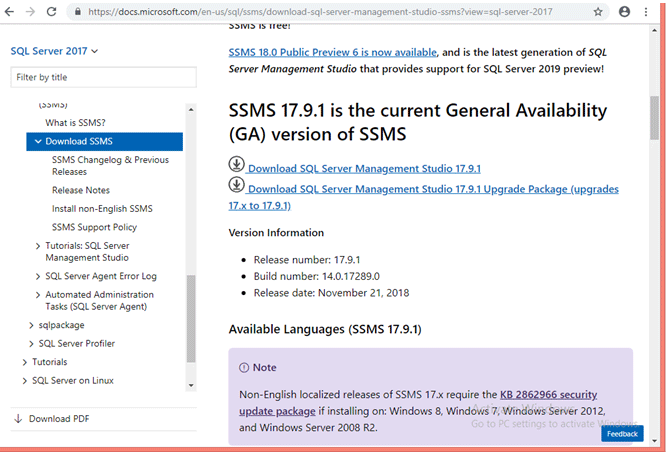
Through this link, you can download SSMS 17.0. The latest version of SQL Server Management Studio is 18.0, which is Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio 2018.
Now the below image shows the download page for Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio 2017.
Steps to Install SQL Server
Let us see the steps required to install SQL Server:
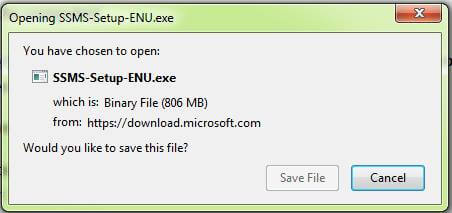
Once you download “SSMS-Setup-ENU.exe”, other windows get open for saving SQL Server Management Studio 2017 exe, and once you click the save file button, it starts the downloading.
Step 1: Next, for the installation, go to the folder where “SSMS-Setup-ENU.exe” is there and then double click the exe file to start the installation.
Step 2: After that, the system will ask the permission that is Click yes to continue installing.
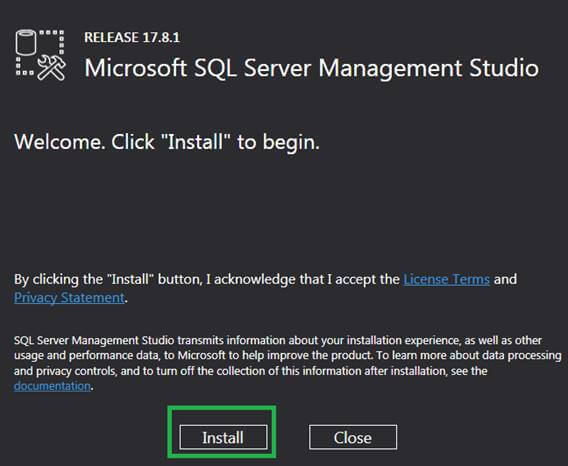
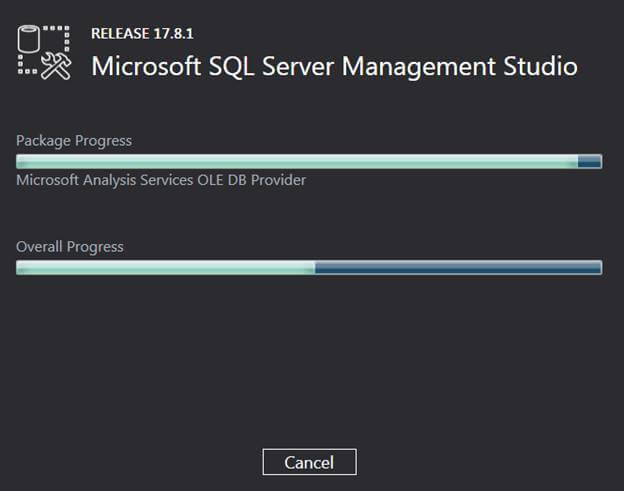
Step 3: Next comes the Installation window. Click the Install to begin the installation.
Then install gets start and then starts the Loading Packages.
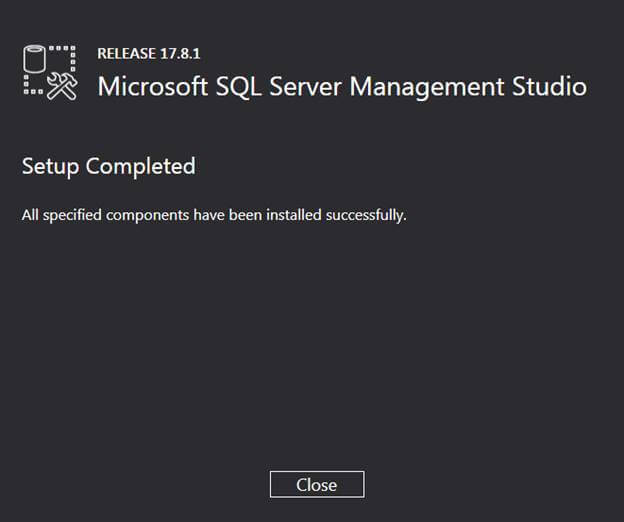
Step 4: When the installation of SQL Server is completed, it asks to close the window, so click the close button and restart your computer.
Step 5: Now, to start with Microsoft SQL Server 2017 tool, click the start button and search for Microsoft SQL Server management studio 17; once you get it to click on it, and it gets starts.
Step 6: Once you start SQL Server Management Studio 17, opening the SQL Server Management Studio 17 the first time will take a few minutes but not the next time when using it.
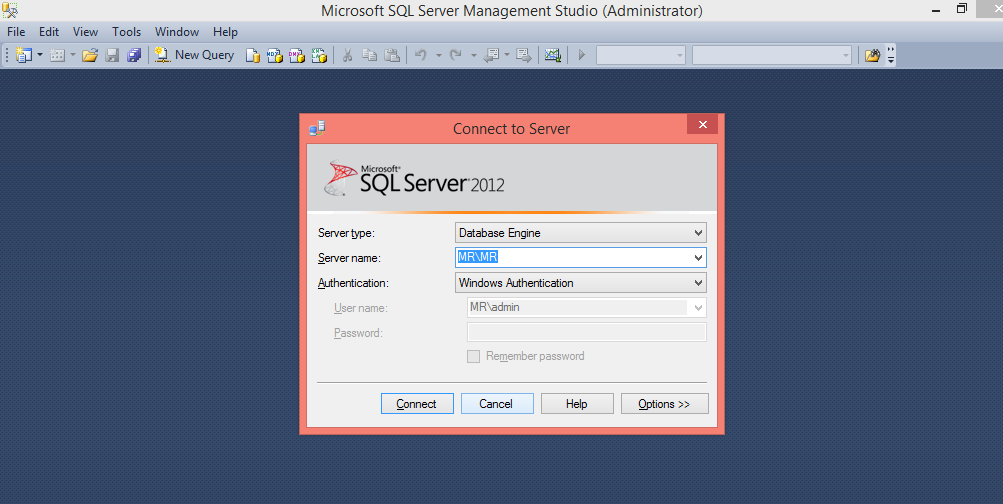
And finally, after opening “SQL Server Management Studio 2017”, it comes with the following window and asks to connect server. So click connect and start using the “SQL Server Management Studio 2017”.
The installation of SQL Server Management Studio is completed; now, we will discuss the feature and components of the SQL Server Management Studio and how to use it. An integrated environment tool, SQL Server Management Studio, can be used to create and manage SQL and also to develop all components of SQL Server, SQL Data Warehouse and even in business intelligence. SQL Server Management Studio provides a number of graphical commands which helps to access to SQL Server and to create and manage SQL server objects.
Components of SQL Server Management Studio
Given below are the components of SQL Server Management Studio to get familiar with the SQL Server Management Studio tool:
- Object Explorer: Object Explorer is used to create, manage and view all of the SQL Server objects like the database, table, view, index and all.
- Template Explorer: Template Explorer is used to build and manage the predefined queries. The predefined queries here help to speed up the development of queries as we just need to customize it.
- Solution Explorer: Solution Explorer used to view the build and open projects and even to manage queries and scripts for administration task.
- Visual Database Tools: SQL Server Management Studio includes visual design tools.
- Query and Text Editors: Query and Text Editors used to write and execute queries and scripts. Once you write the query, execute it with the help of executing button, which is on the top.
Query and Text Editors used to write and execute queries and scripts. Once you write the query, execute it with the help of executing button, which is on the top.
List of Queries
Given below are some of the queries which we can create and run in SQL Server Management Studio.
1. Create a Database
In SQL Server Management Studio, the Adventure work is the sample databases to your SQL Server instance. The AdventureWorks since the 2012 version has not seen any significant changes; the only differences between the various versions of AdventureWorks are the name of the database.
Now create a database named Employee by following one of the two methods:
- Right-click on the database folder in Object Explorer, and then select a new database; the new window gets open, then enter Employee for the field database name and then click ok. The database employee gets created, it can be seen in the Object Explorer.
- Another method is to right-click your server instance in Object Explorer, and then select New Query or the click the New Query command which is on the top of the tool.
The new query window will open and paste the following T-SQL code snippet:
Code:
USE master
GO
IF NOT EXISTS (
SELECT name
FROM sys.databases
WHERE name = N'Employee'
)
CREATE DATABASE Employee
GONow execute the query by selecting the entire query and click Execute or select the entire query and press F5 on your keyboard. After executing the query new database Employee is created and appears in the list of databases in Object Explorer. Right-click the Databases node, and then select Refresh, If it doesn’t appear.
2. Create a Table in the New Database
Next, create a table in the newly created Employee database. To create a table in the Employee database switch the connection context to the Employee database, as the query editor is still in the context of the master database, by executing the following statements.
- — Create a new table called ‘Empdetails’ in schema ’emp’.
- — Create the table in the specified schema.
Code:
CREATE TABLE emp. Empdetails
(
Emp-Id INT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY, -- creating a primary key column
Emp-name [NVARCHAR](20) NOT NULL,
Emp-location [NVARCHAR](20) NOT NULL,
Email [NVARCHAR](20) NOT NULL
);
GOAfter executing the query, the new Empdetails table is created and displayed in the list of tables in Object Explorer under the Employee database.
3. Insert Data into a New Table
- — Insert data into the table.
Code:
insert into emp.Empdetails(Emp-Id, Emp-name,Emp-location,Email)
values(101,'john','Bangalore','[email protected]')After executing the query, the new row is inserted into Empdetails table.
4. Select Data from the Table
- — Create the table in the specified schema.
Code:
select * from emp. EmpdetailsAfter executing the query, all rows with all column is fetch from the Empdetails table.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “install sql server” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.