Updated May 17, 2023
Introduction to Uses of SQL
Business professionals or program developers specifically use SQL or Structured Query Language to administer, update, maintain, and manipulate the databases or tables used for business decision-making. It is usually used to fetch data, update the contents of the table, or operate on the structure of the database or tables using any database tools, which will have a user interface to apply the operations on the database. SQL can be used for both relational and multidimensional types of databases. SQL is a declarative language which means it is a programming paradigm, a style of building the structure and elements of computer programs that express the logic of a computation without describing its control flow.
Some of the famous Databases are listed below:
| Source | Common name | Full name |
| ANSI/ISO Standard | SQL/PSM | SQL/Persistent Stored Modules |
| Interbase / Firebird | PSQL | Procedural SQL |
| IBM DB2 | SQL PL | SQL Procedural Language (implements SQL/PSM) |
| IBM Informix | SPL | Stored Procedural Language |
| IBM Netezza | NZPLSQL[20] | (based on Postgres PL/pgSQL) |
| Invantive | PSQL[21] | Invantive Procedural SQL (implements SQL/PSM and PL/SQL) |
| Microsoft / Sybase | T-SQL | Transact-SQL |
| Mimer SQL | SQL/PSM | SQL/Persistent Stored Module (implements SQL/PSM) |
| MySQL | SQL/PSM | SQL/Persistent Stored Module (implements SQL/PSM) |
| MonetDB | SQL/PSM | SQL/Persistent Stored Module (implements SQL/PSM) |
| NuoDB | SSP | Starkey Stored Procedures |
| Oracle | PL/SQL | Procedural Language/SQL (based on Ada) |
| PostgreSQL | PL/pgSQL | PostgreSQL (implements SQL/PSM) |
| SAP R/3 | ABAP | Advanced Business Application Programming |
| SAP HANA | SQLScript | SQLScript |
| Sybase | Watcom-SQL | SQL Anywhere Watcom-SQL Dialect |
| Teradata | SPL | Stored Procedural Language |
Uses of SQL
The Examples below are based on a dummy table with table name “student_records” columns id, name, address, and mobile.
Constraints: “id” is used as the primary key of the table, and one more column with the name “mobile” and this column contains unique data;
1. DQL
It stands for Data Query Language. It is used to retrieve data from the database.
The SQL statement is SELECT.
Example:
SELECT * from student_records;2. DDL
It stands for Data Definition Language. This is used to define database schema. Thus, it deals with the database schema description and is used to create and modify the structure of database objects. Therefore the SQL statements are CREATE, DROP, ALTER, TRUNCATE, COMMENT, and RENAME.
Example:
CREATE TABLE student_records
(id integer NOT NULL DEFAULT,
name character varying,
address character varying,
mobile numeric,
CONSTRAINT student_records_pkey PRIMARY KEY (id)
)
DROP TABLE student_records;
ALTER TABLE student_records ALTER COLUMN mobile character varying;3. DML
It stands for Data Manipulation Language. It stores, modifies, deletes, and updates data in the database. Thus the SQL statements are INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE.
Example:
INSERT into student_records values (1,"name","address", mobile);
UPDATE student_records set address = "new address" where name= "name";
DELETE from student_records where mobile = [enter_mobile_number];
TRUNCATE table student_records;4. DCL
It stands for Data Control Language. It is used to grant access to data stored in the database.
SQL statements are GRANT and REVOKE.
Syntax:
REVOKE privilege_name
On object_name
From {user_name | PUBLIC | role_name};
GRANT privilege_name
On object_name
To {user_name | PUBLIC | role_name}
[WITH GRANT OPTION];5. Database Transaction Management
Transaction Management means maintaining the transaction related to the database i.e., following the basic rules for ACID properties of the database. The transaction has only two results, i.e., either success or failure. Thus the SQL Statement is TRANSACTION, COMMIT, ROLLBACK, SAVEPOINT.
6. Procedures, User-defined Functions, Triggers, Indexes, and others
We can write procedures, user-defined functions, triggers, indexes, and cursors as per the requirements, which is nothing but SQL statements to make our work easy to meet the business requirements.
7. Reporting Purpose
SQL queries are essential from a reporting perspective, which every project have. We can write queries for standalone reports and fetch data for the report.
8. Manual Analysis
SQL queries are essential for analysis when manual interventions are necessary. With SQL queries, we can filter out the essential data from the structured data, which could be used for analysis.
9. SQL with NTC Hosting
Even the MySQL hosting service can construct big and powerful websites, web-based applications, and programs. MySQL open source database solution and insist on speed, stability, and scalability, then MySQL hosting solution is needed.
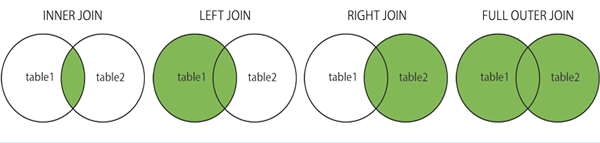
10. SQL Join
A SQL join is an instruction to combine data from two sets of data (i.e. two or more tables).
- (INNER) JOIN: Returns matching values in both tables as an output.
- LEFT (OUTER) JOIN: It returns all records of the left table and the matching records of the right table as output.
- RIGHT (OUTER) JOIN: It returns all records 0f the right table and the matching records of the left table as output.
- FULL (OUTER) JOIN: It returns all records if there is a match in either table i.e. left or right.
11. SQL Union
UNION can join the result set of two or more SELECT statements.
12. SQL Wildcards
A wildcard character is a special character in SQL used to substitute any other character(s) in a string.
SQL Wildcard Operators: ‘%’ and ‘_’ are called wildcard operators.
Note:
- % – Representing zero, one, or multiple characters in a character value ( used while filtering).
- _ – Representing a single character.
Conclusion
So it can be concluded that even today, with the fast-growing technologies and evolution of no SQL databases in the market, Uses of SQL still plays a vital role in structured data. SQL provides flexibility in querying the tabular data with SQL queries which is a great help in many ways.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Uses of SQL” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.