Updated March 10, 2023
Introduction to SQL GROUP BY WHERE
In SQL standard, a GROUP BY clause is used to group rows with identical values for a specified field together and prepare a summary row for these rows using an aggregate function. A WHERE clause is used to filter rows based on a specified condition. When we use GROUP BY clause in conjugation with WHERE clause, the WHERE clause filters the rows first based on the mentioned condition and then GROUP BY clause prepares a summary row only for the filtered rows. It becomes very useful when we want to GROUP only specific rows together. For instance, rows within some specified range of values, dates etc.
Syntax and parameters of SQL GROUP BY WHERE
The basic syntax used for writing GROUP BY with WHERE clause is as follows:
SELECT column_name_1, aggregate_function(column_name_2)
FROM table_name
WHERE condition expression
GROUP BY column_name_1;The parameters used in the above-mentioned syntax are as follows:
- column_name_1: column or field name according to which the rows have to be grouped together.
- column_name_2: column or field name which has to be summarized using an aggregate function.
- table_name: database table from which the said columns will be fetched from.
- condition expression: condition on the basis of which the WHERE clause will filter the rows.
Here we have used the minimum possible clauses and commands; we can use JOINS, HAVING BY, ORDER BY etc., based on the requirement.
Examples of SQL GROUP BY WHERE
Given below are the examples of SQL GROUP BY WHERE:
In order to illustrate the usage and functionality of the GROUP BY clause with a WHERE clause, let us first create a dummy table called “sales”. Here is the CREATE TABLE statement for the same.
Code:
CREATE TABLE sales (
order_id int,
salesman_name character varying(50),
product_id character varying(50),
sales_region character varying(50),
sales_date date
);Output:
The table has been successfully created. Our next task is to insert a few records in it to work with.
Here is the insert statement for the same.
Code:
INSERT INTO public.sales(
order_id, salesman_name, product_id, sales_region, sales_date)
VALUES (1,'Mohit K','Book11','New Delhi','2020-05-01'),
(2,'Rey Holt','Book11','Mumbai','2020-05-02'),
(3,'Swati Singh','Book24','New Delhi','2020-05-03'),
(4,'Indrani K','Book24','Mumbai','2020-05-01'),
(5,'Dave Prakash','Book11','Mumbai','2020-05-02'),
(6,'Joshua S','Book24','New Delhi','2020-05-03'),
(7,'Mrinali Pal','Book11','New Delhi','2020-05-04'),
(8,'Mohit K','Book24','New Delhi','2020-05-02'),
(9,'Rey Holt','Book24','Mumbai','2020-05-05'),
(10,'Indrani K','Book11','Mumbai','2020-05-04'),
(11,'Joshua S','Book24','New Delhi','2020-05-05'),
(12,'Mohit K','Book11','New Delhi','2020-05-04');Output:
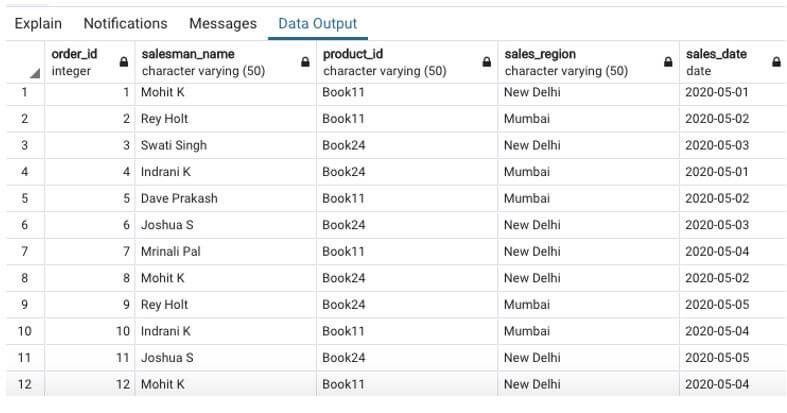
The command got executed successfully. Let’s check using a SELECT statement if the desired rows have been inserted.
Code:
SELECT * FROM sales;Output:
Example #1
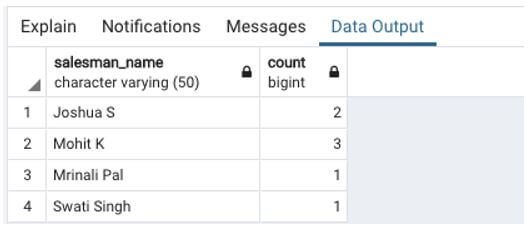
Find the total number of sales made by each salesman in the New Delhi region.
Code:
SELECT salesman_name, count(order_id)
FROM sales
WHERE sales_region = 'New Delhi'
GROUP BY salesman_name;Output:
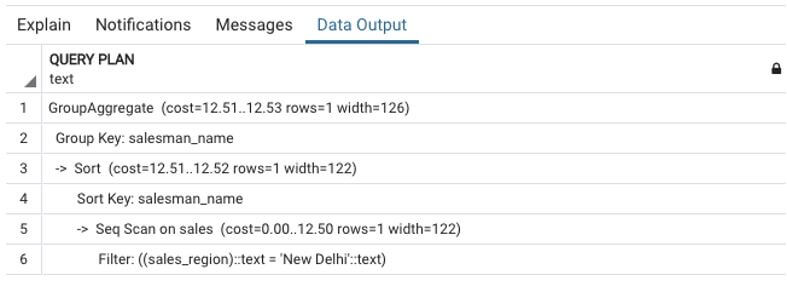
We can clearly observe from the result of the SELECT query that the WHERE clause has first filtered the rows having ‘New Delhi’, and then GROUP BY clause has grouped the filtered rows together.
For detailed information, you may refer to the image of the query plan below.
Example #2
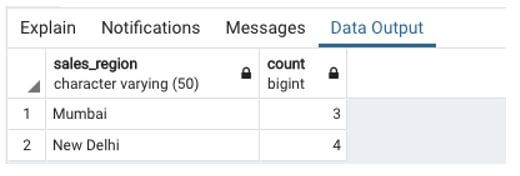
Find the total number of sales made in each region between 1st May 2020 and 3rd May 2020.
Code:
SELECT sales_region, count(order_id)
FROM sales
WHERE sales_date BETWEEN '2020-05-01' AND '2020-05-03'
GROUP BY sales_region;Output:
GROUP BY WHERE with HAVING clause:
Many beginner-level SQL developers find it hard to understand the difference between HAVING BY and WHERE clauses because they both serve the same purpose; that is, they filter records. A HAVING clause, when used in conjugation with the GROUP BY clause, filters grouped rows, whereas the WHERE clause filters records before grouping them. A HAVING clause is always used with GROUP BY, whereas WHERE can be used in any SELECT statement.
Example #3
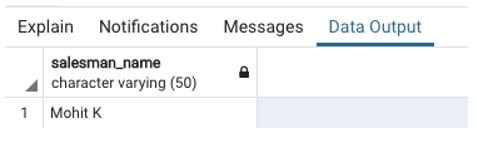
Find the salesman who made more than 2 sales in the period from 1st May 2020 to 5th May 2020.
Code:
SELECT salesman_name
FROM sales
WHERE sales_date BETWEEN '2020-05-01' AND '2020-05-05'
GROUP BY salesman_name
HAVING count(order_id) > 2;Output:
GROUP BY WHERE with ORDER BY clause:
Example #4
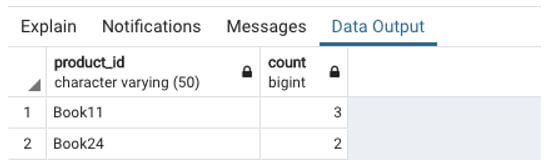
Find the product and the number of salesmen that sold the particular product in the Mumbai region.
Code:
SELECT product_id, count(salesman_name)
FROM sales
WHERE sales_region = 'Mumbai'
GROUP BY product_id
ORDER BY count(salesman_name) DESC;Output:
Conclusion
In this article, we saw how to use the GROUP BY clause with the WHERE clause. A WHERE clause is usually used in conjugation with GROUP BY to prepare a summary row for only those rows that satisfy a particular condition.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL GROUP BY WHERE” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.