Introduction to Hedge Fund Strategies Managers
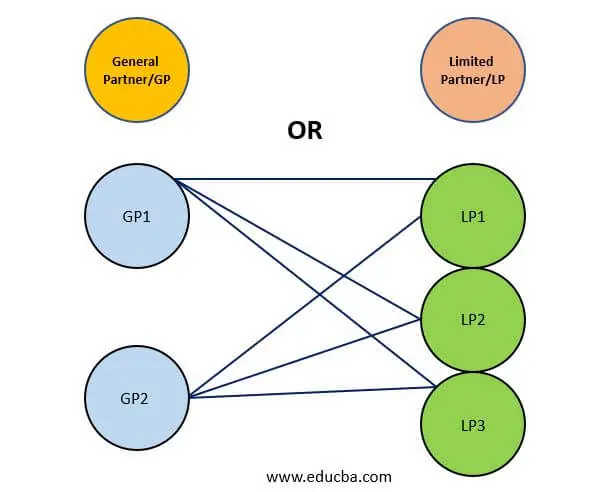
A hedge fund is an investment partnership between the fund manager (called the general partner) and investors in the hedge fund (called limited partners). Hedge fund strategies can carry a huge investment risk, and chasing the bull market or following a herd mentality can get you financially trampled. Plunging cash into a high-performing fund without doing your homework can result in a poor grade at the end of the trading session. So, here’s your financial market survival toolkit with handy tips to guide you through the ins and outs of hedge fund strategies.
Meaning of a Hedge Fund Strategies Managers
A hedge fund is a term for investments made by limited partners who contribute money, which the general partner manages.
The hedge fund definition operates on one key principle: Maximize returns and minimize risks. Hence, one refers to it as “hedge” fund management.
History of Hedge Fund Strategies
Hedge fund strategies existed because this partnership aimed to make money, regardless of whether there was a bull market or a bear. Managers hedge themselves against losses by following several hedge fund strategies.
Structure of a Hedge Fund Strategies
Hedge Fund vs. Mutual Funds
A hedge fund strategies have certain points in common with a mutual fund, which are as follows:
- Both are pooled investment vehicles.
- You can use either to invest in securities such as equities, options, and bonds.
- Separate managers run hedge fund strategies, while sub-advisors run the mutual fund.
General/Limited Partnership Model
- The typical hedge fund strategy structure is two-tier, comprising the general/limited partnership model.
- Within this structure, the funds are operated by the general partner, and there should be a minimum of one limited partner who makes investments and has limited liability/liability for paid-in money.
- Such a partnership can have multiple general and limited partners. However, some SEC rules limit the number of investors barred from registration.
- A typical partnership structure is a limited liability company, or LLC, because it is a flow-through tax unit, and investors can be held in limited liability, equalling their investment amount. You will need an operating agreement for your limited liability company, or LLC, to formally and legally define the roles and responsibilities of those involved in its creation and operations going forward, so keep this in mind if you decide this is the right structure for your hedge fund.
- General partner markets and manages the funds, including hiring a fund manager and administrating fund operations.
One Partner or Many?
Hedge Funds take the High Road, and Mutual Funds the Low
The fee structure is one of the chief points of difference between Hedge Funds vs Mutual Funds. Mutual Funds involve lower fees, while fees paid by investors in the case of hedge fund strategies are higher and include additional fees not charged by an MF.
Hedge Fund: Term Structure
Terms offered by each fund are unique, making it a tangible point of difference. Terms are linked to the following factors:
Subscriptions and redemptions
Lock-Ups
Some funds require a lock-up commitment, which can either be a hard lock (preventing withdrawal of funds by an investor for a full-time period) or a soft lock (fund withdrawal is possible following payment of a penalty ranging from 2 to 10%).
Distinctive Features of Hedge Fund Strategies
No Regulation: Hedge fund strategies are not under any regulation apart from limits on the number of investors they can have or advertise to the general public.
Riskier: Hedge fund strategies are riskier than traditional mutual fund investments. This is because hedge fund strategies do not have to report their underlying positions to any regulatory agency or members of the public.
Seeing is Believing: The Need for Transparency
Investors have demanded more transparency from hedge fund strategies, even though top hedge fund managers do not want to show their cards and reveal their position.
Below are the Important Hedge Fund Strategies
Equity Market Neutral
- In this hedge fund strategy, funds identify (or at least try to) over and undervalued equity securities. At the same time, there is the neutralization of portfolio exposure to market risk through a combination of short and long positions.
- Portfolios are neutral with respect to market, sector, industry, and currency/dollar and have a portfolio beta of 0 value.
- How is this ensured? The long and short positions have equal potential for related market or sector factors.
The thumb rule: Overvaluation is slower to correct than undervaluation.
Reason: Many investors face limitations about shorting of stocks.
Benefiting from Mis Pricing: Convertible Arbitrage
- These hedge fund strategies can help capitalists with mispricing in convertible securities, such as convertible bonds, warrants, and preferred stock.
- Managers buy/sell a security and hedge part/all of the risks linked to it.
- Example: Buying a convertible bond and shorting the associated stock to lower risk.
Fixed Income Arbitrage: Over and Undervalued Bonds Important
- Here, the funds seek to identify over and undervalued bonds based on expected changes in term structure and credit quality of issues/market sectors.
- One neutralizes this type of portfolio against directional market movements through a combination of long and short positions.
Profit in the Face of Default: Distressed Securities
- Portfolios of distressed securities are invested in the debt and equity of companies facing or undergoing liquidation.
- Traditional investors prefer to transfer risks when there is a danger of default. Thus, funds are held long in an account of the non-liquidity of distressed debt and equity, making shorting difficult.
Catching the Price Spread: Merger/Deal Arbitrage
- This type of hedge fund strategy can capture the price spread between the current prices of the securities and their expected value following a positive event such as a takeover, M&A, spinoff, or more associated with multiple hedge fund companies.
- Merger arbitrage involves purchasing the target firm’s stock, following a merger announcement, and shorting the revenant amount of the acquirer’s stocks.
Merger arbitrage derives a return from news of acquisitions and mergers.
A deal is subject to the following conditions:
- Regulatory approvals
- A positive vote by target company shareholders
- No adverse change in material terms in the target’s financial position.
Non-Neutral Portfolios: Hedged/Long-Short Equity
- This hedge fund example aims to identify over and undervalued securities, thereby dealing in highly concentrated, typically non-neutral portfolios. The value of the short position may be a fraction of the long, and the portfolio may have a net exposure to the equity market in the long term.
- The first hedge fund in financial history, launched by A.W. Jones in the late 1940s, used these hedge fund strategies.
- It still accounts for a massive share of equity hedge fund assets.
- Concept: Investment means encashing on WINNERS as well as LOSERS
- Mantra: Pledge long positions in winners as collateral to fund short positions in losers
- Result: A combined portfolio creates more profit than loss and lowers the market risk
Seeing the Bigger Picture: Global Macro
This type of hedge fund examples encashes on systematic movements in financial as well as non-financial markets via trading in the following:
- Futures
- Currencies
- Option Contracts
- Global Macro = Major Market Trends,
- Individual Security Opportunities
Emerging Markets Strategy: Spotlight on Less Mature Markets
These are funds that have links to emerging, less mature markets. Short selling is not permitted in markets where futures and options are impossible. Funds are long in such a strategy.
FOF: A Money Mammoth
FOF, or Funds of Funds, is a fund that makes investments in multiple underlying top hedge funds (typically 10 to 30).
Some FOFs are even more diversified; these are liquid and available to individual investors.
Learning from Management Masters: How Hedge Fund Managers Operate
Convertible Arbitrage
- This is when hybrid securities come into use, combining a bond with an equity option.
- Managers maintain a delta-neutral position where bonds and stocks offset each other as the market fluctuates.
- This hedge fund strategy thrives on volatility; the higher the stakes, the more the profit.
Event-Driven
- Managers use such hedge fund strategies when the biggest hedge funds purchase company debt from firms facing financial bankruptcy.
- In this hedge fund example, managers typically focus on senior debt. If a company has already filed for bankruptcy, the junior class of debt may be a wiser hedge.
- In such a strategy of hedge fund definition, investors need to be patient. This is because corporate reorganization can take a lot of time.
Credit or Capital Structure Arbitrage
- In this credit strategy, managers watch out for the relative value between senior and junior securities of a single corporate issuer.
- Securities of equivalent credit quality are taken from different issuers.
Credit Hedge Funds = Focus on Credit, Not Interest
- These funds grow when credit spreads narrow during strong economic growth and vice versa
Fixed Income Arbitrage
- Managers glean returns from risk-free government bonds, making a leveraged guess on how the yield curve’s shape will change.
- High leverage comes into use for capitalizing returns. The flipped? Leverage causes a greater risk if the manager is incorrect.
Macroeconomic Strategies
- This plan analyzes how macroeconomic trends impact interest rates, currencies, commodities, or equities.
- Future and currency forwards are most commonly traded in this form of hedge fund careers.
Leverage
This is one of the best (and worst) tactics managers employ over time. It is the best because strong trading or investment returns are possible. It is also worse if it forces a sell-off, as hedge funds receive margin calls and are forced to sell positions to meet them.
Long Only
These hedge fund strategies are used when a hedge fund owns long positions in stocks or other assets, looking for an alpha to the upside to outdo benchmarks. For the hedge fund example, if the S&P500 is the benchmark, it is up 10%, and the hedge fund is up 12%; an extra 2% difference between the two is an alpha generated by a portfolio manager.
Short Only
In this hedge fund strategy, the manager sells stock shorts. Portfolio managers who engage in shorting have been crushed given the market’s rising tide, which has uplifted sentiments. An example of a Short Only strategy is MySpace, once a leader in social networking and now a virtual non-entity in social media.
Fair Trade/Long/Short Strategy
The result is when the fund matches stocks in the same sector, which is long or owns stocks and engages in shorting fair trade.
Market Neutral
Net exposure to funds = 0 if long and short positions have equal investment.
The flipside: Massive moves upward or downward will negate the other side
Relative Value Arbitrage
A strategy used to hedge funds trading debt
Man Vs Machine: Quantitative Hedge Fund Management
In this type of hedge fund definition, computer programming uses statistical models and data to locate the alpha camouflaged by market abnormalities.
Risk Measures Used in Hedge Fund Strategies
SD or Standard Deviation: Defined as a level of volatility of returns measured in terms of percentage provided on an annual basis.
Decoding the Results: Variability of annual returns and funds can be compared with SD.
If 2 funds of the same annual returns have different SDs, the one with the lower SD will be more attractive and vice versa.
Additional Metrics
- Value At Risk/VaR: measures dollar loss expectation occurring with a probability of 5 in 100 or 5%.
- Downside capture: Degree of correlation of fund to markets which are sliding
- Rule of thumb: The lower the downside capture, the better the fund is at preserving wealth in the face of a meltdown or vice versa
- Drawdown: Maximum drawdown measures the percentage fall in cumulative return from previous highs. You can assess which funds preserve wealth…these will be the ones that minimize drawdowns.
- Leverage: If this increases, funds sell assets at massive discounts to cover margin calls. This serves as a good measure of the health of the hedge fund. Lower leverage is just what the doctor ordered.
- Qualitative indices: These include an assessment of the manager, a scale of operations, and back-office administration, to name just a few.
- Soft Close Versus Hard Close: Soft close means no additional investors will be allowed, while hard close means there will be absolutely no additional investments.
Why Invest in Hedge Funds?
- Risk reduction
- Flexible mandates
- Return Enhancement
What to Watch Out For Due Diligence/Caveat Emptor?
- A low-volatility hedge fund can explode (courtesy of the subprime mortgage crisis in 2007 and its associated market meltdown in 2008). So allocation considerations are very important
- The allocation should consider the overall risk.
- Another important point to look out for is the level of gross and net exposure of the overall portfolio when adding hedge funds to a portfolio.
- The definition of the measurement criteria in quantitative and qualitative terms is vital.
Define Measurement Criteria
One should define criteria in both quantitative and qualitative metrics.
- Usually, hedge fund managers send a pitch book describing the firm and its many aspects, such as strategy, principles, and performance. Analysts and investors should ensure they have accessed the pitch book for data.
- Compare the hedge fund strategies to those within a similar category to assess how funds performed.
- Additional analysis can then be made to decide whether the hedge fund strategies should be invested.
- A background check of the firm and an assessment of its back-office operations are some of the qualitative aspects of due diligence.
Conclusion
A hedge fund definition is about securing gains and cutting down on losses. Effective hedge funds perform well based on concrete parameters and associated criteria for tangible reasons. Financial wizardry requires the right formula for success. Investors must be alert to get maximum returns and minimum losses from hedge funds. Capitalizing on markets (whether bull or bear) has never been easier.
Recommended Articles
Here are some further related articles to learn more: