Updated February 28, 2023
Introduction to Fzero Matlab
Functions are defined as the relationship between the dependent and independent sides. Generally, functions can be classified into linear and nonlinear functions. Linear functions are those that have the highest component in the equation as 1 and it follows a straight line while in nonlinear functions at least one equation has the power more than 1 and it does not follow a straight line. In Matlab, the function which is used to find the roots of the nonlinear function is fzero. It tries to find a point where the function at the respective point is zero.
Functions of fzero in Matlab
In Matlab, fzero functions is used to find a point where the given objective function changes its sign. It returns the values depending on whether the function is continuous or discontinuous in nature. Please find the below syntax that is used in Matlab:
- a= fzero(func,a0): This is used to give a point i.e. a where the function of the respective point is zero. The exact answer to the function is that when the function changes its sign.
- a= fzero(func,a0, options): This is used to find to change the process of the solution by mentioning the options in the syntax.
- a= fzero(problem): This syntax is used to find the root solution by mentioning it in ‘problem’.
- [a,fval,exitflag, output] = fzero(___): This syntax is used to find the output in fval mentioned in the syntax, exitflag tells us about the reason why fzero terminated and output is a structure which contains information on the process of the solution.
The input and output arguments as mentioned in the above syntax needs to have certain criteria. ‘func’ is one of the input argument which is the input function that requires to be solved. It can be specified as a function handle or name of the function. It accepts and returns a scalar quantity. The data types that are accepted are in the form of function handle, char or string. The initial or starting value ‘a0’ can be specified as a real scalar or two-element vector which is real in nature. If the initial value is specified as a real scalar, then fzero starts at a0 and searches a point(a1) where the func(a1) is equal to zero. It decreases the interval of iteration where the function changes its sign to reach the required solution. Similarly, if the initial value ‘a0’ is a two-element real vector then fzero checks whether the function of two initial points i.e. func(a0(1)) and func(a0(2)) have the respective opposite signs or not. If they don’t have the opposite sign, then it will give an error. It decreases the interval of iteration where the function changes its sign to reach the required solution. The data type that is accepted is of type double. Please find the below examples that depict the use of fzero in Matlab:
Examples of Fzero Matlab
Following are the example of fzero Matlab are:
Example #1
To find the value of the cos function where it is zero near to 4:
Code:
func = @cos; % function
a0 = 4; % initial point
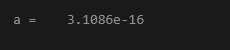
a = fzero(func,a0)
Output:
Example #2
To find the zero of the function which falls in an interval:
Code:
func = @cos; % function
a0 = [1 2]; % initial interval
a = fzero(func,a0)
Output:
‘options’ is one of the input arguments that is mentioned in the above syntax is used to create or change the options for the process of the solution. It can be specified as a structure. Please find the below options that are used while using fzero functions in Matlab:
- Display Option: This is used to decide various levels of the display which can be:
- ‘off’ is used when we do not want to display any output.
- ‘iter’ option is used when we want to show the output at each iteration.
- ‘notify’ option is used when the required function does not converge.
- ‘final’ option is used to display the final output in the whole iterative process.
- FunValCheck option: This is used to check whether the objective function values are valid or not. It can have two values ‘On’ and ‘Off’. If the value is On, then it shows error as the required objective function has returned values that are either complex or infinity. If the value is off, then there is no error in the whole process.
- PlotFcns Option: This is used to plot the progress of the algorithm in its execution. We can select from the predefined plots or we can write our own. We can pass a function handle or an array of different function handles to the required function, the default being none. @optimplotx option is used to draw the plot in its current point during the execution. @optimplotfval is used to plot the value of the function.
The data type that is accepted is structure. Another last input argument is ‘problem’ which is given in the form of structure. The output argument ‘a’ displays the location at which sign changes or its root, returning a scalar quantity. ’exitflag’ is another output argument that tells us the reason why the fzero algorithms stopped. It can have different values like 1, -1, -3, -4, -5, -6 and each value has its own description and reason. ’output’ is another output argument that gives the information about the whole process used to find roots. It can be mentioned in the form of structure and it has fields like ‘iterations’,’ algorithm’,’ message’,’funcCount’ etc.
Example #3
To find the root of the given function that has an extra parameter:
Code:
func = @(a,c) sin(c*a); % parameterized function mentioned
c = 3; % parameter mentioned
func1 = @(a) func(a, c); % function of ‘a’ alone mentioned
a = fzero(func1,0.1)
Output:
Conclusion
fzero is widely used in Matlab, so it is important to understand it’s working. There are certain limitations that should be seen while dealing with the fzero function, one of them is; it counts zero a point where the required function crosses the x-axis and if it does not cross x-axis then it executes the function till infinity.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Fzero Matlab. Here we discuss the Introduction and working of Fzero in Matlab along with different examples and its code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –