Updated October 25, 2023
Definition of Forex Market
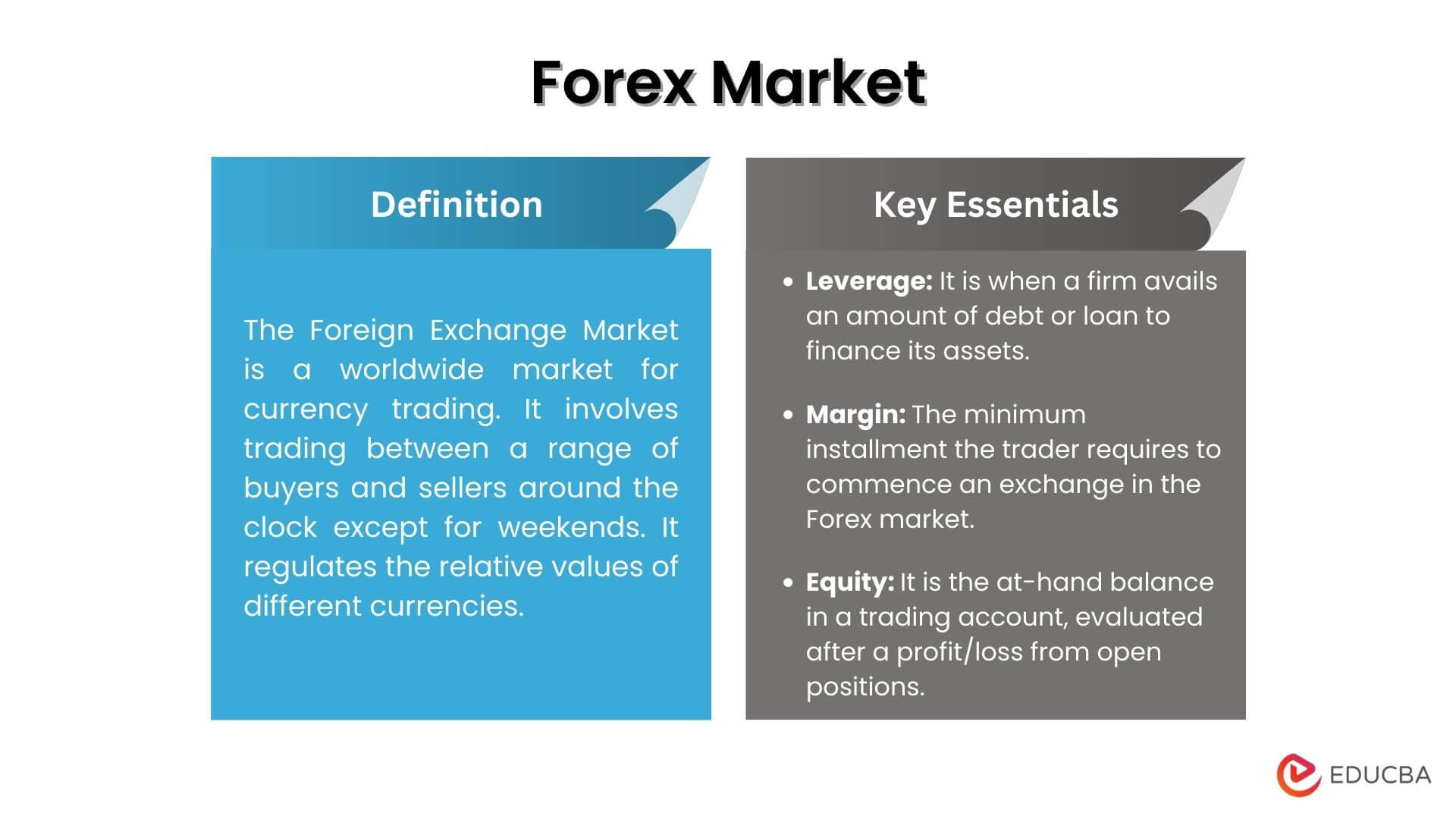
The Foreign Exchange Market (Forex Market, FX, or Currency Market) is a worldwide regionalized market for currency trading. Forex Market regulates the relative values of different currencies. It involves trading between a range of buyers and sellers around the clock, except for weekends.
In addition, there are dealers from the banking sector & insurance sector who are actively involved in Forex trading.
Key Takeaways
- The Foreign Exchange Market, commonly known as the Forex Market, is a worldwide market regionalizing currency trading.
- The market boasts high liquidity, operates 24/7 (except on weekends), offers lower trading costs, and distributes geographically. The three critical market essentials are leverage, margin, and equity.
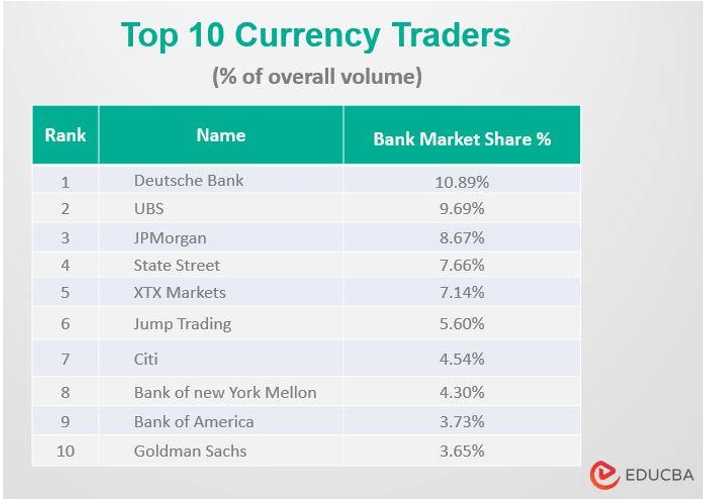
- The Centrals banks and other Commercial and Investment banks are the largest participants in the Forex market. Furthermore, Hedgers, Speculators, and brokers actively participate in the markets.
- Foreign exchange forwards, Currency futures, Currency swaps, and Currency options are a few instruments of the Forex market.
Characteristics of the Forex Market
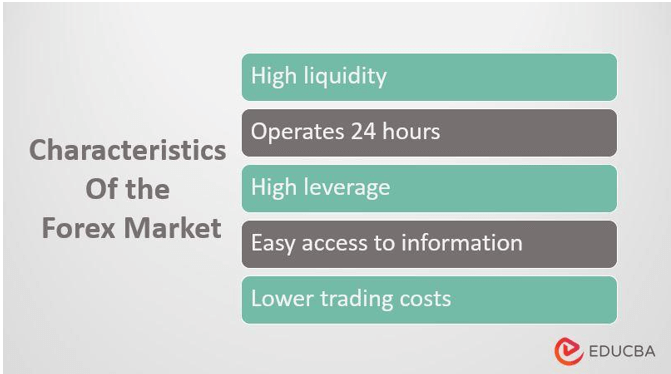
- The enormous trading volume with negligible variation in exchange rates leads to high liquidity.
- Its allocation is geographical.
- The market operates uninterrupted, i.e., the Forex trading hours are 24 hours a day, except for weekends.
- The availability and access to information on the Forex Market provide easy surveillance of Currency prices.
- It retains a low trading cost, which reduces the chance of enduring a loss.
- The usability of leverage to elevate one’s profit or loss margin.
The Three Key Essentials of the Forex Market
- Leverage: In the Forex market, it is known as leverage when a firm avails an amount of debt or loan to finance its assets. A firm is highly leveraged when it has less equity than debt.
- Margin: It is the minimum installment the trader requires to commence an exchange in the Forex market. Suppose a trader borrows an amount to obtain or purchase securities or stocks. Then, it is referred to as “buying on margin.”
- Equity: Traders establish the at-hand balance in a trading account as equity by evaluating it after factoring in the profit or loss from open positions.
Participants
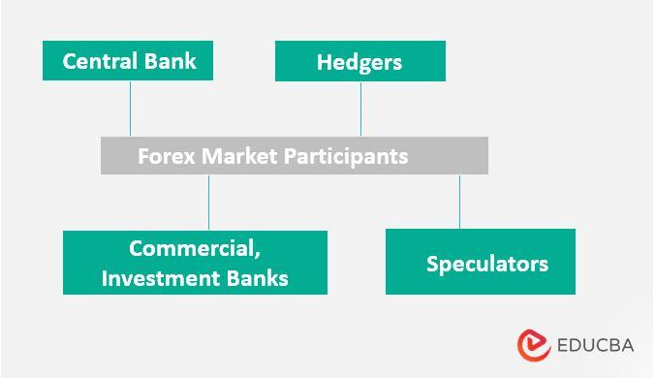
1. Central Banks
Central banks are the most dominant participants in the Forex markets. In the Forex market, the Central bank determines the rate of their respective currency. Moreover, the Central banks take the necessary measures to meet economic goals, i.e., to stabilize their economy. In many countries, Central banks act as an extension of the government & conduct their policy in agreement with the government.
2. Banks & Other Financial Institutions
Apart from the central banks, commercial banks, investment banks, and various other banks are the largest participants in foreign exchange transactions. Generally, people who require money for small purposes, i.e., studying abroad, traveling, and so on, deal with local banks. Therefore, banks act as brokers or dealers to those willing to buy/sell a currency at the bid/ask rate. Through the Forex markets, the banks exchange currency at a higher price than they paid to obtain it.
3. Hedgers
Dealing with the volatility of fluctuating currencies and foreign exchange risk is a big problem for many multinational companies. The foremost thing the shareholders & management of any company hates is uncertainty. Therefore, banks employ hedging strategies in the Forex market to deal with these uncertainties. Either locks a specific exchange rate for the future or removes all the exchange rate risk from transactions. The people who carry out the hedging strategies are known as hedgers.
4. Speculators
Another kind of participant in the Forex market is those who do not hedge against fluctuations in exchange rates. Rather, speculators try to benefit by taking advantage of the fluctuating exchange rate levels.
Instruments of Forex Market
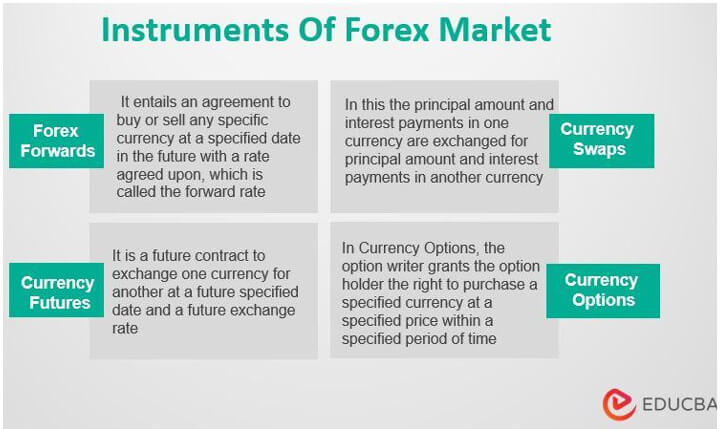
1. Foreign Exchange Forwards
Foreign exchange forwards are a contract to deal with the exchange of currencies. It entails an agreement to buy or sell any specific currency at a predetermined date with an agreed-upon rate called the forward rate.
In this case, if a buyer and seller agree on an exchange rate for a future date, the transaction will occur regardless of the market rates. Usually, the buyer & seller decides the transaction date, and the time period of the trade can be a day, a few days, months, or even years.
2. Currency Futures
Also known as Foreign exchange (Forex), a Future is a futures contract to exchange one currency for another at a specified date and a future exchange rate. It is similar to a forward contract but with a few exceptions. Currency futures contracts are traded on exchange markets, and forward contracts are traded on over-the-counter markets (OTC). In addition, futures contracts are settled down daily on a market-to-market basis. In contrast, forward contracts are settled only at expiration.
This contract has physical delivery, i.e., the buyer expects the delivery of a specified standard commodity at a specified location. In this type of contract, an investor can close their contracts any time before the contract’s delivery date. Investors enter into such types of contracts for speculating or hedging purposes.
3. Currency Swaps
Currency swaps are closely related to interest rate swaps, traded over the counter, and known as over-the-counter derivatives. In a foreign currency swap, borrowings are exchanged, where the principal amount and interest payments in one currency are exchanged for the principal amount and interest payments in another. Generally, long-term debt or foreign liability corporates enter into currency swaps to get cheaper debt and hedge against exchange rate fluctuations. Swaps consist of fixed and floating rates of interest. An example of a swap transaction is, paying a fixed dollar and receiving floating foreign currency, i.e., Pound interest.
4. Currency Options
In Currency Options, the option writer grants the option holder the right to purchase a specified Forex market instrument, i.e., currency at a specified price within a specified period. If the option holder chooses to exercise the right, the option writer should fulfill it. Futures and Forwards contracts confer obligations on both parties to sell and buy a commodity on an end-specified date. However, an options contract gives the right to one party and an obligation to the other.
A financial derivative signifies a contract the option writer (seller) sells to the option holder (buyer). This type of contract offers the buyer the right but not the obligation to buy or sell a stock or security at an agreed-upon price on a future specified date. Currency options are of two types, Call option & Put option. The Call option means the right to buy, and the Put option is the right to sell.
An investor can hedge against foreign currency risk by purchasing any currency options. For example, suppose an investor believes that the GBP/INR will increase from 83.00 to 85.00, i.e., it will become more expensive for an Indian investor to buy Great Britain Pound. Thus, the investor would buy a call option on GBP/INR to gain from an increase in the exchange rate.
The Global Forex Market
Around 500 years ago, traders set up Amsterdam’s first Foreign exchange market. It helped stabilize the currency exchange. Soon enough, Forex trades began throughout the world. By 1913 in London, trading firms expanded from 3 to 71 in less than ten years. Active since the 1970s, it is now the world’s largest financial market.
While financial institutions and banks are the most dominant participants, the latest technology has made it reachable to a broader audience. The resulting community has 9.6 million people who now trade online. Even though the largest Forex trading centers are based in the UK and USA, Asia and the Middle East constitute one-third of online traders.
Forex Market in India
The introduction of forex derivatives in India took place in the early 90s. Due to the Indian economy’s liberalization, there was a significant inflow of foreign currency capital into India. As a result, risk management, globalization of trade, and free movement of financial assets through derivative products have become a requirement in India.
Over the years, the Indian Forex market has developed significantly. As per the BIS (Bureau of Indian Standards) Triennial Survey Report of 2019, concerning daily turnover, the Indian Forex market is the 16th largest Forex market in the world. The stable growth of the Indian economy & expansion of the industrial sectors in India highly contributes to the rapid growth of the Forex Market.
Mumbai is the main center of the Indian Forex Market & other cities like Kolkata, Chennai, Delhi, Bangalore, and Cochin are the commercial capitals of the country. Indian Forex market got a boost when RBI accepted the proposal of SEBI to approve the trade of INR & GBP, INR & EURO, and INR & YEN. All these currencies were an addition to the prevailing pair of currencies, i.e., INR & USD.
Conclusion
It has been growing rapidly and will continue to grow. Forex market activity is mainly concentrated in foreign & a few private sector banks. However, today, even the public sector banks are participating in this market as market makers, not just users.
It helps an investor hedge or speculates from currency fluctuation risk; it is essential to consider the risks. A few are extreme leverage, lack of transparency, especially in complex products, counterparty exposure, general hidden risk, etc.
Increasing convertibility (simplicity of converting one currency to another) on the capital account would quicken the integration of Indian financial markets with international markets. Nevertheless, increasing convertibility also carries the risk of removing the narrowness of the Indian markets to external shocks, like the South East Asian crisis. Nonetheless, appropriate transition management will increase the growth of financial markets and the economy.
Infographic
Learn the juice of this article in just a single minute, Forex Market Infographic
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the Forex market? How does the Forex market work?
Answer: The Foreign Exchange Market is a global currency trading market. It is a platform for various investors or traders to buy or sell different currencies to make profits.
A trader chooses a currency pair, analyses the market, and then picks either to sell or to buy. For one trader selling the currency pair, there is another buying it.
Q2. Who controls the Forex market? Which is the best Forex market?
Answer: No single authority controls the Forex Market. Instead, the central banks, along with their governments, are the one that decides the value of their respective currencies.
Traders can find the best trading opportunities in the London Forex market because it trades in the heaviest volumes. Therefore, it is nearly the best Forex market.
Q3. What is Forex trading? How to trade in the Forex market?
Answer: Forex trading is a system where traders and investors speculate on the currency rates by studying the market to generate profits. The trading of currencies occurs in pairs. To start trading in Forex, you must first open a trading account with a broker. Then, after consistently analyzing the market or a specific currency pair, you select a buy/sell position in the market.
Q4. How do beginners learn Forex trading?
Answer: Acquiring fundamental knowledge about the market should be the first step. Study and understand the basic terms and operations. Know your finances and prepare a trading strategy. Taking valuable forex trading courses with established institutions will be beneficial.
Q5. What time does the Forex Market open?
Answer: It is spread worldwide over international time zones; it is open 24 hours a day. Unlike stocks, traders can trade currencies 24/7 as the market only closes on weekends.
Recommended Articles
Here are a few links to articles that will help you learn about Forex Trading.