Updated July 17, 2023
Introduction to Fixed Cost
Fixed cost is the necessary cost that is unchanged even if there is a shift (rise/fall) in a company’s sales or production activity.
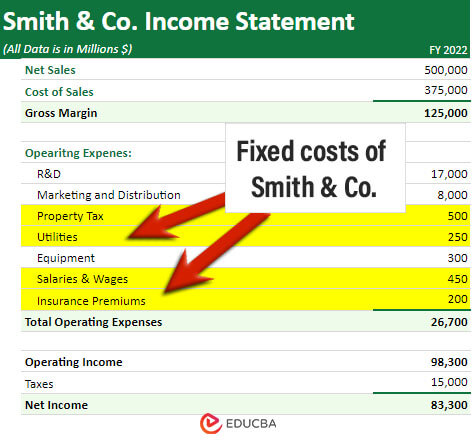
For example, Smith & Co’s income statement shows that the company holds utility bills, property taxes, salaries, wages, and insurance premiums as fixed costs. The total amount accounts for $1,400 million.
Fixed costs remain constant over a specified period, such as a financial year, quarter, month, or any other period. One can forecast or predetermine it for a particular period. Since the cost remains constant throughout the specified period, reporting and auditing become very easy. Suppose the business stops for any reason, the indirect costs would still be payable.
Key Highlights
- A fixed cost is an obligation a company bears and must pay regardless of the incurred profit or loss.
- One calculates it by subtracting the total cost of production from the product of the number of units produced and the variable cost per unit.
- The factors contributing to it are insurance, wages, rent, maintenance, etc.
- It may impact profitability at varying points on the income statement, and it might be direct or indirect.
- It is also helpful for investors, as it helps them assess the riskiness of an investment in the company.
Examples
Overhead costs are expenses that a business incurs and must pay, regardless of its level of profit or loss. Some of the common factors that contribute to overhead costs include:
- Rent or mortgage payments: Whether a business has a slow or busy month, it must pay the same rent or mortgage payment each month.
- Insurance premiums: Insurance helps businesses to cover unexpected events such as fire, flood, or theft. The payment for insurance remains the same for each financial year.
- Utility bills: Businesses pay the same monthly fee for utilities such as water and electricity, regardless of usage.
- Equipment leases or purchases: Organizations must pay for equipment leases or purchases while purchasing an asset.
- Labor costs: Labor costs include both variable and fixed costs. Payments to full-time employees generally come under fixed costs.
- Licenses: Many businesses require licenses or permits to operate lawfully and must renew them. For instance, businesses that sell alcohol need to apply for and renew their liquor licenses annually.
- Maintenance: Costs associated with maintenance include cleaning supplies, machinery repairs, and yearly tune-ups for vehicles. These expenses are generally constant and occur on a predetermined schedule.
- Loans: Many companies take out loans to launch their businesses, and they must repay them monthly.
Fixed Cost Formula
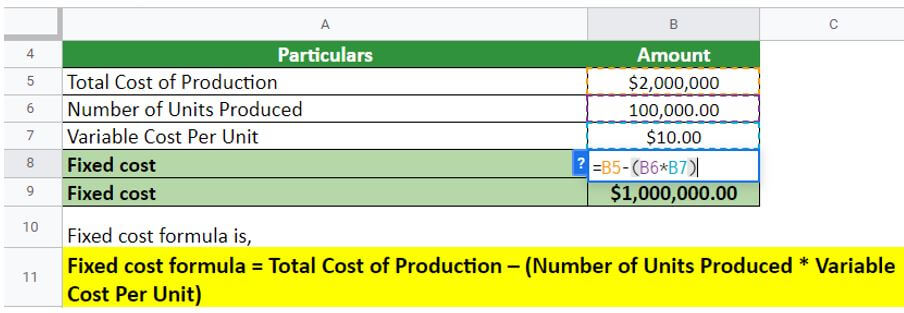
We calculate fixed cost by subtracting the product of the number of units produced and the variable cost per unit from the total cost of production. Simply put, one derives it by subtracting the variable cost from the total cost.
The formula for fixed cost is:
The variables used in this formula are:
- Total Cost of Production: This is the sum of all costs incurred in producing a good or service.
- Number of Units Produced: This refers to the total number of units produced during a specific accounting period.
- Variable Cost Per Unit: This is the cost of producing one unit of a product or service, including materials, labor, and other expenses that vary based on production volume.
How to Calculate Fixed Cost? Excel Examples
Example #1
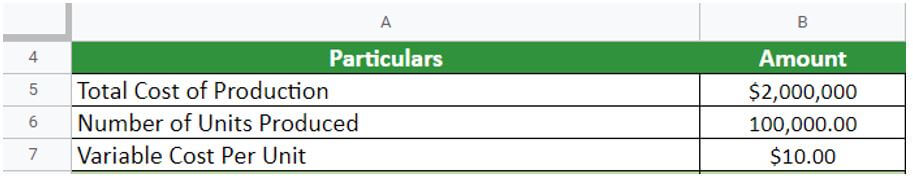
Let’s assume that Gifts & Co. produces 100,000 units of goods per year, and the total cost of production is $2,000,000. Also, the variable cost per unit is $10, and the company produces 100,000 units. Calculate the fixed cost:
Given:
Solution:
In the above scenario, the fixed cost for the company would be $1,000,000, which means that the company has to clear this cost irrespective of the company’s overall performance.
Example #2
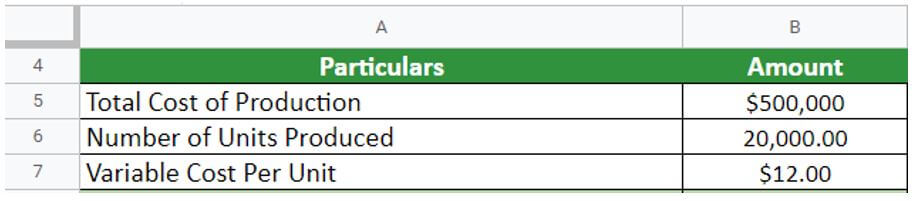
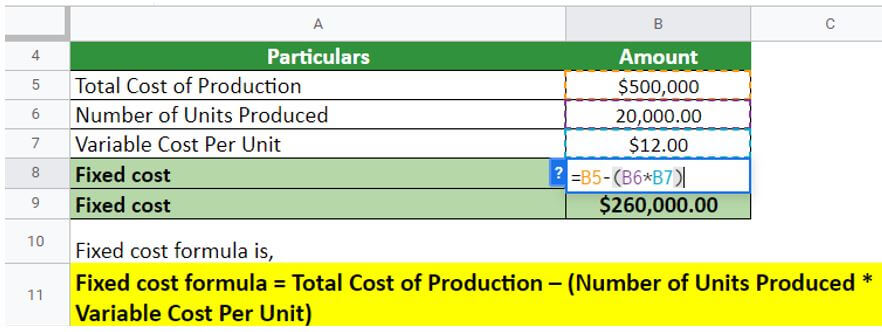
Now let’s take the example of XYZ limited. They have provided the following details:
- Number of units produced = 20000
- Total cost of production per unit = $25
- Variable cost of production= $12 per unit
Calculate the fixed cost for the company.
Given:
Solution:
In the above scenario, the fixed cost for the company is $260000. These are some costs that the company is liable to pay despite the rise or fall in profit.
Example #3
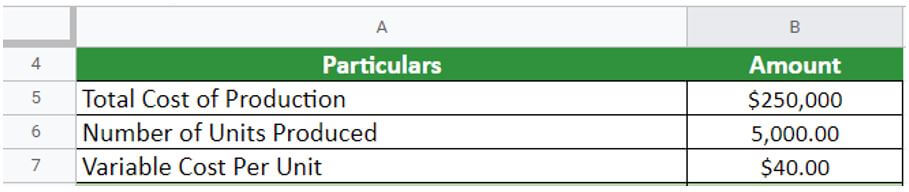
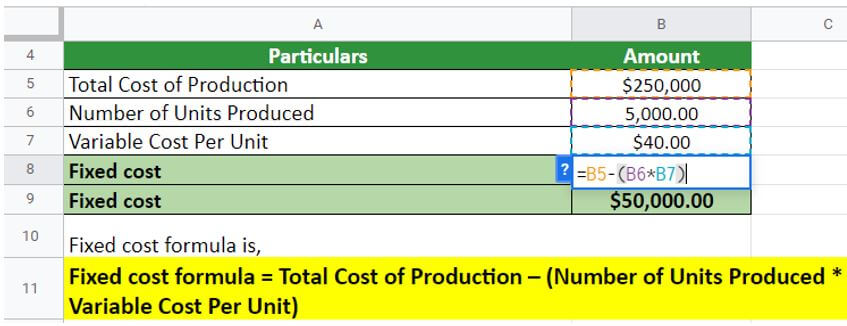
ABC Limited is a bag manufacturing company that produced 5000 bags in January 2022. The total cost of production is $250000 as per the production manager. The company also estimated that the variable cost per unit is $40 per unit. Calculate the fixed cost for the company.
Given:
Solution:
The fixed cost for the company is $50000. These costs are likely attributed to employees’ wages, materials required for bag production, insurance charges, etc.
Example #4
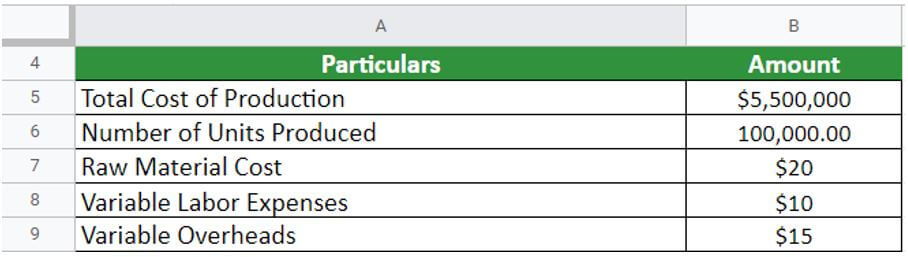
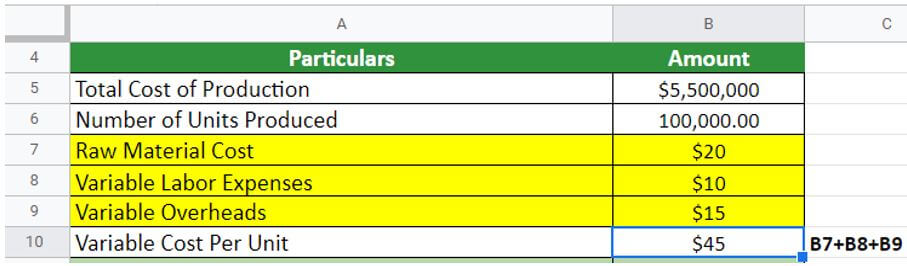
Here is another example from Shoe Limited, which manufactured 100000 units of shoes in the financial year 2021. Accordingly, the company has provided the following details:
- Raw material cost = $20
- Variable labor expenses = $10 per unit
- Variable overheads = $15 per unit
- Total cost of production = $5500000
Calculate the fixed cost for the company.
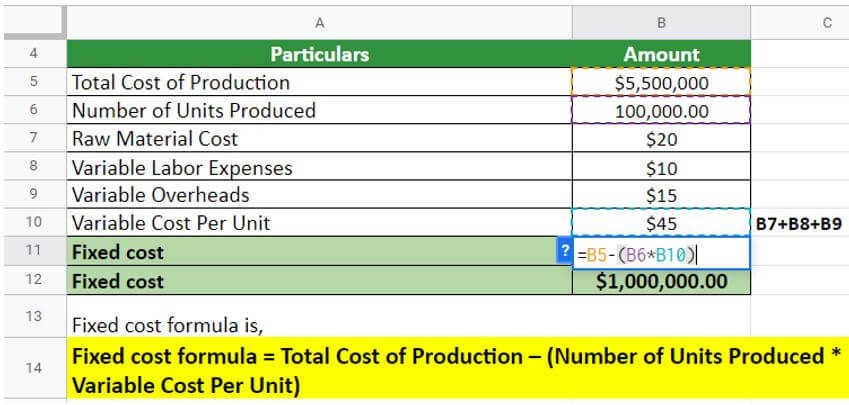
Given:
Now, let’s calculate the total variable cost per unit:
In this scenario, the total variable cost per unit = 20+10+15 = $45 per unit
Solution:
Thus, the fixed cost for the company will be $1000000, and the company must pay this regardless of the incurred profit or loss.
Types
Sunk Costs
- Sunk costs refer to expenses that have already been incurred and cannot be recovered.
- An example would be the purchase price of a piece of machinery that is no longer in use.
Committed Costs
- Committed costs are expenses that have been incurred but can be changed in the future.
- An example would be the monthly rent for factory space. If the business decides to move to a new location, the committed cost will change accordingly.
Fixed vs. Variable Costs
| Fixed Cost |
Variable Cost |
| Fixed Costs are constant. | Variable Costs vary with production output. |
| Occurs even if the company’s output is zero. For instance, a company may have to pay rent for its factory regardless of whether or not it is making any product. | Variable costs are those liabilities that incur when the company is actually carrying out production. |
| Includes interest on loans, insurance, rent, property taxes, etc. The company is liable to pay such expenses despite the rise and fall in the business. | It is the cost of raw materials for production. Thus, if there is no production activity, the company need not bear any costs. |
| Does not fluctuate more and is easier to predict than the variable costs. | Unlike fixed cost, it is always fluctuating. |
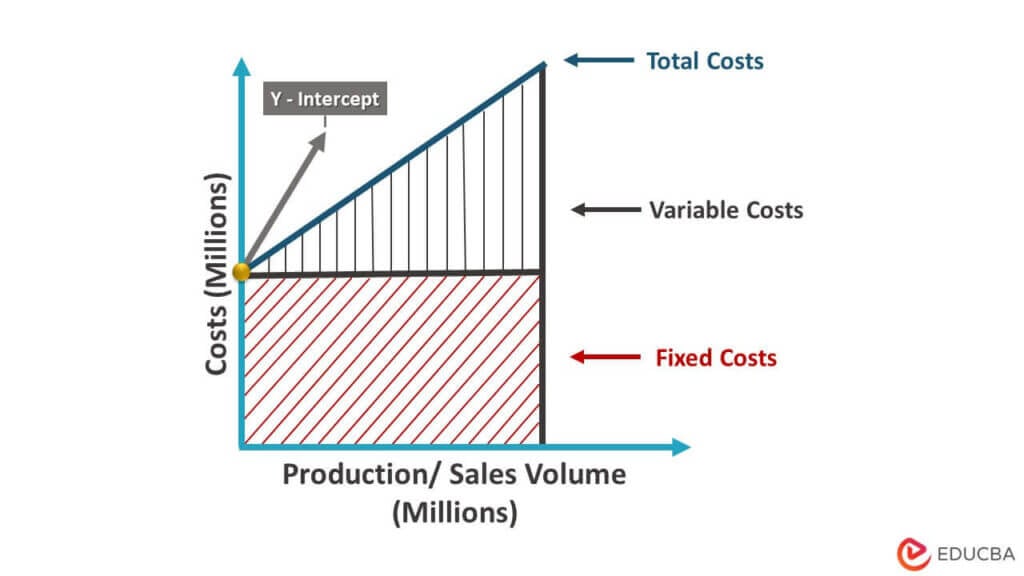
Fixed Cost Graph
- The graph above depicts the company’s total indirect costs, which are expenses that do not vary with production or sales volume, such as rent, property taxes, and interest on the debt.
- The vertical axis represents the costs (in millions), while the horizontal axis represents production or sales volume (also in millions).
- The upper shaded region represents the variable costs, while the line parallel to the y-axis represents the fixed costs.
- The y-intercept is the meeting point on the y-axis, which represents the fixed costs of the company at the beginning of the production cycle, i.e., when the production is zero.
- This graph is a valuable tool for management as it provides a clear picture of the company’s overall financial health.
- Investors can also benefit from this graph as it can help them assess the risk associated with investing in the company.
Fixed Cost in Break-even Analysis
- In break-even analysis, fixed cost is a key component. It is the total cost of production that does not vary with output.
- Unlike the fixed cost, the variable cost can vary and depends solely on the production output level of services and goods.
- The break-even point is the point at which a company’s revenues exactly cover its expenses. At this point, the company is neither making a profit nor a loss.
- One determines the break-even point by dividing the total costs by the unit selling price minus the variable costs per unit. The formula for the break-even point is as follows:
For example, suppose a company has fixed expenses of $100,000 and variable costs of $10 per unit produced. The unit selling price is $20. In that case, the break-even point would be $100,000 / ($20 – $10) = 500 units. At this point, the company will have enough revenue to cover its expenses but not enough to turn a profit. To achieve profitability, the company must produce and sell more units.
Importance
- Fixed costs can be direct or indirect and impact the business’s profitability.
- If fixed costs are not monitored and kept below a certain level, they can negatively impact the business’s stock value.
- Since fixed costs do not change over a specified period, management can make informed decisions best suited to market conditions, and that can boost sales or reduce variable costs.
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages |
Disadvantages |
| Fixed and does not change. Thus, the management can keep it as a predetermined amount and make decisions. | Requires heavy monitoring so that no more factors increase the business’s cost. |
| Based on a specific period and does not change with changes in business activities and outputs. | It can change in the future due to changes in norms, policies, schedules, or agreements. |
| Once the overhead costs are identified, they do not change until the specified period of an agreement or a schedule, thereby bringing stability to the business. | The profit of businesses with high overhead costs will have a negative impact when sales decline. |
| The fixed is relatively easy to record and audit since it does not change for a period of time. | Impacts the business’s profitability, and any increase in indirect costs in the future would result in reduced profits. |
Calculator
Use the following calculator for Fixed Cost calculations.
| Total Cost of Production | |
| Number of Units Produced | |
| Variable Cost Per Unit | |
| Fixed Cost = | |
| Fixed Cost = | Total Cost of Production - (Number of Units Produced * Variable Cost Per Unit) |
| = | 0 - (0* 0) = 0 |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What are variable and fixed costs?
Answer: “Fixed costs” are defined as constant expenses regardless of a company’s level of production activity. However, “variable cost” refers to a type of cost that fluctuates in response to changes in production levels.
Q2. What is the fixed cost per unit?
Answer: Fixed cost per unit, also known as the average cost, refers to the cost of producing each merchandise, including all fixed costs associated with running a business. It helps businesses determine a price point for their goods and services. It is important because a business cannot generate profit if one does not include it in the product’s price.
Q3. What are the 3 elements of cost?
Answer: The three elements of cost are direct material, direct labor, and overhead.
- Direct material is the cost of the raw materials for producing a product, including lumber, steel, fabric, and other materials used in the manufacturing process.
- Direct labor is the cost of labor necessary to produce a product, including workers who receive payment by the hour or by piecework.
- Overhead is the cost of indirect expenses incurred while producing a product, including rent, utilities, property taxes, and insurance.
Q4. Is depreciation a fixed cost?
Answer: Depreciation is often thought of as a fixed cost because it is a cost that is incurred regardless of whether or not the business is operating. However, depreciation is a variable cost because it depends on the usage of the assets. In short, the more an asset comes into use, the higher its depreciation expense will be.
Q5. What is the average fixed cost?
Answer: Fixed cost remains unaffected by a business’s output or activity level. This means the average overhead cost will be the same over a set period, no matter if there is a rise or fall in the production level. For example, if the monthly rent is $2,000 and 100 widgets are produced at $4 each, the average fixed cost per widget is $20 (($2,000 + $400)/100).
Q6. What does Fixed cost include?
Answer: Many items can come under the domain of fixed cost. The most common types are advertising, office expenses, rent, salaries, and utilities. These costs will not change no matter how much or how little business occurs. Other items that can be included are insurance and interest payments.
Q7. What happens to the average fixed cost as output increases?
Answer: As output increases, the average fixed cost decreases. This is because fixed costs are spread out over a larger number of units of output, so each unit of output has a smaller share of the fixed costs.
Recommended Articles
Here are some further related articles for expanding understanding: