Introduction to Final Class in Java
A class declaration with the word Final is known as the final class. Final Class in Java can not be inherited & can not be extended by other classes. A final class can extend other classes; It can be a subclass but not a superclass. When creating an immutable class, the final class is the best answer. The final class is a declaration that says it’s final, i.e., this class has no subclass & can not be extended further. The final class keeps some more importance besides immutability.
Sometimes, it is best practice to use the final class for security purposes, As some classes perform security-related things like authentication and authorization. In such a scenario, strings and methods inside of the class should not be modified in the whole life cycle of the application, then making the class final is a better practice.
Making the class, Final improves the efficiency of the application.
Syntax:
final class Student {
private int age = 3;
}
/* // Trying to inherit the Student class
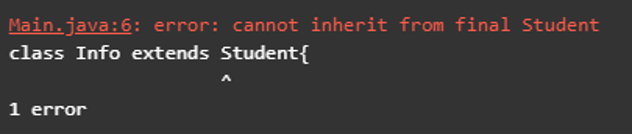
class Info extends Student{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//creating instance of the HeavyVehicle class
System.out.println(“I am unable to inherit the class with the final keyword”);
}
}The above-given class with the final word is final. Extending this final class with another will produce errors such as “error: cannot inherit from final Student,” as given in the screenshot below.
How does Final Class work in Java?
When declaring a class with the final keyword, It enables JVM to make assumptions & optimization. Once you add the final keyword to any class in Java, the reference for that class cannot be changed. The compiler will check if any referencing is retaking place, producing an error.
What happens if we declare any class final & instantiate any final class? Then it becomes created in the pool area; objects created in the pool have a special immutability feature. Some of the best examples of immutable java classes are String, Integer, Double, etc.
If you declare a class as final, then it implicitly declares all methods of that class as final. The final is a modifier in Java; you can use the final keyword on a variable, method, or class. Once the modifier was added to the class, all variables & methods of that class would be immutable implicitly. Making a class immutable provides several benefits, such as It is read-only & can not be safely shared in multiple threads without any synchronization.
Examples of Final Class in Java
Given are the following examples of Final class in Java:
Example #1
The HeavyVehicle class does not allow inheritance in the given program since it is declared a final class.
Code:
//This class will not be extended
final class HeavyVehicle{
void messages(){
System.out.println("Your Vehicle Insurance is going to be expire in the next month");
}
}
// Inheriting HeavyVehicle class is not allowed as it is a final class
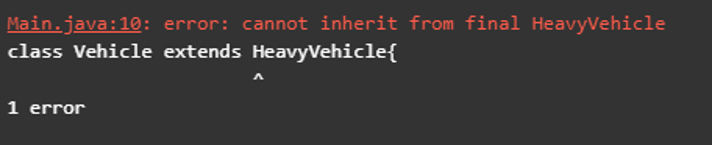
/*class Vehicle extends HeavyVehicle{
}
*/
//main class
class Car{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//creating instance of the HeavyVehicle class
HeavyVehicle hvObj = new HeavyVehicle();
hvObj.messages();
}
}If we try to inherit the HeavyVehicle class, we will get the following error, as given in the screenshot below.
Now we will move to the next class, where we create an instance of the final class to use its method. Below is the output of the program after skipping the inheritance process.
Example #2
In this program, the HeavyVehicle class is declared a final class, so it can not be extended in the other class, so it explicitly passes its reference to the Vehicle class method.
Code:
//This class will not be extended
final class HeavyVehicle{
public double getDistanceCanCover(int mileage, double fuelStatus) {
return mileage * fuelStatus;
}
}
class Vehicle{
private int mileage;
private double fuelStatus;
Vehicle(int mileage, double fuelStatus){
this.mileage = mileage;
this.fuelStatus = fuelStatus;
}
public void DisplayDistanceCanCover(HeavyVehicle hvObj) {
double distCanCover = hvObj.getDistanceCanCover(this.mileage, this.fuelStatus);
System.out.println("Distance Vehicle can cover in the available fuel: " + distCanCover);
}
}
//main class
class Car {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//creating instance of the HeavyVehicle class
HeavyVehicle hvObj = new HeavyVehicle();
//creating instance of the Vehicle class
Vehicle vehObj = new Vehicle(30, 3.5);
//calling the method of the
vehObj.DisplayDistanceCanCover(hvObj);
}
}In the above-given example, we can see how a final class can be used effectively. The output of the above-given program is given below.
Output:
Example #3
In this example, the final class inherits the other class, i.e., Student, but no other classes can extend the Info class because it is a final class.
Code:
class Student{
public void showDetails(String name, String email, int age) {
System.out.println("\nStudent Name : "+ name);
System.out.println("\nStudent Email : "+ email);
System.out.println("\nStudent Age : "+ age);
}
}
// Trying to inherit the Student class
final class Info extends Student{
//main method of java to start program execution
public static void main(String[] args) {
//creating instance of this class
Info infoObj = new Info();
//calling here method of the parent class
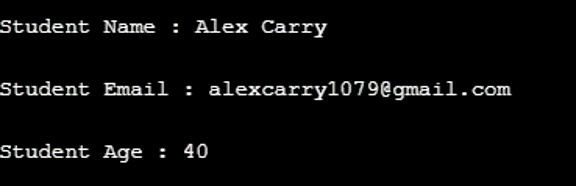
infoObj.showDetails("Alex Carry", "[email protected]", 40);
}
}Output:
Conclusion
In the above-given article, we went through the importance of the Final class in Java. I also reviewed that people commonly refer to the final class in Java as an immutable class. I noticed some essential points related to declaring a final class. In the given example, we can see how the final class can be used effectively in other classes by passing it through references.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Final Class in Java. Here we discuss how does Final Class work in Java? Along with the respective examples. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –