Updated June 28, 2023
Introduction to Java Period
A java period is a class used to measure time in years, months, and days. The package of the Period class in java is java.time.Period. The Period class object specifies the period of time or is used to determine the difference between two times in years, months, and days. A Period object is immutable and thread-safe also as the Period object is immutable, so we cannot change its values once it is created. But, we can create new Period objects based on another Period object. The Period class inherits an object class ( as the object is the superclass of all classes in java) and implements the ChronoPeriod interface.
Syntax:
The syntax of the Period class declaration in java is as follows:
public final class Period extends Object implements ChronoPeriod, Serializable
{
// variables and method of the class Period
}Methods to Explain Java Period
The lists of Period class methods are explained below with example code; an example code can be used further for similar methods (as for each method example code not given):
- long get(TemporalUnit unit): Return the value of the requested unit.
- The static period between(LocalDate startInclusive, LocalDate endExclusive): Return Period object is the period between two dates of the number of years, months, and days.
Code:
import java.time.Period;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.temporal.ChronoUnit;
public class PeriodClassDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Period p = Period.between(LocalDate.ofYearDay(2017, 20), LocalDate.ofYearDay(2017, 30) );
System.out.println(p);
System.out.println(p.get(ChronoUnit.DAYS));
System.out.println(p.get(ChronoUnit.MONTHS));
System.out.println(p.get(ChronoUnit.YEARS));
}
}Output:
- Temporal addTo(Temporal temporal): Return Period object, which is the addition of temporal and this Period object.
Code:
import java.time.Period;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.temporal.ChronoUnit;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
public class PeriodClassDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
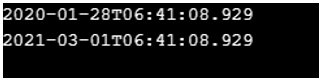
Period period = Period.of(1,1,1);
LocalDateTime d = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println(d);
d = (LocalDateTime)period.addTo(d);
System.out.println(d);
}
}Output:
- boolean equals(Object otherPeriod): Checks this Period with specified period and return Boolean.
- boolean isNegative(): Return True if this period is negative.
- boolean isZero(): Return True if this period is negative.
Code:
import java.time.Period;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.temporal.ChronoUnit;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
public class PeriodClassDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
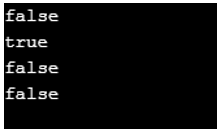
Period p1 = Period.of(1,1,1);
Period p2 = Period.of(10,5,2);
Period p3 = Period.of(10,5,2);
System.out.println(p1.equals(p2));
System.out.println(p2.equals(p3));
System.out.println(p2.isNegative());
System.out.println(p2.isZero());
}
}Output:
- static Duration from(TemporalAmount amount): Obtains an instance of the period from a temporal amount.
Code:
import java.time.Period;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.temporal.ChronoUnit;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
public class PeriodClassDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Period p = Period.from(Period.of(10, 5, 2) );
System.out.println(p);
}
}Output:
- IsoChronology getChronology(): Return the chronology of this period, which is of the ISO calendar system.
- int getDays(): Return Period in days.
- int getMonths(): Return Period in months.
- List<TemporalUnit> getUnits(): Return set of units supported by this period.
- int hashCode(): Return hash code for this period.
Code:
import java.time.Period;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.temporal.ChronoUnit;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
public class PeriodClassDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
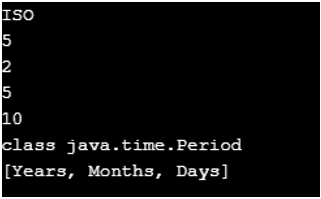
Period p = Period.from(Period.of(10, 5, 2) );
System.out.println(p.getChronology());
System.out.println(p.get(ChronoUnit.MONTHS));
System.out.println(p.getDays());
System.out.println(p.getMonths());
System.out.println(p.getYears());
System.out.println(p.getClass());
System.out.println(p.getUnits());
}
}Output:
- Period minus(TemporalAmount amountToSubtract): Returns object resulting from this period subtracted with the specified period.
- Period minusDays(long daysToSubtract): Returns object they subtracted with the specified Days.
- Period mindsmonths(long months): Returns object, the result of this period subtracted with the specified months.
- Period minusYears(long years): Returns object, which is the result of this period subtracted from the specified years.
- Period multipliedBy(long multiplicand): Returns a period object multiplied by the scalar.
- Period negated(): Returns a period object that results from this period with the length negated.
- Period normalized(): Returns a period object that results from this period with normalized in the years and months.
- static period of(int years, int months, int days): Returns a Period object representing several years, months, and days.
- static Period ofDays(int days): Returns a Period object of several days.
- static Period ofMonths(int months): Returns a Period object of several months.
- static Period ofWeeks(int weeks): Returns a Period object of several weeks.
- static Period ofYears(int years): Returns a Period object of several weeks.
Code:
import java.time.Period;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.temporal.ChronoUnit;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
public class PeriodClassDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Period p1 = Period.of(10,5,2);
Period p2 = Period.of(20,5,2);
System.out.println(p1.getDays());
System.out.println(p2.getDays());
System.out.println(p1.minus(p2).getDays());
System.out.println(p1.minusDays(2).getDays());
System.out.println(p1.minusMonths(1).getDays());
System.out.println(p1.minusYears(1).getDays());
System.out.println(p1.multipliedBy(2).getDays());
System.out.println(p1.negated().getDays());
System.out.println(p1.normalized().getDays());
Period p3 = Period.ofDays(1);
System.out.println(p3.getDays( ));
Period p4 = Period.ofMonths(2);
System.out.println(p4.getMonths());
}
}Output:
- static Period parse(CharSequence text): Return Period object from a text, for example, PnYnMnD.
- Period plus(TemporalAmount amountToAdd): Return the period object of this period with added the specified period.
- Period plusDays(long daysToAdd ): Return a period object of this period with added the specified days.
- Period plusMonths(long monthsToAdd): Return a period object of this period with added the specified months.
- Period plusYears(long yearsToAdd): Return a period object of this period with added the specified years.
Code:
import java.time.Period;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.temporal.ChronoUnit;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
public class PeriodClassDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Period p1 = Period.of(10,5,2);
Period p2 = Period.parse("P1Y2M3D");
System.out.println(p2.getMonths());
Period p3 = p1.plus(Period.ofDays(5));
System.out.println(p3);
}
}Output:
- Temporal subtractFrom(Temporal temporal): Return Subtraction of this period from a temporal object.
- String toString(): Return this period in string representation, such as PT8H6M12.345S.
- long toTotalMonths(): Return the total number of months in this period.
- Period withDays(int days): Return a period object of this period with the specified amount of days.
- Period withMonths(int months): Return a period object of this period with the specified amount of months.
- Period withYears(int years): Return a period object of this period with the specified amount of Years.
Code:
import java.time.Period;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.temporal.ChronoUnit;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
public class PeriodClassDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
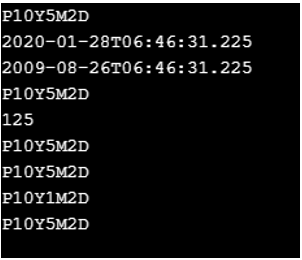
Period p1 = Period.of(10,5,2);
System.out.println(p1);
LocalDateTime d = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println(d);
d = (LocalDateTime)p1.subtractFrom(d);
System.out.println(d);
System.out.println(p1.toString());
System.out.println(p1.toTotalMonths());
System.out.println(p1.withDays(2));
System.out.println(p1.toString());
System.out.println(p1.withMonths(1));
System.out.println(p1.toString());
}
}Output:
Conclusion
The Period class is one of the built-in class in java, which is used to measure time in years, months, and days and add, subtract, and convert the period, or in simple words, the period class allows one to operate on day or month, or year period. The period class is available in java.time.Period package of java.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Java Period. Here we discuss the basic concept and lists of Period class methods with example code and outputs, respectively. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –