What is Economic Utility?
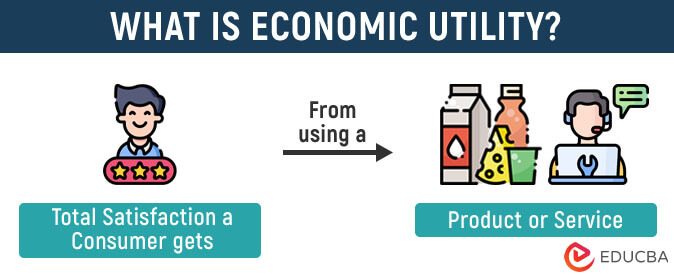
Economic utility refers to the amount of fulfillment or satisfaction a person receives from consuming a particular product or service at a specific time. In other words, it is the satisfying power of any good or commodity.
Daniel Bernoulli, an 18th-century Swiss mathematician, first proposed this concept. According to the economic utility theory, a rational consumer wants to get maximum satisfaction from spending the least amount of money. Since then, economists have used this concept to explain how consumers choose what to buy and how much to spend.
Economic utility is an entirely subjective concept. People can derive different levels of utility from the same product based on various factors. For instance, the satisfaction of a cold glass of water after spending 8 hours in the sun would be drastically different from consuming the same glass of water while lounging in your home.
Economic Utility Types (with Examples)
We can divide economic utility into four main types:
- Form
- Time
- Place
- Possession
We will now discuss each form of economic utility in detail:
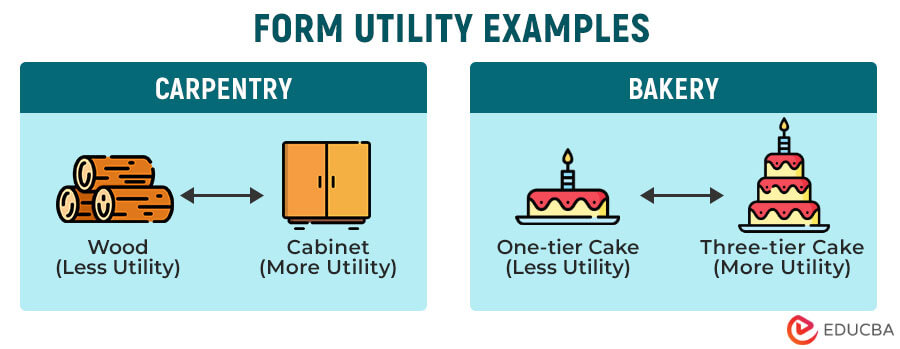
1. Form Utility
Form utility is the value that the customer sees in a finished product. It means that the utility comes from a product’s physical form, such as functionality, features, design, shape, etc. Thus, companies focus on increasing the benefits that the finished product provides the consumer.
Example #1: A company uses wood (raw material) to make a finished wooden cabinet. This way, the company adds significant value to the wood that has less utility for the customer by making it into a product (cabinet) that has greater utility.
Example #2: Let’s consider a bakery selling cakes. The economic utility of a customized three-tier wedding cake would be far more than a simple chocolate cake. Therefore, with each cake layer, the bakery adds more utility to the cake. That is, the more ingredients, decorations, and efforts go into the product, the more its utility increases.
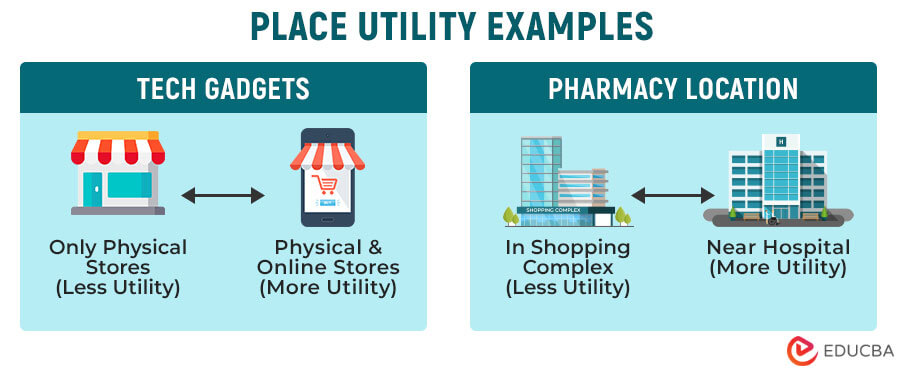
2. Place Utility
Place utility comes from the location where the product or service is available. The accessibility of the product increases its attractiveness to consumers. Therefore, a product that is easily accessible and available in various locations may give consumers a higher level of place utility.
Example #1: Suppose you sell popular high-tech AI gadgets. However, you only have a few physical stores and no online presence. As most of the younger generation buys online, the place utility of your gadgets is less as they are not easily accessible. However, if you decide to sell your gadgets online, the product’s place utility will increase.
Example #2: If you want to start a pharmacy, picking a spot close to a hospital or clinic is a good idea. That’s because people are more likely to buy medicine right after seeing a doctor. However, opening the pharmacy in the middle of a shopping area might not be as convenient for customers, reducing the shop’s place utility.
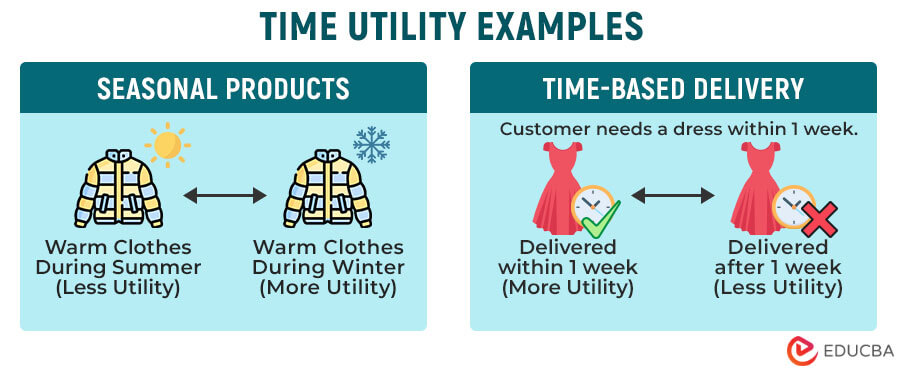
3. Time Utility
Time utility is the utility that the consumer gets from the timing of a product or service’s availability. If the products and services are available when the customer needs them, the time utility of the product will be the highest. For instance, a customer may need a specific good depending on the season or festival.
Example #1: As we know, the demand for warm clothes increases during the winter. Thus, if you decide to sell products as per the season, you provide maximum time utility to the customers.
Example #2: Suppose you run an online apparel brand, and a customer orders a prom dress she needs in a week. Now, the earlier you deliver the dress, the higher will be the time utility. Suppose you fail to deliver the dress within the week; it will have no utility for the customer as she needs the dress in that specific time frame.
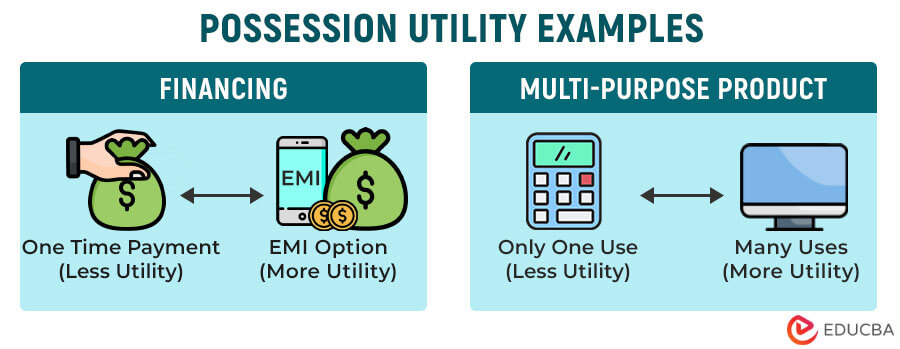
4. Possession Utility
Possession utility is the amount of satisfaction a person derives from owning a specific product or service. If a product is useful for multiple purposes, the possession utility of the product increases.
Example #1: Suppose you want to purchase a high-end gaming laptop, which is quite expensive, and you can’t afford to pay the money at once. However, the company offers easy EMI options, which makes it easier for you to buy the laptop, increasing its possession utility.
Example #2: Imagine you used to sell items like video games, typewriters, and calculators separately, and customers only bought them when they needed them. But now, you are selling computers that can replace all those products. This means customers can do many things with just one product, making it more valuable. This increases the benefit of owning the computer, increasing the possession utility.
How to Measure Economic Utility?
Measuring economic utility is not easy, as how much satisfaction a person receives from consuming a product is subjective. However, economists widely use the following two measurement methods:
1. Ordinal Utility
Modern economists like John Hicks and R.J. Allen introduced the concept of ordinal utility. They believed that people could not express the utility derived in numbers. As per them, ranking products based on the preference of one product over another is more realistic and practical. Therefore, the ordinal utility uses ranks to measure a consumer’s preference for one product over another.
2. Cardinal Utility
Traditional and neo-classical economists are more in favor of this method. As per cardinal utility, a person can assign a numerical value to the satisfaction they derive from a product. “Utils” is the measuring term for a cardinal utility where one util refers to one unit of satisfaction.
When you measure economic utility this way, you can use two concepts: Total and Marginal Utility.
- Total Utility: It is the total satisfaction a consumer derives from consuming all units of a product. For example, a child eating a bag of chips will get more satisfaction from eating the whole packet compared to satisfaction from one piece of chip in the bag.
- Marginal Utility: It is the amount of satisfaction a consumer gets from consuming one extra unit of a product. However, the Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility says that when you have more units of a product, each extra unit may not make you as happy as the first. For example, with chips, if a child eats more and more packets, they won’t enjoy each new packet as much as the first one.
Total and Marginal Utility Example
Here is how you can calculate total and marginal utility.
Question:
Suppose you are hungry and you buy 6 bananas. When you eat the first banana, you achieve a certain level of satisfaction, let’s say 30 utils. As you eat more bananas, your total utility keeps increasing until you are full. Let’s say you are full by the 4th banana. After this point, the total utility will decrease with each banana you eat.
Given:
Suppose you assign the following utils to each quantity consumed. Here, Q is the quantity consumed, and TU is the total utility.
| Quantity Consumed (Q) | Total Utility (TU) |
| 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 30 |
| 2 | 40 |
| 3 | 45 |
| 4 | 45 |
| 5 | 42 |
| 6 | 37 |
Now, let’s calculate marginal utility and see how satisfaction changes with each additional banana consumption.
Marginal Utility Formula
The table below shows the different values of total and marginal utility. We have applied the above formula to calculate the marginal utility (in column 3) and added calculations in the last column.
| Quantity Consumed (Q) | Total Utility (TU) | Marginal Utility (MU) | Calculation of Marginal Utility |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | – |
| 1 | 30 | 30 | (30-0)/(1-0) = 30 |
| 2 | 40 | 10 | (40-30)/(2-1) = 10 |
| 3 | 45 | 5 | (45-40)/(3-2) = 5 |
| 4 | 45 | 0 | (45-45)/(4-3) = 0 |
| 5 | 42 | -3 | (42-45)/(5-4) = -3 |
| 6 | 37 | -5 | (37-42)/(6-5) = -5 |
Result:
- The total utility (TU) gradually reaches its maximum point and then starts decreasing.
- The marginal utility (MU) decreases with every additional unit of quantity consumed.
- When TU is at its maximum (45) at the 4th unit, MU is 0. It is the saturation point where consuming one more unit of a product no longer adds to the total satisfaction.
Importance
Understanding the economic utility of a product or service enables businesses to:
- Improve the value of the products and services: When a business knows the type of utility consumers derive from a product, they can develop their marketing strategies to highlight those features. This will attract consumers toward those products and increase the perceived value of those products.
- Determine the best production and pricing levels: This theory helps businesses determine how many items they can sell and what the optimal price should be.
- Improve customer satisfaction: By offering products or services that offer various types of utility, businesses can increase customer satisfaction and loyalty, ultimately leading to more sales.
- Innovate and differentiate their products and services: Businesses can innovate and differentiate their products and services from their competitors by focusing on different types of utility. This helps them stay ahead of the competition.
Final Thoughts
Economic utility is an important economic idea because it helps us understand why people buy things and what makes products popular. It not only helps in understanding consumer behavior but can also help in influencing it. Companies can launch marketing campaigns to create utility for a new product before introducing it into the market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. How does economic utility affect an individual’s decisions?
Answer: The economic utility concept helps you decide which products to purchase given your budget. According to utility theory, most people want to achieve maximum utility by spending minimum money. So, you will end up buying products that make you happier at less cost.
Q2. How does economic utility affect pricing?
Answer: Understanding the economic utility of products can help companies determine the price of the products. Goods and services with higher utility are more in demand; therefore, companies can set a higher price point for those products and vice-versa.
Q3. Are utility and demand the same thing?
Answer: No, they are two different concepts. Utility refers to how you feel after consuming a product at a specific price. Conversely, demand is the ability and willingness of a person to buy a product at a particular price.
Q4. What is the difference between economic utility and market value?
Answer: Economic utility is the satisfaction or utility a consumer derives from a product or service. On the other hand, market value is the amount a customer is willing to pay for the product or service.
There is a direct relationship between economic utility and the market value of a product or service, as the higher the economic utility of a product or service, the higher its market value will be.
Recommended Articles
We hope you enjoyed reading this article about economic utility. You may also take a look at some of the useful articles here: