Updated July 19, 2023
Introduction to Dimsum Bond
Dimsum bonds are debt instruments that are similar to euro bonds and are issued outside of China by a Chinese company or foreign company but denominated in the Chinese renminbi and also settled in RMB.
Dim sum bonds were initially issued in Hongkong and were named after renowned cuisine in Hongkong, dim sum. In 2007, the Chinese development bank first issued the dimsum bond. Till 2010, only entities from Hongkong and China could issue these bonds. After this, changes in policy by the Chinese government and deregulation included foreign corporations and entities, e.g, McDonald’s to issuing renminbi-denominated bonds. China construction bank was the first bank to issue dimsum bonds in London in 2012 followed by non-Chinese banks such as HSBC and Banco do Brasil.
How Does it Work?
In order to raise money in assets that are denominated in the Chinese renminbi, international investors may participate in dimsum bond markets. foreign companies who are willing to invest in debt issued in renminbi or yuan but are not able to do so due to strict debt regulations incorporated by the Chinese government can do so by investing in dimsum bonds as these bonds do not require approval from people republic of china (PRC) or Chinese/Hongkong authorities.
Synthetic Dimsum Bonds: Bonds that are issued in the Chinese renminbi but settled in some other currency such as EUR are called synthetic dimsum bonds or RMD bonds.
Features of Dimsum Bonds
Some of the features are given below:
- Investors: The investor base for dimsum bonds is very less as compared to US bonds. Most investors of dim sum include private banking clients, international investors, and commercial banks.
- Credit Rating: Credit rating is usually market-driven for dimsum bonds and is similar to other foreign bonds issued by Chinese entities and is not affected by currency.
- Liquidity: The liquidity of dim sum bonds is still moderate.
- Maturity: Maturity for dim sum bonds is mostly 3 years or less.
- Security: Investors’ security is still being evolved and is quite low compared to the US bond market.
Components of Dimsum Bond
Below are the components:
- Face Value: the Par value or principal amount that the bond issuer has to repay the investor at maturity or at the expiration of the contract.
- Coupon Amount: the amount that the bond issuer will pay on each coupon date to the investor. sometimes instead of the coupon amount, the coupon rate is provided by the issuer.
For example, a 10% coupon rate on a 100$ face value means that investors will receive 10% x $100 face value = $10o n each coupon date.
- Coupon Dates: the dates on which the bond issuer will pay the Coupon amount to the investor. In the US, usually semi-annual coupons are paid, i.e., a bond issuer will pay the Coupon amount to the bondholder after every 6 months.
- Maturity Date: the date on which the bond will mature or the date on which the contract between the bond issuer and bondholder ends and the issuer will pay the investor the face value of the bond.
- Issue Price: the original price of the bond at which the bond issuer sells the bond.
- Yield to Maturity: The expected rate of return if a bond is held until it matures.
Bond Valuation
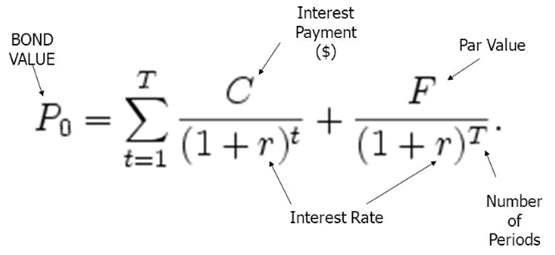
The bond price is the present value of all the future cash flows generated by a bond. It refers to the sum of the present values of all coupon payments plus the present value of the face value at maturity. bond price(p0) for a coupon bond with coupon amount (c ), face value (f), maturity (t), and yield to maturity (r) can be calculated as:
Source: Slide Player
An example of bond valuation for a single-yield coupon bond is provided in an Excel sheet.
Factors Affecting Dimsum Bonds
- Yield: The continuous raise in demand for dimsum bonds has led the bond yield to strangely low levels with the credit spread declining from positive to negative in 2015.
- Hedging Costs: Costs including hedging affects overall funding costs, which often impact the issuance of dim sum bonds.
- Currency Volatility: The abrupt ups and downs of Chinese yuan can impact the issuance of dim sum bonds.
Advantages of Dimsum Bonds
Some of the advantages and disadvantages are given below:
Advantages
Some of the advantages are given below:
- Diversified Issuers: Due to no restrictions on the type of issuer, anyone from small investors to multinational companies can issue dim sum bonds. NBFCs and real estate developers are also issuing dimsum bonds.
- Chinese Renminbi Exposure: An investor who is interested in raising funds in renminbi can use dimsum bonds as one way to gain exposure.
- Low Coupon Rate: Due to high credit quality and growing demand for renminbi bonds, the coupon rate is quite low as compared to other high-rated bonds.
- Hedging: If an investor has already invested in the Chinese economy and wants to reduce exposure to exchange rate risk, he can simply do it by hedging. investing in renminbi by using bonds can be suitable to hedge the exposure.
Disadvantages
Some of the disadvantages are given below:
- Economy Risk: Investing in dim sum bonds brings up an additional risk due to government or market instability of the Chinese economy. Sudden changes in political situations may incur losses.
- Risks that are Hard to Quantify and Correlated: Dimsum bonds may be used to raise exposure in the renminbi. abrupt changes in currency value and in cases of economic crisis, it gets difficult to quantify the risk associated and deduce the correlation among several factors.
- Volatility: The issuance of dim sum bonds has decreased in the recent past due to high volatility and China’s low economic growth.
- Availability of Panda Bonds in the Market: Panda bonds are almost similar to dim sum bonds except that panda bonds can be issued in China by foreign entities. In this case, domestic investors are the main target for foreign issuers, while in the case of dimsum bonds, international investors are the major investors.
Conclusion
Dim sum bonds are similar to euro bonds and are issued outside of China but denominated in the Chinese renminbi and also settled in RMB. Dimsum bonds are very much suitable for investors who want to raise funds in the renminbi. but at the same time, dimsum bonds bring up the currency and country-specific risks.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Dimsum Bond. Here we also discuss the introduction and how dimsum bond works along with its advantages and disadvantages. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –