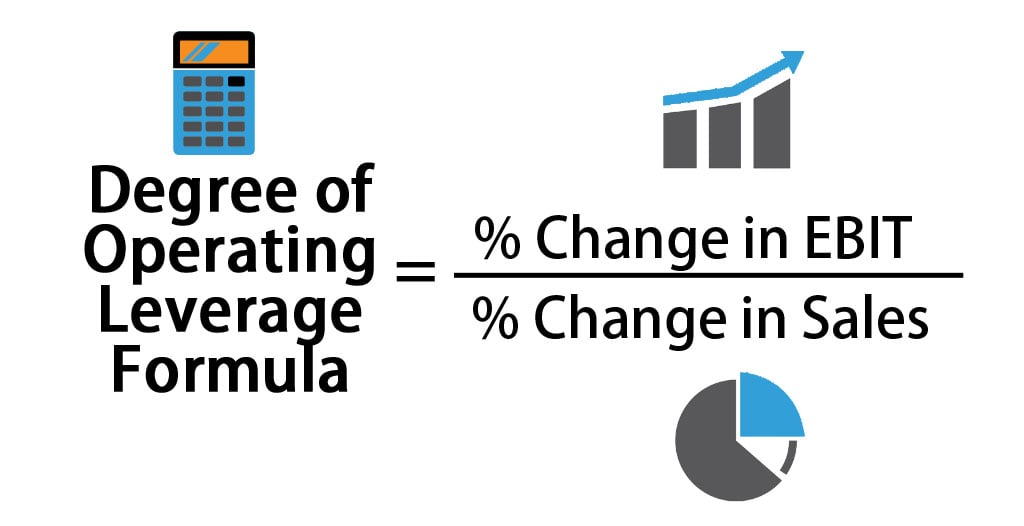Updated July 28, 2023
Degree of Operating Leverage Formula (Table of Contents)
- Degree of Operating Leverage Formula
- Examples of Degree of Operating Leverage Formula (With Excel Template)
- Degree of Operating Leverage Formula Calculator
Degree of Operating Leverage Formula
The degree of operating leverage (i.e. DOL) is a type of multiple that measures how much the firm’s operating income (i.e. EBIT) will change in response to a change in sales. Companies or firms with a large or huge proportion of the fixed costs to the variable costs will have higher operating leverage levels.
The formula to calculate the degree of operating leverage is as follows:
where
- % Change in EBIT = (EBIT current year – EBIT previous year) / EBIT previous year
- % Change in Sales = (Sales current year – Sales previous year) / Sales previous year
Examples of Degree of Operating Leverage Formula (With Excel Template)
Let’s take an example to understand the calculation of the Degree of Operating Leverage formula in a better manner.
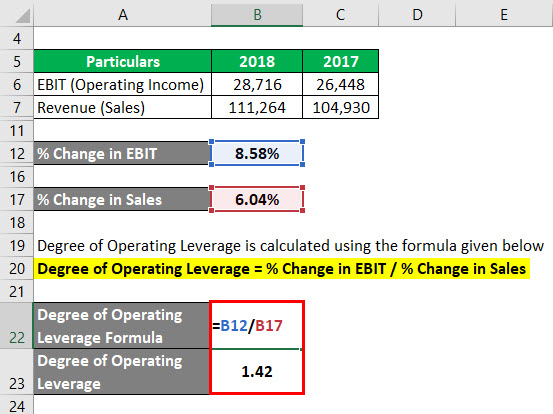
Example #1
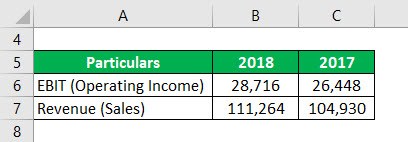
ABC Inc. has approached Tim, a financial analyst, as it wants to know the fluctuations in its operating income and revenue changes. Tim has recommended using the degree of operating leverage. He has gathered the following details from the financial statements of the company.
Solution:
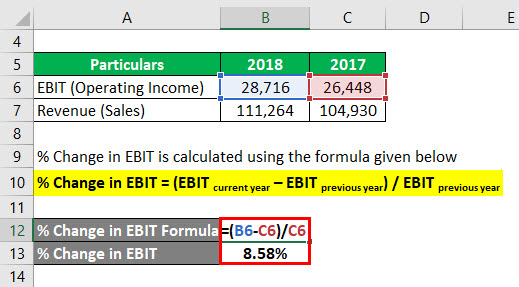
The formula to calculate % Change in EBIT is as below:
% Change in EBIT = (EBIT current year – EBIT previous year) / EBIT previous year
- % Change in EBIT = (28,716 – 26,448) / 26,448
- % Change in EBIT = 8.58%
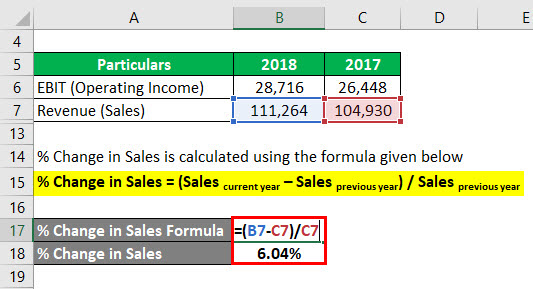
The formula to calculate % Change in Sales is as below:
% Change in Sales = (Sales current year – Sales previous year) / Sales previous year
- % Change in Sales = (111,264 – 104,930) / 104,930
- % Change in Sales = 6.04%
The formula to calculate Degree of Operating Leverage is as below:
Degree of Operating Leverage = % Change in EBIT / % Change in Sales
- Degree of Operating Leverage = 8.58% / 6.04%
- Degree of Operating Leverage = 1.42
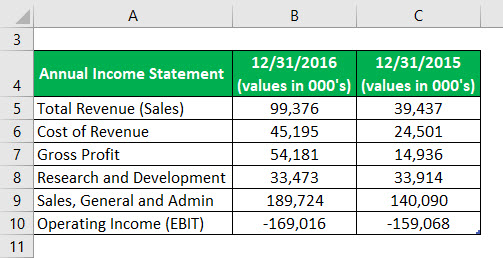
Example #2
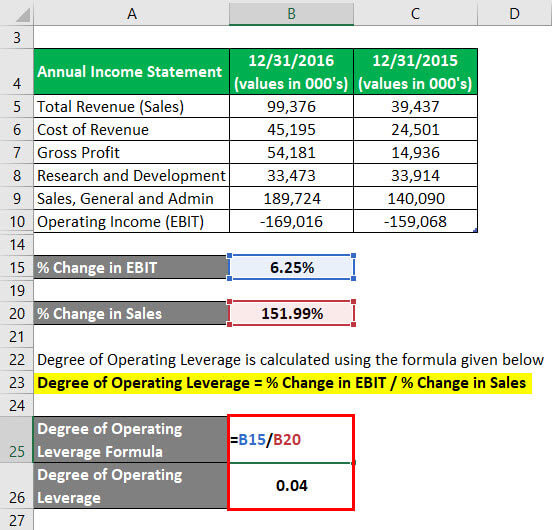
Following is an extract from the annual report of Exas Inc. You are required to calculate the degree of operating leverage.
Solution:
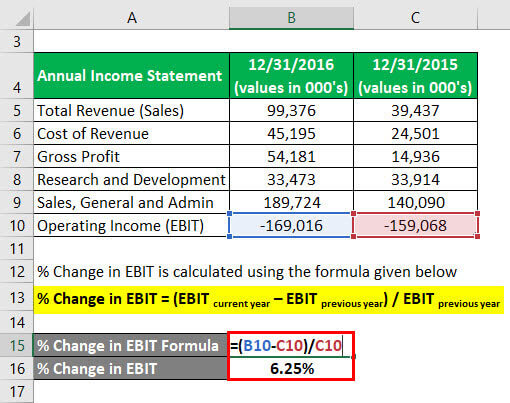
The formula to calculate % Change in EBIT is as below:
% Change in EBIT = (EBIT current year – EBIT previous year) / EBIT previous year
- % Change in EBIT = ((-169,016) – (-159,068)) / (-159,068))
- % Change in EBIT = 6.25%
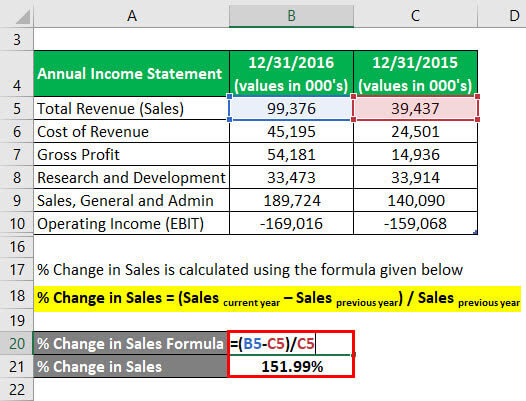
The formula to calculate % Change in Sales is as below:
% Change in Sales = (Sales current year – Sales previous year) / Sales previous year
- % Change in Sales = (99,376 – 39,437) / 39,437
- % Change in Sales = 151.99%
The formula to calculate Degree of Operating Leverage is as below:
Degree of Operating Leverage = % Change in EBIT / % Change in Sales
- Degree of Operating Leverage = 6.25% / 151.99%
- Degree of Operating Leverage = 0.04
Example #3
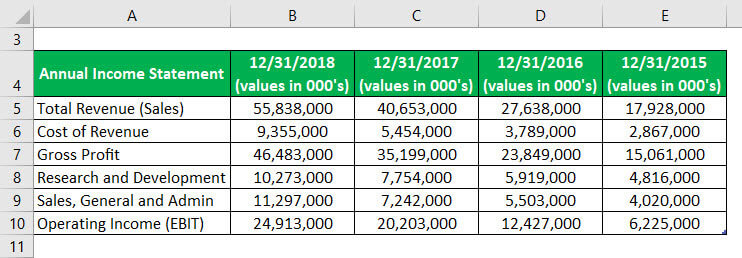
Following is an extract from the annual report of Facebook Inc. you are required to calculate the degree of operating leverage for consecutive years.
Solution:
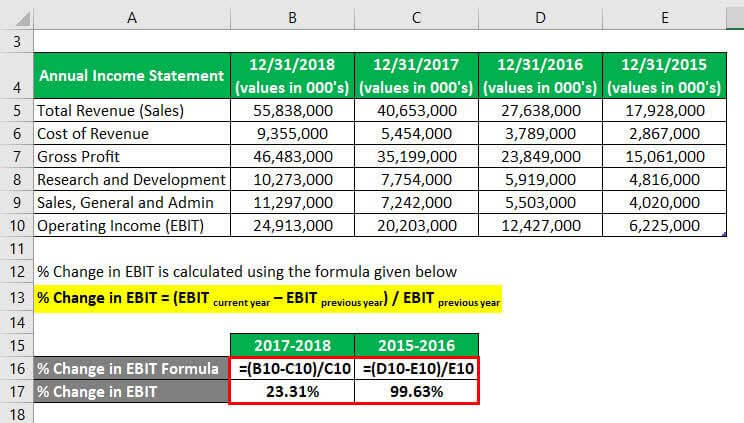
The formula to calculate % Change in EBIT is as below:
% Change in EBIT = (EBIT current year – EBIT previous year) / EBIT previous year
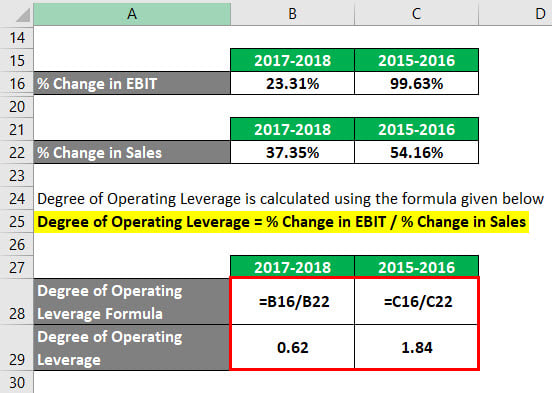
For 2017-2018
- % Change in EBIT = (24,913,000 – 20,203,000) / 20,203,000
- % Change in EBIT = 23.31%
For 2015-2016
- % Change in EBIT = (12,427,000 – 6,225,000) / 6,225,000
- % Change in EBIT = 99.63%
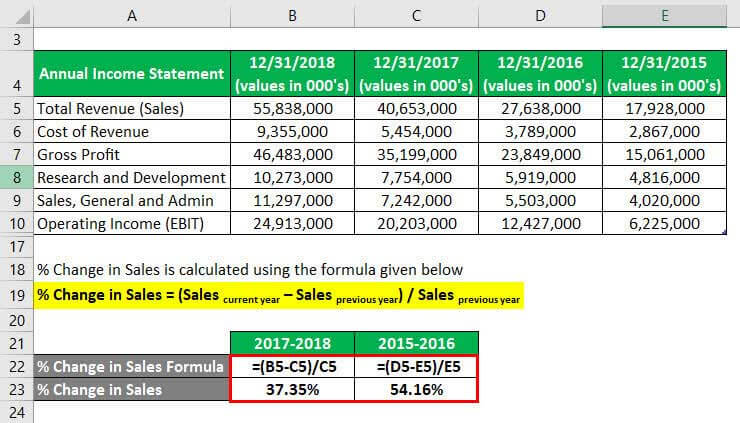
The formula to calculate % Change in Sales is as below:
% Change in Sales = (Sales current year – Sales previous year) / Sales previous year
For 2017-2018
- % Change in Sales = (55,838,000 – 40,653,000) / 40,653,000
- % Change in Sales = 37.35%
For 2015-2016
- % Change in Sales = (27,638,000- 17,928,000) / 17,928,000
- % Change in Sales = 54.16%
The formula to calculate Degree of Operating Leverage is as below:
Degree of Operating Leverage = % Change in EBIT / % Change in Sales
For 2017-2018
- Degree of Operating Leverage = 23.31% / 37.35%
- Degree of Operating Leverage = 0.62
For 2015-2016
- Degree of Operating Leverage = 99.63% / 54.16%
- Degree of Operating Leverage = 1.84
Explanation
The formula for calculating the degree of operating leverage is divided into two parts, i.e. % change in operating income and the second is the % change in revenue. The first part is the change in operating income, as that is the key income part that determines which variables (i.e. expenses) must be done to operate that business. On the other hand, the second part represents the changes in sales which are nothing but changes in net revenue.
Relevance and Uses
The degree of operating leverage can depict the impact of operating leverage on the firm’s or the company’s earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT). Also, the DOL is key if one wants to assess the effect of the variable costs and the fixed costs of the core operations of the entity or the business.
A high degree of operating leverage (DOL) does provide an indication that the entity or the company, or the business might have a high proportion of fixed operating costs as compared to its operating costs that are variable in nature, which could mean that the company is using more fixed assets to support its key business. It would also mean that the entity or the company can make more money or earn more revenue from every additional sale while keeping the entity’s fixed costs intact. So, the company or the entity will have a high Degree of Leverage by making fewer sales with higher margins. As a result, fixed assets, like plants, property, and equipment, will acquire a higher value without incurring additional costs. At the end of the day, the firm’s or the company’s profit margin may expand with the earnings that are increasing faster than its revenues.
On the other hand, a low Degree of Operating Leverage suggests that the entity or the company has a lower proportion of fixed operating costs as compared to its variable operating costs, which would mean that it uses lesser fixed assets to support its key activities of the business while sustaining a low gross profit margin.
Degree of Operating Leverage Formula Calculator
You can use the following Degree of Operating Leverage Calculator
| % Change in EBIT | |
| % Change in Sales | |
| Degree of Operating Leverage Formula | |
| Degree of Operating Leverage Formula = |
|
|
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the Degree of Operating Leverage formula. Here we discuss calculating the Degree of Operating Leverage along with practical examples. We also provide a Degree of Operating Leverage calculator with a downloadable Excel template. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –